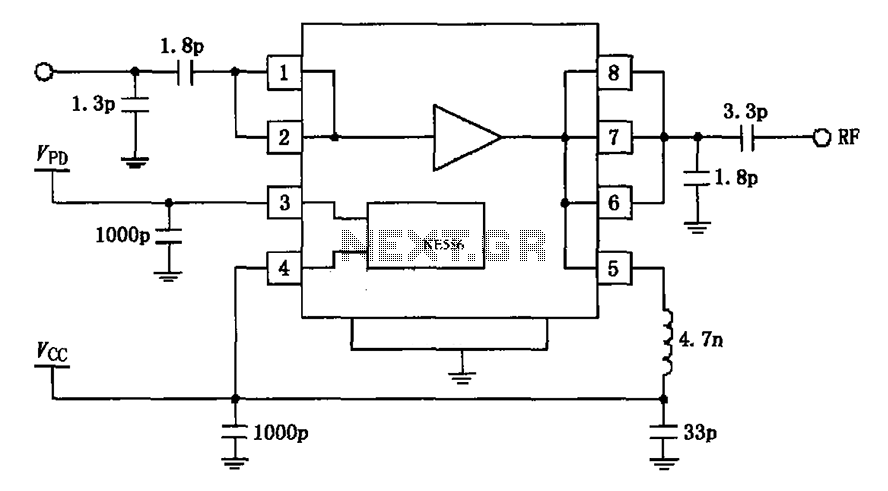
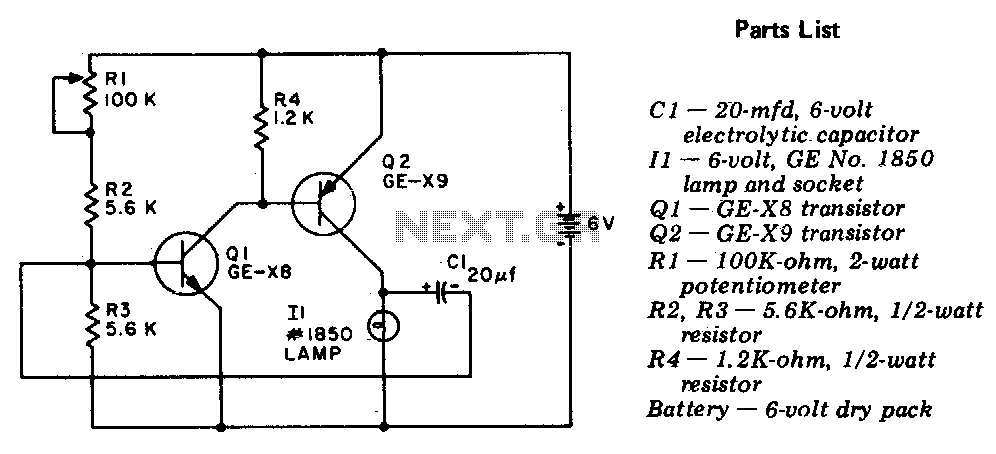
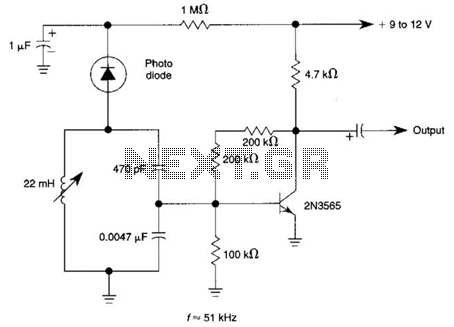
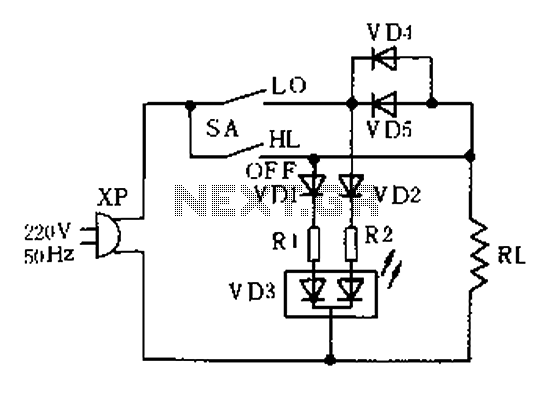
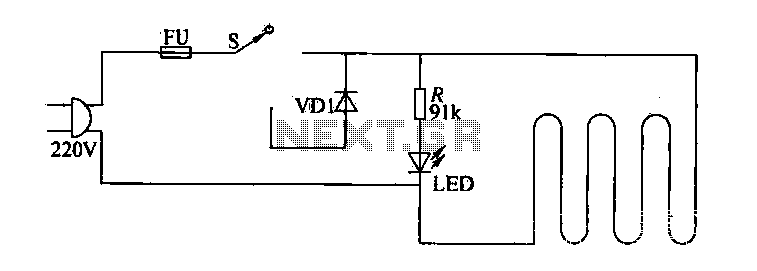
Light Sensor Circuit
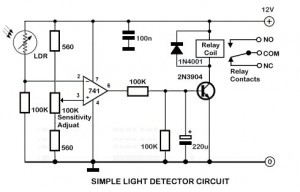
An ambient light sensor circuit is a circuit that utilizes light intensity to perform various applications.
An ambient light sensor circuit typically consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or phototransistor that detects the intensity of ambient light. The sensor converts the light intensity into a corresponding electrical signal, which can then be processed by other components in the circuit.
The primary components of this circuit include the light sensor (LDR or phototransistor), a resistor, and an operational amplifier (op-amp) or microcontroller for signal processing. The LDR exhibits a decrease in resistance with an increase in light intensity, allowing it to function effectively in varying lighting conditions. When light falls on the LDR, the resistance decreases, causing an increase in voltage across it, which can be measured and interpreted.
In typical applications, the output from the ambient light sensor can be used to control devices such as automatic lighting systems, where the lights are turned on or off based on the surrounding light levels. This can enhance energy efficiency by ensuring that lights are only active when necessary. Additionally, the circuit can be integrated into smart home systems, allowing for automated adjustments to lighting based on the time of day or occupancy.
For optimal performance, the circuit may include a calibration mechanism to adjust sensitivity levels, ensuring accurate readings in different environments. Furthermore, the use of filtering capacitors can stabilize the output signal and reduce noise, which is particularly important in environments with fluctuating light conditions.
Overall, the ambient light sensor circuit is a versatile and essential component in modern electronic systems, contributing to energy conservation and automation in various applications.Ambient Light Sensor Circuit Light sensor circuit, such as the name is a circuit that utilizes the light intensity / beam for the other applications do. 🔗 External reference
An ambient light sensor circuit typically consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or phototransistor that detects the intensity of ambient light. The sensor converts the light intensity into a corresponding electrical signal, which can then be processed by other components in the circuit.
The primary components of this circuit include the light sensor (LDR or phototransistor), a resistor, and an operational amplifier (op-amp) or microcontroller for signal processing. The LDR exhibits a decrease in resistance with an increase in light intensity, allowing it to function effectively in varying lighting conditions. When light falls on the LDR, the resistance decreases, causing an increase in voltage across it, which can be measured and interpreted.
In typical applications, the output from the ambient light sensor can be used to control devices such as automatic lighting systems, where the lights are turned on or off based on the surrounding light levels. This can enhance energy efficiency by ensuring that lights are only active when necessary. Additionally, the circuit can be integrated into smart home systems, allowing for automated adjustments to lighting based on the time of day or occupancy.
For optimal performance, the circuit may include a calibration mechanism to adjust sensitivity levels, ensuring accurate readings in different environments. Furthermore, the use of filtering capacitors can stabilize the output signal and reduce noise, which is particularly important in environments with fluctuating light conditions.
Overall, the ambient light sensor circuit is a versatile and essential component in modern electronic systems, contributing to energy conservation and automation in various applications.Ambient Light Sensor Circuit Light sensor circuit, such as the name is a circuit that utilizes the light intensity / beam for the other applications do. 🔗 External reference