lm75 temperature sensor with 7 segment display output
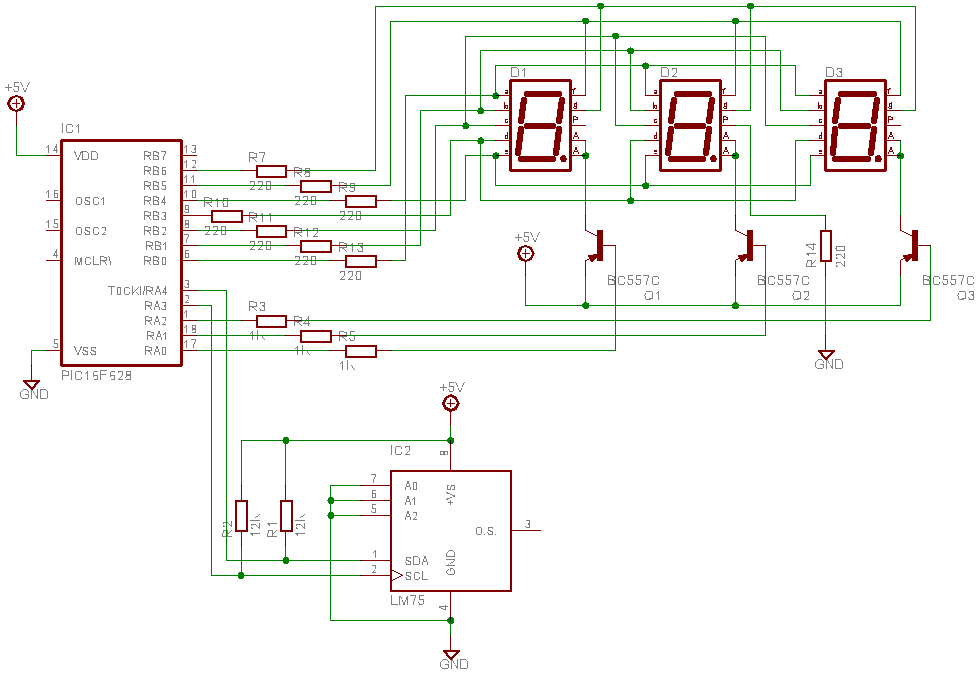
This is a test project assembled quickly on a solderless breadboard. It utilizes an LM75 temperature sensor to read the current temperature through the I2C communication protocol and displays the result.
The project employs the LM75, a digital temperature sensor with I2C interface, which allows for easy integration with microcontrollers. The LM75 operates within a temperature range of -55°C to +125°C and provides a 9 to 12-bit temperature resolution. The sensor communicates with a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, over the I2C bus, which simplifies wiring and allows for multiple devices to share the same communication lines.
In the schematic, the LM75 is connected to the microcontroller via two wires: the Serial Data Line (SDA) and the Serial Clock Line (SCL). Pull-up resistors are typically included on these lines to ensure proper signal levels. The microcontroller is programmed to initiate communication with the LM75, request temperature data, and process the received digital value to convert it into a readable temperature format.
The display component of the project could be an LCD or OLED screen, which is driven by the microcontroller. The microcontroller processes the temperature data obtained from the LM75 and formats it for output on the display. The display is connected to the microcontroller using appropriate data and control lines, depending on the display technology used.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, ensuring that both the LM75 and the microcontroller receive the appropriate voltage levels, typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on the specific components used in the project.
Overall, this project serves as a fundamental demonstration of using a digital temperature sensor with I2C communication, showcasing the integration of sensors and displays in electronic circuit design.This is a test project built hastily on a solder less breadboard. It uses a LM75 to read the current temperature via I2C and displays the result.. 🔗 External reference
The project employs the LM75, a digital temperature sensor with I2C interface, which allows for easy integration with microcontrollers. The LM75 operates within a temperature range of -55°C to +125°C and provides a 9 to 12-bit temperature resolution. The sensor communicates with a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, over the I2C bus, which simplifies wiring and allows for multiple devices to share the same communication lines.
In the schematic, the LM75 is connected to the microcontroller via two wires: the Serial Data Line (SDA) and the Serial Clock Line (SCL). Pull-up resistors are typically included on these lines to ensure proper signal levels. The microcontroller is programmed to initiate communication with the LM75, request temperature data, and process the received digital value to convert it into a readable temperature format.
The display component of the project could be an LCD or OLED screen, which is driven by the microcontroller. The microcontroller processes the temperature data obtained from the LM75 and formats it for output on the display. The display is connected to the microcontroller using appropriate data and control lines, depending on the display technology used.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, ensuring that both the LM75 and the microcontroller receive the appropriate voltage levels, typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on the specific components used in the project.
Overall, this project serves as a fundamental demonstration of using a digital temperature sensor with I2C communication, showcasing the integration of sensors and displays in electronic circuit design.This is a test project built hastily on a solder less breadboard. It uses a LM75 to read the current temperature via I2C and displays the result.. 🔗 External reference