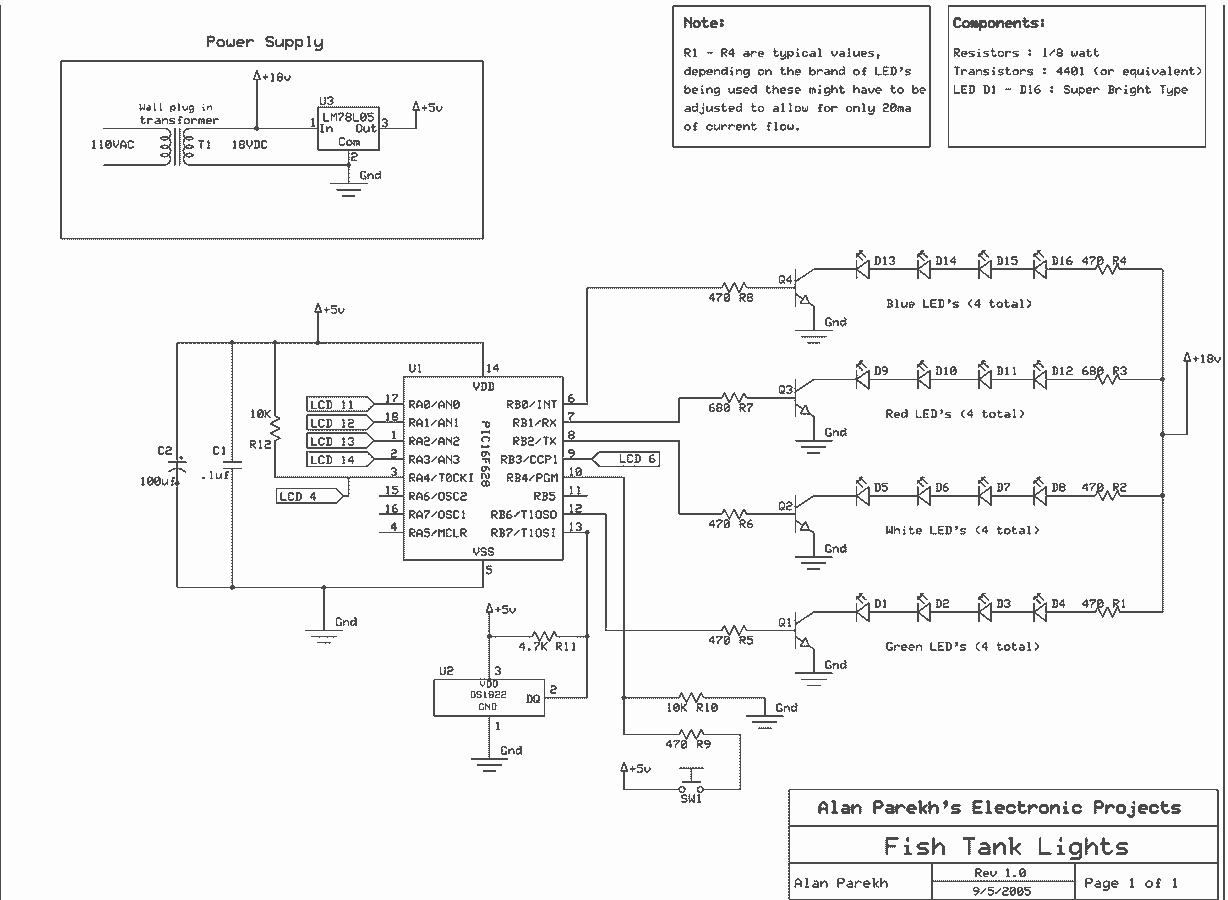
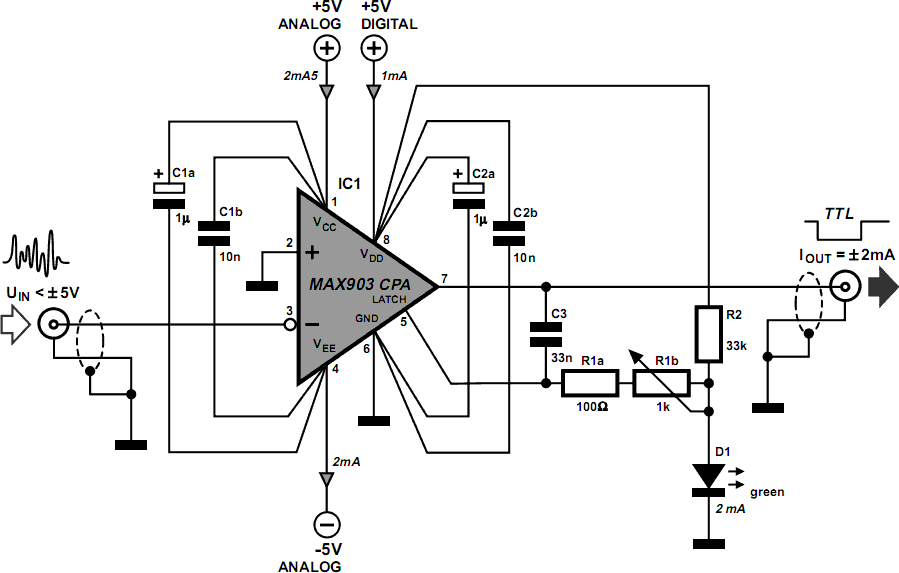
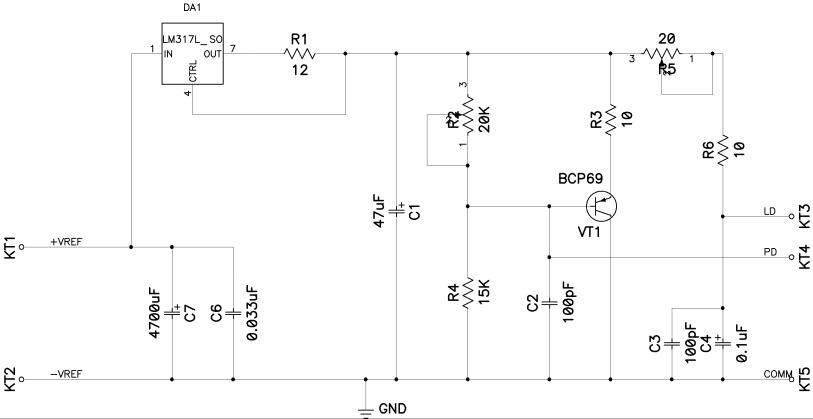
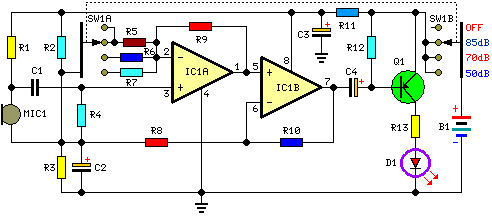
Lie Detector
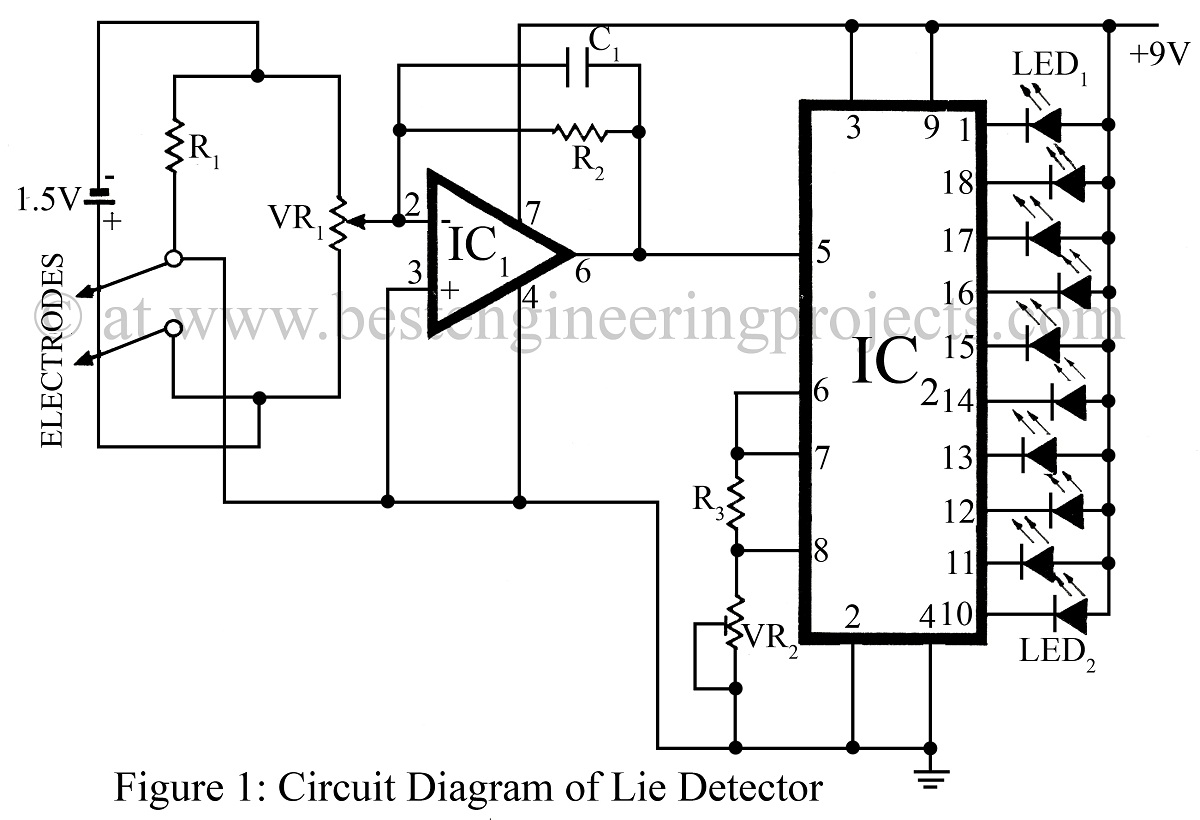
The lie detector presented here has been designed to detect skin resistance and provide a visual indication, verified electronic project.
The lie detector circuit operates on the principle that skin resistance varies with emotional states, particularly during stress or deception. The primary component of this circuit is a microcontroller or an operational amplifier configured to measure the resistance of the skin. The circuit typically includes electrodes that are attached to the skin, which capture the galvanic skin response (GSR).
The schematic may include a resistor divider circuit, where the skin resistance is one of the resistors, and a fixed resistor is used to create a voltage drop that can be measured. The output from this voltage divider can be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) within the microcontroller, which processes the signal and determines the skin resistance value.
To provide a visual indication of the measured resistance, the circuit may incorporate an LED display or an LCD screen. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger the visual indicators based on predefined thresholds of skin resistance, which correlate to the likelihood of deception.
Power supply considerations are also essential; the circuit may be powered by a battery or a DC power source, with appropriate voltage regulation to ensure stable operation of the electronic components. Additional features could include audio alerts or logging capabilities to record the resistance values over time for further analysis.
Overall, the circuit design combines various electronic components to create a functional lie detector that visually indicates changes in skin resistance, thereby providing insights into the emotional state of the subject being tested.The lie detector presented here has been designed to detect skin resistance and to give visual indication, verified electronic project. 🔗 External reference
The lie detector circuit operates on the principle that skin resistance varies with emotional states, particularly during stress or deception. The primary component of this circuit is a microcontroller or an operational amplifier configured to measure the resistance of the skin. The circuit typically includes electrodes that are attached to the skin, which capture the galvanic skin response (GSR).
The schematic may include a resistor divider circuit, where the skin resistance is one of the resistors, and a fixed resistor is used to create a voltage drop that can be measured. The output from this voltage divider can be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) within the microcontroller, which processes the signal and determines the skin resistance value.
To provide a visual indication of the measured resistance, the circuit may incorporate an LED display or an LCD screen. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger the visual indicators based on predefined thresholds of skin resistance, which correlate to the likelihood of deception.
Power supply considerations are also essential; the circuit may be powered by a battery or a DC power source, with appropriate voltage regulation to ensure stable operation of the electronic components. Additional features could include audio alerts or logging capabilities to record the resistance values over time for further analysis.
Overall, the circuit design combines various electronic components to create a functional lie detector that visually indicates changes in skin resistance, thereby providing insights into the emotional state of the subject being tested.The lie detector presented here has been designed to detect skin resistance and to give visual indication, verified electronic project. 🔗 External reference