LED Tester
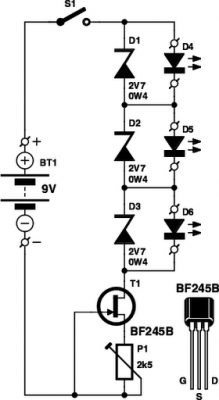
These small electronic lamps are incredibly useful and have a remarkably long lifespan. Approximately 40 years after Nick Holonyak developed the first LED, they have become essential components in various applications. Any dedicated electronics hobbyist typically keeps a selection of them in their collection. However, before utilizing LEDs, it is advisable to test them. An LED tester allows for this verification even in low-light conditions.
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are available in various colors and sizes, making them versatile for numerous applications, from indicator lights to complex displays. The longevity and efficiency of LEDs, often exceeding 50,000 hours of operational life, make them a preferred choice in modern electronics.
To ensure the proper functionality of an LED before deployment, an LED tester can be employed. This device typically consists of a power source, a current-limiting resistor, and a socket or clip to hold the LED. The power source can be a simple battery or a dedicated power supply, and the resistor is crucial for preventing excess current from damaging the LED.
When testing an LED, the user connects the LED to the tester, ensuring the correct polarity is observed, as LEDs are directional components. The tester then applies a voltage across the LED, allowing it to illuminate if functioning properly. This process can be performed in a dark environment to easily observe the emitted light, confirming the LED's operational status.
In summary, the integration of LEDs into electronic projects is facilitated by their practicality and efficiency. Utilizing an LED tester provides a straightforward method for verifying the condition of these components, ensuring reliability in various electronic applications.You have to admit that these tiny electronic lamps are handy, and they last almost forever. Around 40 years after Nick Holanyak developed the first LED, they have become just about indispensable. Any self-respecting electronics hobbyist always has a few in his junk box. But before you use LEDs, it?s a good idea to check them out. With a LED tester, you can even do it in the dark!. 🔗 External reference
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are available in various colors and sizes, making them versatile for numerous applications, from indicator lights to complex displays. The longevity and efficiency of LEDs, often exceeding 50,000 hours of operational life, make them a preferred choice in modern electronics.
To ensure the proper functionality of an LED before deployment, an LED tester can be employed. This device typically consists of a power source, a current-limiting resistor, and a socket or clip to hold the LED. The power source can be a simple battery or a dedicated power supply, and the resistor is crucial for preventing excess current from damaging the LED.
When testing an LED, the user connects the LED to the tester, ensuring the correct polarity is observed, as LEDs are directional components. The tester then applies a voltage across the LED, allowing it to illuminate if functioning properly. This process can be performed in a dark environment to easily observe the emitted light, confirming the LED's operational status.
In summary, the integration of LEDs into electronic projects is facilitated by their practicality and efficiency. Utilizing an LED tester provides a straightforward method for verifying the condition of these components, ensuring reliability in various electronic applications.You have to admit that these tiny electronic lamps are handy, and they last almost forever. Around 40 years after Nick Holanyak developed the first LED, they have become just about indispensable. Any self-respecting electronics hobbyist always has a few in his junk box. But before you use LEDs, it?s a good idea to check them out. With a LED tester, you can even do it in the dark!. 🔗 External reference