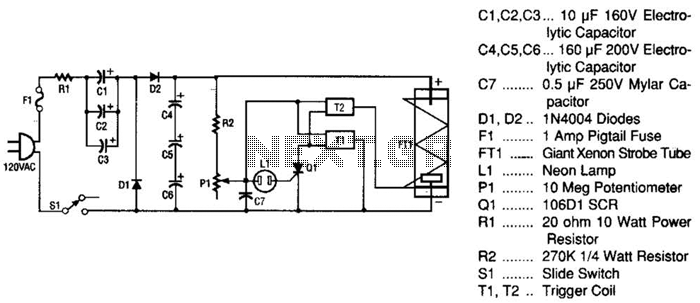
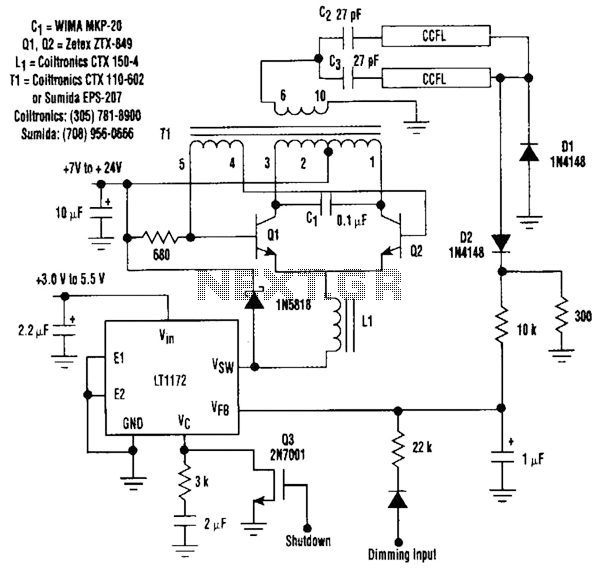
Lamp relay delay circuit
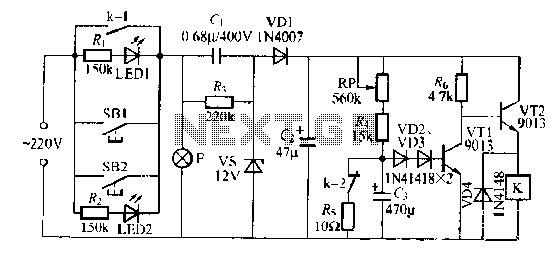
The lamp relay delay circuit is illustrated in Figure 7. Components S131 and SB2 are light buttons mounted in different locations. The lamp can operate with F. LEDs (LED1 and LED2) should be installed in SB1 and SB2 to indicate the switch position, facilitating ease of use. When the lights are needed, pressing either SB1 or SB2 will activate lamp E, causing LED1 and LED2 to turn off. Simultaneously, a galvanic current flows through components J, C, VS, VD1, and other basic electrical elements forming a step-down regulator rectifier circuit, providing a steady output of approximately 12V DC. Since the resistance of RP is significantly less than ten ohms, VT1 remains off while VT2 conducts, which energizes relay K, causing contact K1 to close, thereby locking the circuit. Concurrently, contact K2 opens. The voltage across the two capacitors prevents sudden voltage changes, keeping VT1 in the off state, allowing lamp F to remain illuminated. The 12V DC, regulated by RP and R, maintains the current at a high level. When the voltage rises to 3.065V, diodes VD2 and VD3 conduct, turning off VT1 and VT2, releasing relay K, resetting contacts K1 and K2, and turning off lamp F along with LED1 and LED2, which indicate the switch position. The resistor RP can be adjusted to set the delay time. Relay K is a JRX-13F, a small electromagnetic relay rated for 12V DC, featuring two changeover contacts, adequately meeting the circuit requirements.
The lamp relay delay circuit operates based on a combination of resistive and capacitive components that establish a time delay for the activation and deactivation of the lamp. The circuit's design incorporates a step-down regulator that converts higher voltage inputs into a stable 12V DC output, essential for the reliable operation of the relay and associated components. The use of LEDs for switch position indication enhances user interaction by providing visual feedback regarding the circuit's state.
The relay employed in this design, the JRX-13F, is particularly suited for applications requiring compact size and reliable operation. Its two changeover contacts allow for versatile circuit configurations, enabling the design to accommodate various load requirements. The interaction between the relay and the capacitors is critical; as the capacitors charge, they create a delay in the relay's response, allowing for controlled operation of the lamp. The adjustment of the resistor RP allows for fine-tuning of the delay time, providing flexibility in the circuit's performance based on specific application needs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of electronic components to achieve a desired functionality, demonstrating the principles of relay operation, voltage regulation, and delay mechanisms effectively.Lamp relay delay circuit shown in Figure 7], S131, SB2 are lights button mounted anti-machi not a different place, the lamp can operate F. LEDs LEDl, LFr) 2 should be installed in SB1 and SB2 at the "Peter asked in switch position indication easy to use.
When the lights required, just press the SB1, SB7 any one towel a lamp E on the light-emitting. LEDI, LED2 goes off. and the same time at both ends of the lamp post .1 NIE galvanic suffer through (J, c ,, VS, VD1 and other simple electrical composed of step-down regulator rectifier circuit, in (Both ends of the steady output of about 1 2V given DC voltage. Since the feet. RP resistance is much less than ten Torr, VT1 off, VT2 conduction, so the relay K station, station electric shock kl closing station, the circuit self-locking.
At the same time, jump off contact k2 Since two capacitors G J terminal voltage can not mutation, VTI remains off state so that a lamp F may continue to emit light. then, 12V DC by the RP, R to allow electricity to make (1 Galvanic callosum constantly J high, when rose 3 0 65V just, VD2, VD3 and are conduction VT1, VT2 off energized relay K release, its contact kl, k2 reset, turn off the lamp F, called with LED1, LED2 and light indication switch position.
trimming pruning when the resistor RP coup lights can delay l Division, K called using JRX-13F, DClZV other small type electromagnetic relay which has two changeover contacts, can be full enough Bong circuit requirements.
The lamp relay delay circuit operates based on a combination of resistive and capacitive components that establish a time delay for the activation and deactivation of the lamp. The circuit's design incorporates a step-down regulator that converts higher voltage inputs into a stable 12V DC output, essential for the reliable operation of the relay and associated components. The use of LEDs for switch position indication enhances user interaction by providing visual feedback regarding the circuit's state.
The relay employed in this design, the JRX-13F, is particularly suited for applications requiring compact size and reliable operation. Its two changeover contacts allow for versatile circuit configurations, enabling the design to accommodate various load requirements. The interaction between the relay and the capacitors is critical; as the capacitors charge, they create a delay in the relay's response, allowing for controlled operation of the lamp. The adjustment of the resistor RP allows for fine-tuning of the delay time, providing flexibility in the circuit's performance based on specific application needs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of electronic components to achieve a desired functionality, demonstrating the principles of relay operation, voltage regulation, and delay mechanisms effectively.Lamp relay delay circuit shown in Figure 7], S131, SB2 are lights button mounted anti-machi not a different place, the lamp can operate F. LEDs LEDl, LFr) 2 should be installed in SB1 and SB2 at the "Peter asked in switch position indication easy to use.
When the lights required, just press the SB1, SB7 any one towel a lamp E on the light-emitting. LEDI, LED2 goes off. and the same time at both ends of the lamp post .1 NIE galvanic suffer through (J, c ,, VS, VD1 and other simple electrical composed of step-down regulator rectifier circuit, in (Both ends of the steady output of about 1 2V given DC voltage. Since the feet. RP resistance is much less than ten Torr, VT1 off, VT2 conduction, so the relay K station, station electric shock kl closing station, the circuit self-locking.
At the same time, jump off contact k2 Since two capacitors G J terminal voltage can not mutation, VTI remains off state so that a lamp F may continue to emit light. then, 12V DC by the RP, R to allow electricity to make (1 Galvanic callosum constantly J high, when rose 3 0 65V just, VD2, VD3 and are conduction VT1, VT2 off energized relay K release, its contact kl, k2 reset, turn off the lamp F, called with LED1, LED2 and light indication switch position.
trimming pruning when the resistor RP coup lights can delay l Division, K called using JRX-13F, DClZV other small type electromagnetic relay which has two changeover contacts, can be full enough Bong circuit requirements.