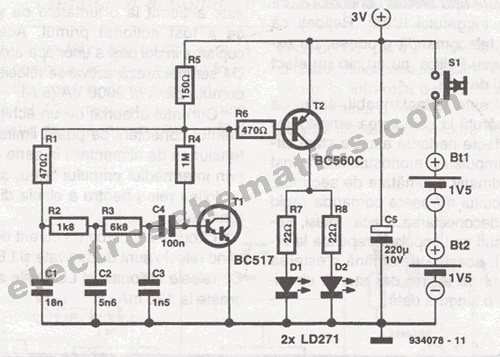
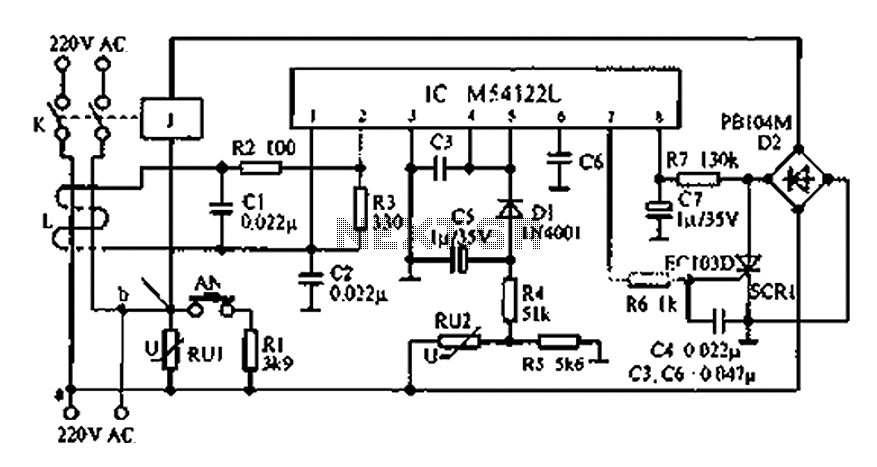
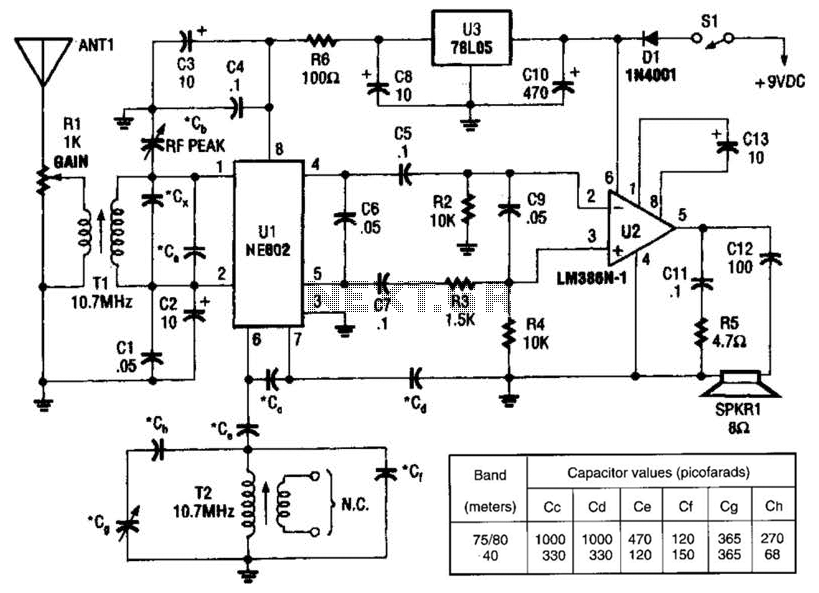
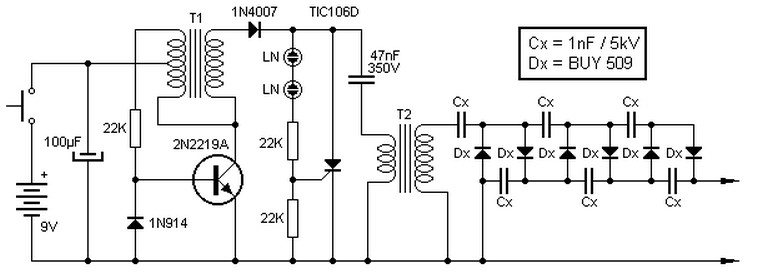
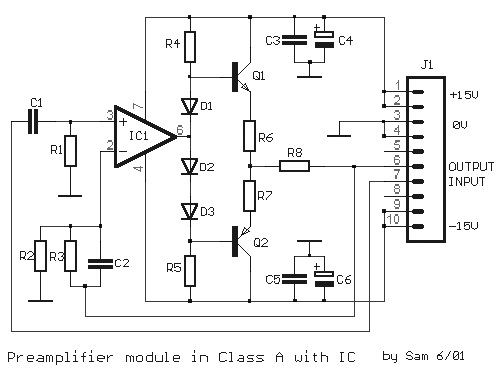
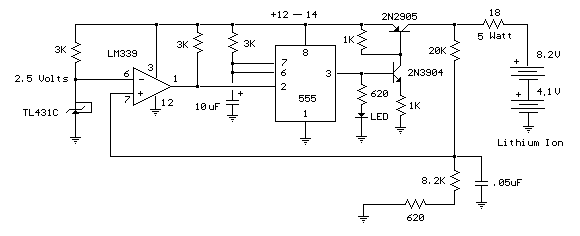
Lithium charger circuit
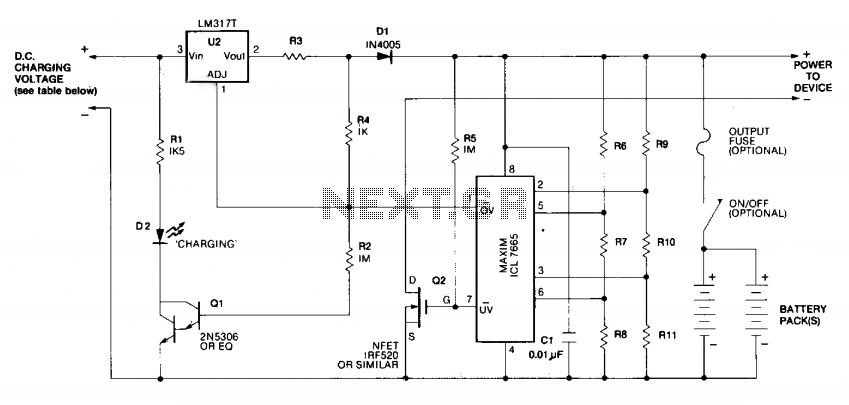
Charging is achieved using a constant current of 60 mA for AA cells, reaching a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell, at which point the charging process must be terminated. The charging system is designed for multi-cell battery packs consisting of 2 to 6 series-connected cells or series/parallel configurations. It is crucial that all cells within the pack are at the same state-of-charge (voltage) before initiating the charging process. The maximum upper cutoff voltage is 15.6 volts (6 x 2.6 V).
The charging system described operates under a constant current method, which is a common approach for charging rechargeable battery cells. The specified charging current of 60 mA is optimal for AA cells, ensuring that the batteries are charged efficiently without overheating or damaging the cells. The cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell is critical, as exceeding this voltage can lead to overcharging, which may reduce the lifespan of the batteries or even cause safety hazards.
In the context of multi-cell battery packs, the system is capable of charging configurations ranging from 2 to 6 cells connected in series. This series connection is essential for achieving the necessary voltage levels for various applications. For instance, with 6 cells in series, the total voltage can reach up to 15.6 V (6 x 2.6 V), making it suitable for powering devices that require higher voltage inputs.
It is important to highlight the necessity for all cells in the pack to be at the same state-of-charge before charging begins. This ensures that each cell receives an equal amount of charge, preventing any single cell from becoming overcharged or undercharged, which could lead to imbalances within the pack. Such imbalances can lead to reduced performance and lifespan of the battery pack.
The charging system may also include additional features such as temperature monitoring and safety cutoffs to enhance the reliability and safety of the charging process. Implementing these features can help prevent thermal runaway conditions and ensure that the batteries are charged within safe operating limits. Overall, this charging system is designed to provide efficient and safe charging for multi-cell battery configurations while maintaining the integrity and performance of the individual cells.Charging is accomplished with a constant current of 60 mA for AA cells to a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell at which point the charge must be terminated. The charging system shown is designed for multi-cell battery packs of 2 to 6 series-connected cells or series/parallel arrangements.
It is essential that all cells assembled in the pack be at an identical state-of-charge (voltage) prior to charging. The maximum upper cut-off voltage is 15.6 volts (6 ? 2.6 V).
The charging system described operates under a constant current method, which is a common approach for charging rechargeable battery cells. The specified charging current of 60 mA is optimal for AA cells, ensuring that the batteries are charged efficiently without overheating or damaging the cells. The cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell is critical, as exceeding this voltage can lead to overcharging, which may reduce the lifespan of the batteries or even cause safety hazards.
In the context of multi-cell battery packs, the system is capable of charging configurations ranging from 2 to 6 cells connected in series. This series connection is essential for achieving the necessary voltage levels for various applications. For instance, with 6 cells in series, the total voltage can reach up to 15.6 V (6 x 2.6 V), making it suitable for powering devices that require higher voltage inputs.
It is important to highlight the necessity for all cells in the pack to be at the same state-of-charge before charging begins. This ensures that each cell receives an equal amount of charge, preventing any single cell from becoming overcharged or undercharged, which could lead to imbalances within the pack. Such imbalances can lead to reduced performance and lifespan of the battery pack.
The charging system may also include additional features such as temperature monitoring and safety cutoffs to enhance the reliability and safety of the charging process. Implementing these features can help prevent thermal runaway conditions and ensure that the batteries are charged within safe operating limits. Overall, this charging system is designed to provide efficient and safe charging for multi-cell battery configurations while maintaining the integrity and performance of the individual cells.Charging is accomplished with a constant current of 60 mA for AA cells to a cutoff voltage of 2.4 V per cell at which point the charge must be terminated. The charging system shown is designed for multi-cell battery packs of 2 to 6 series-connected cells or series/parallel arrangements.
It is essential that all cells assembled in the pack be at an identical state-of-charge (voltage) prior to charging. The maximum upper cut-off voltage is 15.6 volts (6 ? 2.6 V).