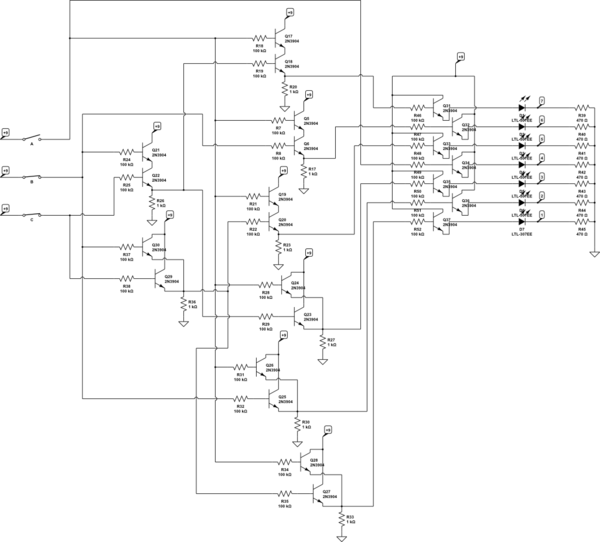
LED driven tail/brake Light Cluster
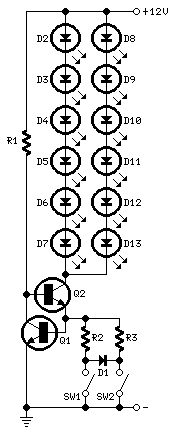
This circuit was designed on request to drive a Light-cluster formed by several LEDs that can be mounted in the vehicle as a tail and brake light. When SW1 is on, the cluster will illuminate at medium brightness. When brakes are operated, SW2 will be closed and the cluster will shine at maximum brightness.
The described circuit serves as a control mechanism for a light-cluster composed of multiple light-emitting diodes (LEDs), intended for use in automotive applications as a tail and brake light. The circuit operates on a dual-state control system, utilizing two switches: SW1 and SW2.
In the normal operating state, when SW1 is closed (turned on), the light-cluster is powered at a medium brightness level. This is typically achieved through a resistor in series with the LED array, which limits the current flowing through the LEDs to prevent overheating and ensure longevity. The medium brightness setting is suitable for standard tail light operation, providing sufficient visibility while minimizing power consumption.
The circuit incorporates a second switch, SW2, which is activated when the vehicle's brake system is engaged. Closing SW2 allows for increased current flow to the LED cluster, resulting in maximum brightness. This is often accomplished by bypassing the resistor or using a relay that connects a lower resistance path to the LEDs, thus allowing a higher current to flow through, which is essential for signaling a braking action to trailing vehicles.
Protection measures, such as diodes, may be included in the circuit design to prevent back EMF from affecting the control circuit, particularly if inductive components are involved. Additionally, a fuse may be integrated to safeguard against overcurrent situations, ensuring that the circuit remains functional without damage during fault conditions.
Overall, this LED driver circuit effectively utilizes simple switch control to provide variable brightness levels, enhancing vehicle safety and compliance with automotive lighting regulations. Proper thermal management and component selection are critical in ensuring the reliability and performance of the light-cluster throughout its operational lifespan.This circuit was designed on request to drive a Light-cluster formed by several LEDs that can be mounted in the vehicle as a tail and brake light. When SW1 is on, the cluster will illuminate at medium brightness. When brakes are operated, SW2 will be closed and the cluster will shine at maximum brightness. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a control mechanism for a light-cluster composed of multiple light-emitting diodes (LEDs), intended for use in automotive applications as a tail and brake light. The circuit operates on a dual-state control system, utilizing two switches: SW1 and SW2.
In the normal operating state, when SW1 is closed (turned on), the light-cluster is powered at a medium brightness level. This is typically achieved through a resistor in series with the LED array, which limits the current flowing through the LEDs to prevent overheating and ensure longevity. The medium brightness setting is suitable for standard tail light operation, providing sufficient visibility while minimizing power consumption.
The circuit incorporates a second switch, SW2, which is activated when the vehicle's brake system is engaged. Closing SW2 allows for increased current flow to the LED cluster, resulting in maximum brightness. This is often accomplished by bypassing the resistor or using a relay that connects a lower resistance path to the LEDs, thus allowing a higher current to flow through, which is essential for signaling a braking action to trailing vehicles.
Protection measures, such as diodes, may be included in the circuit design to prevent back EMF from affecting the control circuit, particularly if inductive components are involved. Additionally, a fuse may be integrated to safeguard against overcurrent situations, ensuring that the circuit remains functional without damage during fault conditions.
Overall, this LED driver circuit effectively utilizes simple switch control to provide variable brightness levels, enhancing vehicle safety and compliance with automotive lighting regulations. Proper thermal management and component selection are critical in ensuring the reliability and performance of the light-cluster throughout its operational lifespan.This circuit was designed on request to drive a Light-cluster formed by several LEDs that can be mounted in the vehicle as a tail and brake light. When SW1 is on, the cluster will illuminate at medium brightness. When brakes are operated, SW2 will be closed and the cluster will shine at maximum brightness. 🔗 External reference