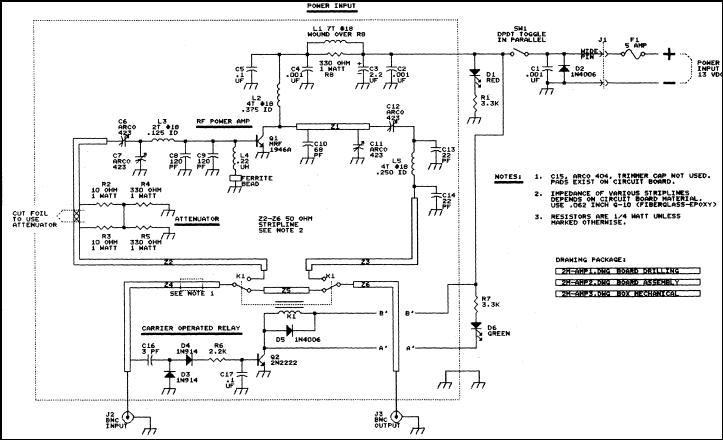
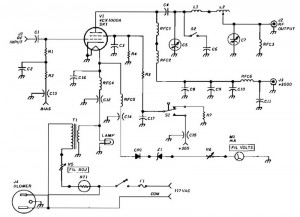
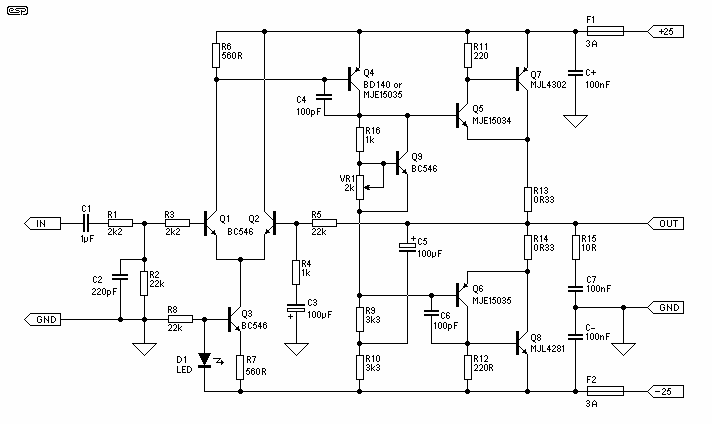
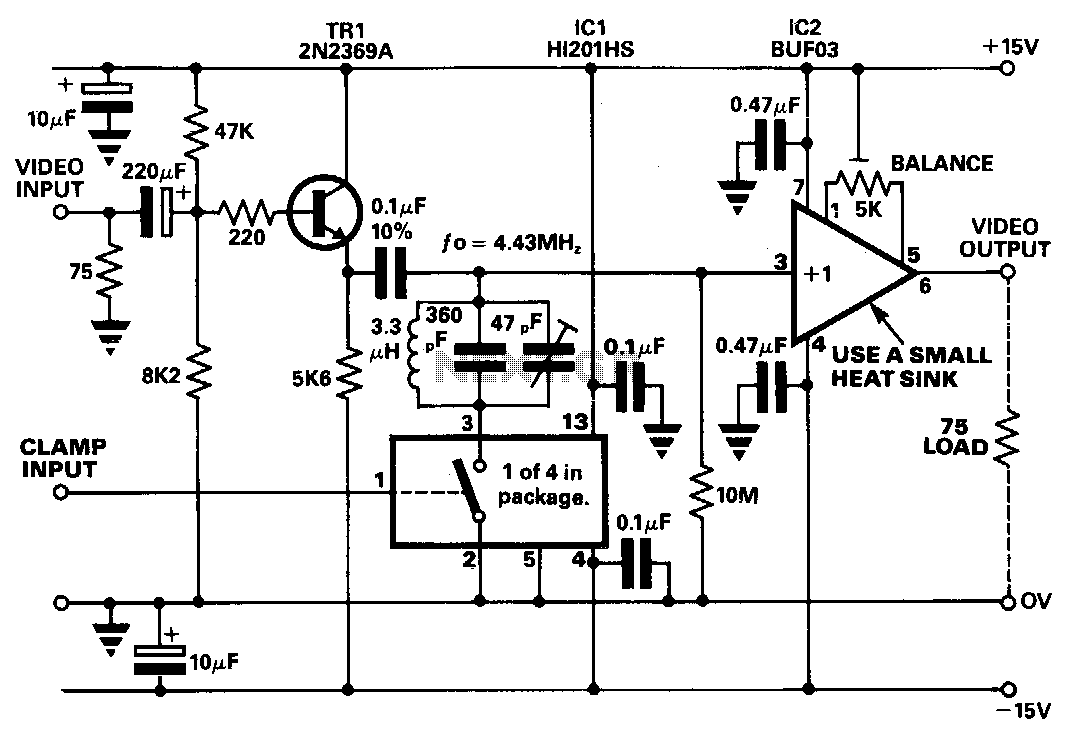
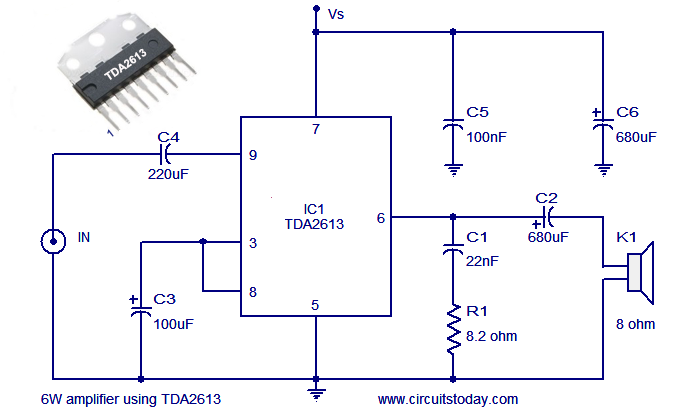
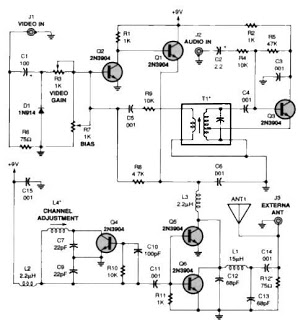
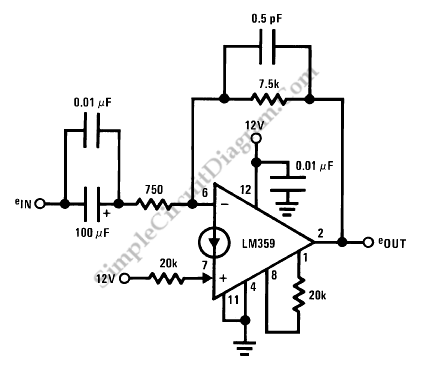
LM359 Video Amplifier
Every electronic device that boosts electrical signals can be called an amplifier. The various amplifier types only differ in some specific features.
Amplifiers are crucial components in electronic circuits, designed to increase the amplitude of electrical signals. They play a vital role in a wide range of applications, from audio equipment to communications systems. Different types of amplifiers include operational amplifiers (op-amps), audio amplifiers, radio frequency amplifiers, and instrumentation amplifiers, each serving specific purposes based on their design and operational characteristics.
Operational amplifiers are versatile devices commonly used in analog circuits. They typically have high input impedance, low output impedance, and a high gain, making them suitable for various applications, including signal conditioning, filtering, and mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation. Op-amps can be configured in various ways, such as inverting, non-inverting, and differential configurations, allowing for flexibility in circuit design.
Audio amplifiers are designed specifically to amplify audio signals to drive speakers or headphones. They can be classified into different classes, such as Class A, Class B, Class AB, and Class D, each with distinct efficiency and linearity characteristics. The choice of amplifier class affects the sound quality, power consumption, and thermal management of the device.
Radio frequency amplifiers are utilized in communication systems to amplify signals in the radio frequency range. These amplifiers are designed to operate efficiently at high frequencies and are often used in transmitters and receivers for wireless communication. Their design considerations include bandwidth, gain, and linearity to ensure signal integrity.
Instrumentation amplifiers are specialized for precise and accurate signal amplification, particularly in sensor applications. They typically feature high common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR) and are used in applications requiring low-level signal amplification, such as medical instrumentation and industrial process control.
In summary, while all amplifiers share the fundamental function of signal amplification, their specific features and configurations cater to a diverse array of applications, each with unique requirements and performance characteristics.Every electronic device that boost electrical signal can be called an amplifier. The various amplifier types only differ in some specific features such as:.. 🔗 External reference
Amplifiers are crucial components in electronic circuits, designed to increase the amplitude of electrical signals. They play a vital role in a wide range of applications, from audio equipment to communications systems. Different types of amplifiers include operational amplifiers (op-amps), audio amplifiers, radio frequency amplifiers, and instrumentation amplifiers, each serving specific purposes based on their design and operational characteristics.
Operational amplifiers are versatile devices commonly used in analog circuits. They typically have high input impedance, low output impedance, and a high gain, making them suitable for various applications, including signal conditioning, filtering, and mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation. Op-amps can be configured in various ways, such as inverting, non-inverting, and differential configurations, allowing for flexibility in circuit design.
Audio amplifiers are designed specifically to amplify audio signals to drive speakers or headphones. They can be classified into different classes, such as Class A, Class B, Class AB, and Class D, each with distinct efficiency and linearity characteristics. The choice of amplifier class affects the sound quality, power consumption, and thermal management of the device.
Radio frequency amplifiers are utilized in communication systems to amplify signals in the radio frequency range. These amplifiers are designed to operate efficiently at high frequencies and are often used in transmitters and receivers for wireless communication. Their design considerations include bandwidth, gain, and linearity to ensure signal integrity.
Instrumentation amplifiers are specialized for precise and accurate signal amplification, particularly in sensor applications. They typically feature high common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR) and are used in applications requiring low-level signal amplification, such as medical instrumentation and industrial process control.
In summary, while all amplifiers share the fundamental function of signal amplification, their specific features and configurations cater to a diverse array of applications, each with unique requirements and performance characteristics.Every electronic device that boost electrical signal can be called an amplifier. The various amplifier types only differ in some specific features such as:.. 🔗 External reference