Keypad Talking To LCD Via AT89S51
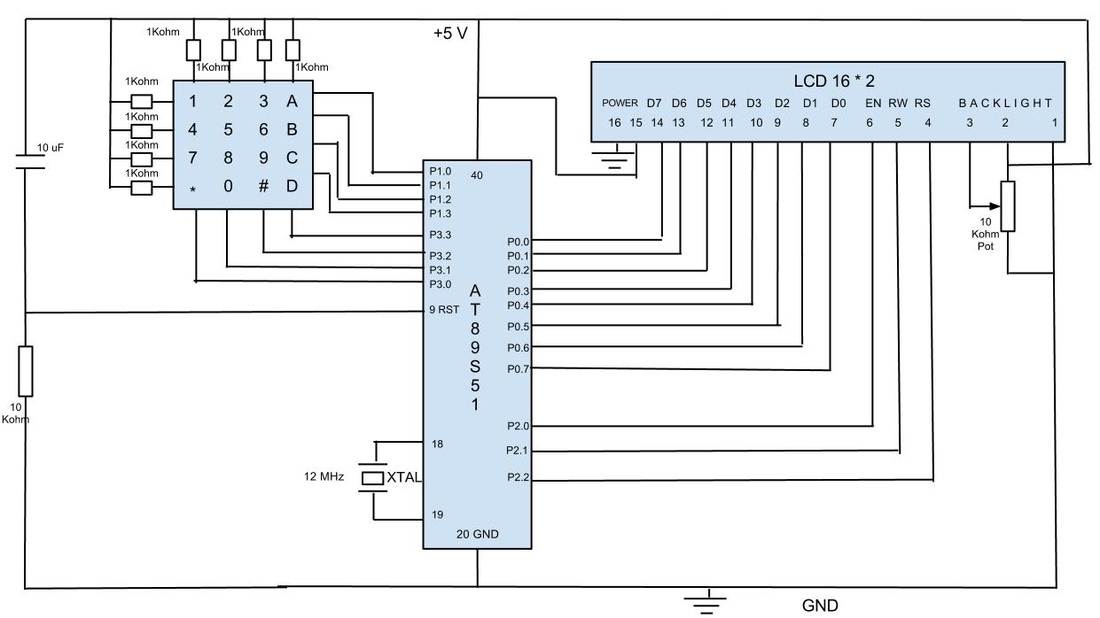
In previous posts, a schematic for interfacing a keypad and LCD using the 8051 architecture was presented. This blog post details the complete implementation of the interface using the AT89S51 microcontroller with programming in assembly language. It is assumed that the reader has a basic understanding of the technical background for both the keypad and the LCD. Follow the schematic provided and solder the components onto a general-purpose PCB. Note: It is recommended to first solder the LCD and verify its functionality by uploading the code to display characters before proceeding to the keypad phase. This phased approach is beneficial. After ensuring all connections are correct, confirm that the LCD's brightness is adjustable with a potentiometer when the system is powered using a 5-volt power supply. The next step involves uploading the code to capture keypad data and display it on the LCD. It is encouraged that individuals write the code independently, thus it will not be shared here. Once the code has been burned, place the AT89S51 on the IC socket and test the system; the pressed key should be displayed on the LCD.
The schematic involves a typical setup for interfacing an AT89S51 microcontroller with an LCD and a keypad. The AT89S51 is an 8-bit microcontroller based on the 8051 architecture, featuring 4KB of ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, and several I/O ports. The LCD used is typically a 16x2 character display, which requires a set of control and data lines connected to the microcontroller.
The interface begins with connecting the LCD's RS (Register Select), RW (Read/Write), and E (Enable) pins to designated I/O pins on the AT89S51. The data pins D0 to D7 of the LCD are also connected to the microcontroller's I/O pins. A potentiometer is connected to the V0 pin of the LCD to control brightness, allowing the user to adjust the display contrast.
The keypad is typically a 4x4 matrix, requiring a set of rows and columns to be connected to the microcontroller. Each key press connects a specific row and column, which the microcontroller detects by scanning the rows and columns. The microcontroller's firmware is responsible for managing the scanning process, detecting key presses, and sending the corresponding character to the LCD for display.
Power supply for the entire circuit is provided at 5 volts, which is a standard operating voltage for both the AT89S51 microcontroller and the LCD. It is crucial to ensure stable voltage levels to avoid erratic behavior in the components. The assembly code uploaded to the microcontroller should include routines for initializing the LCD, handling keypad input, and updating the display accordingly.
Testing the system involves verifying that the LCD displays the correct character corresponding to the key pressed on the keypad. This comprehensive approach ensures that each component is functioning correctly and that the overall system operates as intended.In few previous post, I showed schematic for interfacing Keypad and LCD using 8051 architecture. This blog post shows complete implementation of the interface using AT89S51 Micro-controller with programming in assembly. Considering that one understands the technical background for Keypad and LCD. Now, follow the schematic given above and solder th e components on the General Purpose PCB : Note : While doing so, first solder LCD and check if it works properly by uploading the code to display the characters and the move on to Keypad phase. Doing in phases helps. Now cross check the connections and also make sure that LCD`s brightness is controllable with the pot when the system in powered using a power supply.
Supply voltage in this case was 5 Volt. Next step is to upload the code for capturing Keypad data and to display same on the LCD. I would encourage individuals to write the code on own, hence not sharing here. And after the code has been burned, place the AT89S51 on IC socket and test the system, whichever key is pressed that key should be displayed on the LCD : 🔗 External reference
The schematic involves a typical setup for interfacing an AT89S51 microcontroller with an LCD and a keypad. The AT89S51 is an 8-bit microcontroller based on the 8051 architecture, featuring 4KB of ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, and several I/O ports. The LCD used is typically a 16x2 character display, which requires a set of control and data lines connected to the microcontroller.
The interface begins with connecting the LCD's RS (Register Select), RW (Read/Write), and E (Enable) pins to designated I/O pins on the AT89S51. The data pins D0 to D7 of the LCD are also connected to the microcontroller's I/O pins. A potentiometer is connected to the V0 pin of the LCD to control brightness, allowing the user to adjust the display contrast.
The keypad is typically a 4x4 matrix, requiring a set of rows and columns to be connected to the microcontroller. Each key press connects a specific row and column, which the microcontroller detects by scanning the rows and columns. The microcontroller's firmware is responsible for managing the scanning process, detecting key presses, and sending the corresponding character to the LCD for display.
Power supply for the entire circuit is provided at 5 volts, which is a standard operating voltage for both the AT89S51 microcontroller and the LCD. It is crucial to ensure stable voltage levels to avoid erratic behavior in the components. The assembly code uploaded to the microcontroller should include routines for initializing the LCD, handling keypad input, and updating the display accordingly.
Testing the system involves verifying that the LCD displays the correct character corresponding to the key pressed on the keypad. This comprehensive approach ensures that each component is functioning correctly and that the overall system operates as intended.In few previous post, I showed schematic for interfacing Keypad and LCD using 8051 architecture. This blog post shows complete implementation of the interface using AT89S51 Micro-controller with programming in assembly. Considering that one understands the technical background for Keypad and LCD. Now, follow the schematic given above and solder th e components on the General Purpose PCB : Note : While doing so, first solder LCD and check if it works properly by uploading the code to display the characters and the move on to Keypad phase. Doing in phases helps. Now cross check the connections and also make sure that LCD`s brightness is controllable with the pot when the system in powered using a power supply.
Supply voltage in this case was 5 Volt. Next step is to upload the code for capturing Keypad data and to display same on the LCD. I would encourage individuals to write the code on own, hence not sharing here. And after the code has been burned, place the AT89S51 on IC socket and test the system, whichever key is pressed that key should be displayed on the LCD : 🔗 External reference