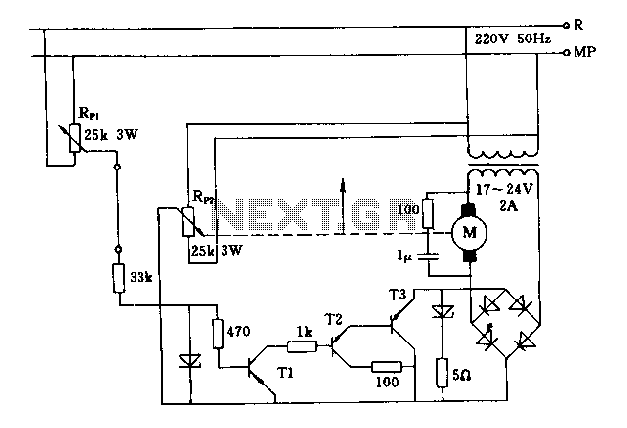
LED Volt Meter Circuit LM324
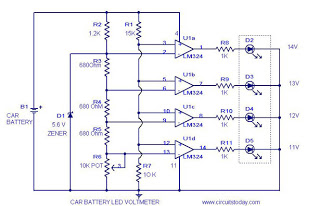
This circuit is a practical device that, when installed in a vehicle, displays the voltage of the car battery using an LED dot display. The meter circuit utilizes four comparators formed from a quad op-amp, specifically the LM324. The inverting inputs of the integrated circuit are set to reference voltages of 5.6V, 5.2V, 4.8V, and 4.4V, which are connected to pins 2, 6, 9, and 13 through resistors R3, R4, R5, and R6, respectively. The battery voltage is directly supplied to the non-inverting input via a voltage divider arrangement using resistors R1 and R7. As the input voltage varies, the output of each op-amp responds accordingly, functioning as voltage comparators, which causes the corresponding LED to illuminate. To set up the circuit, it should be connected to the battery, and resistor R6 must be adjusted to ensure that the desired reference voltages are present at the inverting pins.
The circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of the LM324 quad op-amp, which contains four independent, high-gain, frequency-compensated operational amplifiers. Each op-amp is configured as a comparator, comparing the battery voltage against predetermined reference voltages. The use of resistors R3, R4, R5, and R6 establishes these reference levels, which are critical for accurate voltage monitoring.
The voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R7 scales the battery voltage down to a level that the op-amps can process. This ensures that the non-inverting input receives a voltage that is proportional to the actual battery voltage. When the battery voltage exceeds the reference voltage set at the inverting input, the output of the respective op-amp transitions to a high state, activating the associated LED indicator.
The design allows for a clear visual representation of the battery status; as the voltage increases, different LEDs will light up in succession, providing an immediate indication of the battery's condition. Calibration of the circuit is achieved by adjusting R6, which fine-tunes the reference voltages to match the desired thresholds for battery voltage levels. This adjustment is crucial for ensuring that the circuit accurately reflects the state of the battery, enabling timely maintenance or replacement decisions for the vehicle's power source.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for monitoring car battery voltage, enhancing vehicle reliability and maintenance awareness through its visual LED indicators.It`s a very useful circuit which when installed on your car gives the voltage of you car battery in a LED dot display form. The meter circuit is based on four comparators made of quad op amp LM324. The inverting inputs of IC are kept at at reference voltages 5. 6V, 5. 2V, 4. 8V, 4. 4V respectively at pins 2, 6, 9, 13 by resistors, R3, R4, R5, R6. The battery vol tage is directly fed to the non inverting input through the voltage divider arrangement using R1 and R7. When there is variation in the input supply the out put of each op amp goes high accordingly as they are wired as voltage comparators.
The corresponding LED glows. To setup, connect the circuit to battery, adjust R6 so that required voltages are available at the inverting pins( refer description to get the required voltages). 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of the LM324 quad op-amp, which contains four independent, high-gain, frequency-compensated operational amplifiers. Each op-amp is configured as a comparator, comparing the battery voltage against predetermined reference voltages. The use of resistors R3, R4, R5, and R6 establishes these reference levels, which are critical for accurate voltage monitoring.
The voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R7 scales the battery voltage down to a level that the op-amps can process. This ensures that the non-inverting input receives a voltage that is proportional to the actual battery voltage. When the battery voltage exceeds the reference voltage set at the inverting input, the output of the respective op-amp transitions to a high state, activating the associated LED indicator.
The design allows for a clear visual representation of the battery status; as the voltage increases, different LEDs will light up in succession, providing an immediate indication of the battery's condition. Calibration of the circuit is achieved by adjusting R6, which fine-tunes the reference voltages to match the desired thresholds for battery voltage levels. This adjustment is crucial for ensuring that the circuit accurately reflects the state of the battery, enabling timely maintenance or replacement decisions for the vehicle's power source.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for monitoring car battery voltage, enhancing vehicle reliability and maintenance awareness through its visual LED indicators.It`s a very useful circuit which when installed on your car gives the voltage of you car battery in a LED dot display form. The meter circuit is based on four comparators made of quad op amp LM324. The inverting inputs of IC are kept at at reference voltages 5. 6V, 5. 2V, 4. 8V, 4. 4V respectively at pins 2, 6, 9, 13 by resistors, R3, R4, R5, R6. The battery vol tage is directly fed to the non inverting input through the voltage divider arrangement using R1 and R7. When there is variation in the input supply the out put of each op amp goes high accordingly as they are wired as voltage comparators.
The corresponding LED glows. To setup, connect the circuit to battery, adjust R6 so that required voltages are available at the inverting pins( refer description to get the required voltages). 🔗 External reference