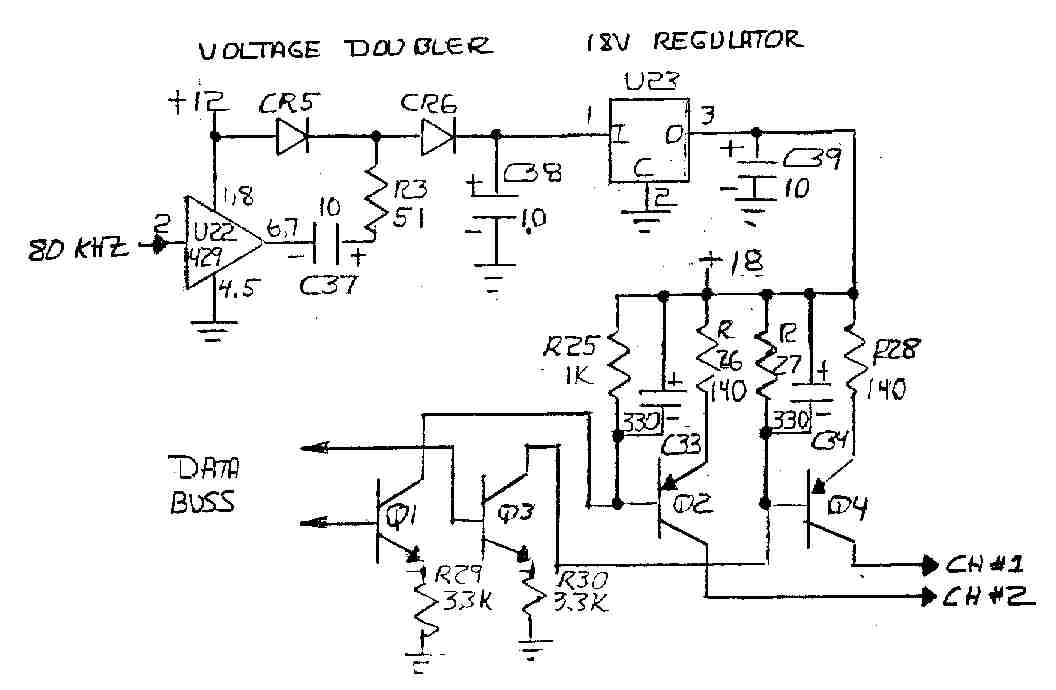
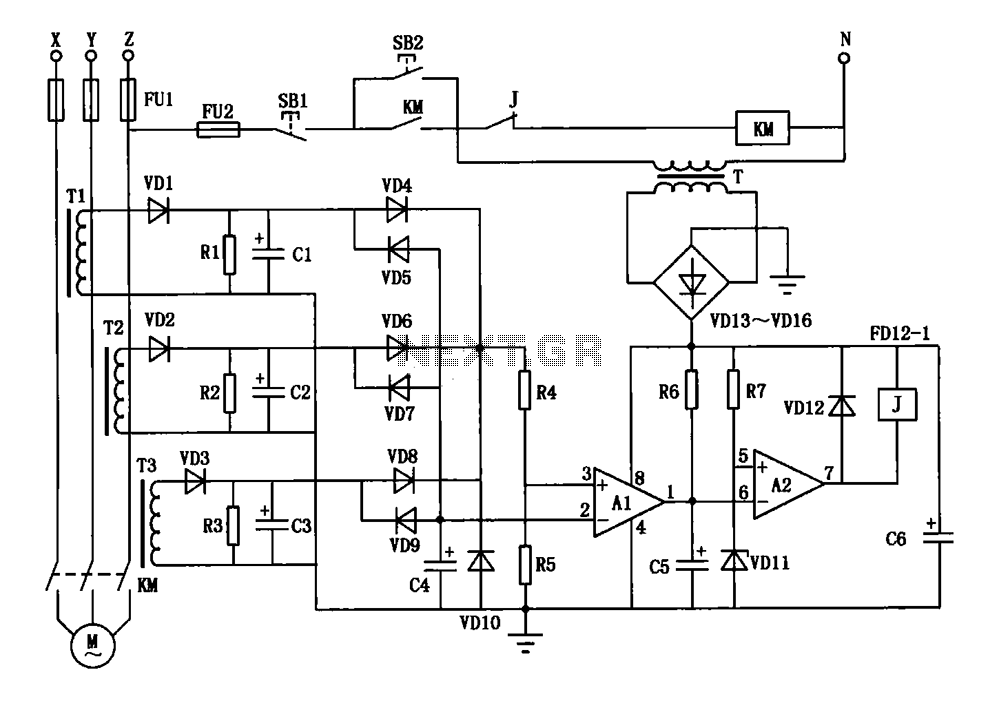
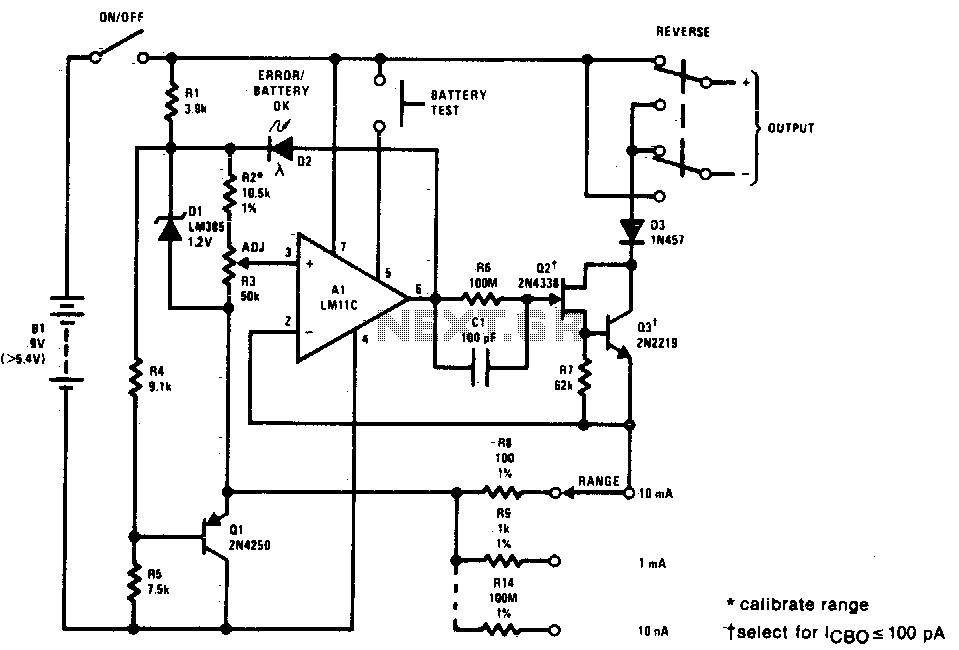
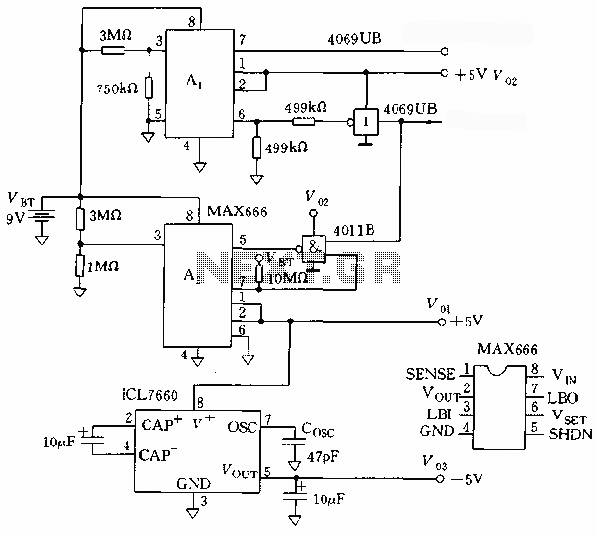
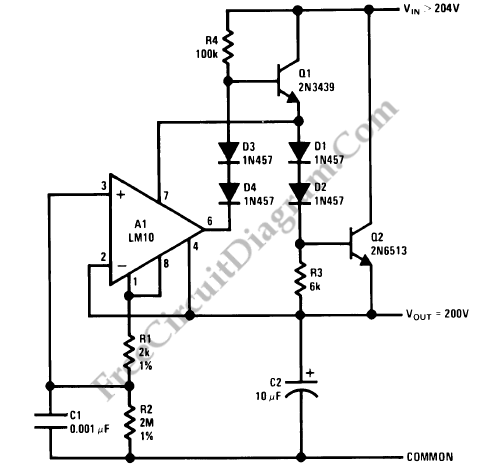
LM10 Current Regulator
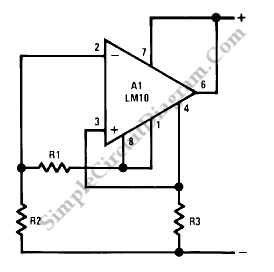
A current regulator functions as a load when connected to a voltage source or in series between a voltage source and an actual load. The primary characteristic of a current regulator is to maintain a constant current output regardless of variations in the load resistance or supply voltage.
A current regulator circuit is designed to ensure that a specific current flows through a load, providing stability in applications where current fluctuations could lead to undesirable performance or damage. The circuit typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp), a reference voltage source, and a pass element such as a transistor or MOSFET.
In operation, the op-amp compares the voltage across a sensing resistor, which is in series with the load, to a predetermined reference voltage. When the load current increases and the voltage across the sensing resistor exceeds the reference voltage, the op-amp's output will adjust the gate or base of the pass element, reducing the current flow to maintain the desired output. Conversely, if the load current decreases, the op-amp will increase the output to allow more current to flow.
This feedback mechanism allows the current regulator to adapt to changes in load conditions while ensuring that the current remains stable. The design can be applied in various scenarios, including LED drivers, battery chargers, and precision current sources in laboratory settings. Proper selection of components, including the op-amp, pass element, and sensing resistor, is crucial for achieving the desired performance and stability in the current regulation process.Current regulator acts like a load when connected to a voltage source, or in series between voltage source and real load. The main characteristic of a current.. 🔗 External reference
A current regulator circuit is designed to ensure that a specific current flows through a load, providing stability in applications where current fluctuations could lead to undesirable performance or damage. The circuit typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp), a reference voltage source, and a pass element such as a transistor or MOSFET.
In operation, the op-amp compares the voltage across a sensing resistor, which is in series with the load, to a predetermined reference voltage. When the load current increases and the voltage across the sensing resistor exceeds the reference voltage, the op-amp's output will adjust the gate or base of the pass element, reducing the current flow to maintain the desired output. Conversely, if the load current decreases, the op-amp will increase the output to allow more current to flow.
This feedback mechanism allows the current regulator to adapt to changes in load conditions while ensuring that the current remains stable. The design can be applied in various scenarios, including LED drivers, battery chargers, and precision current sources in laboratory settings. Proper selection of components, including the op-amp, pass element, and sensing resistor, is crucial for achieving the desired performance and stability in the current regulation process.Current regulator acts like a load when connected to a voltage source, or in series between voltage source and real load. The main characteristic of a current.. 🔗 External reference