Motion Detector Sensor Circuit
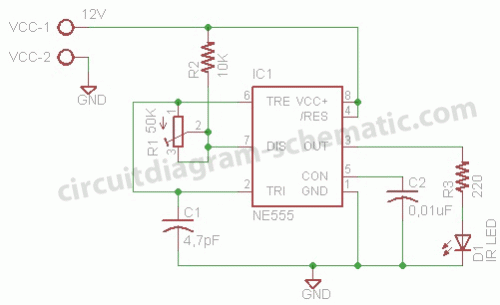
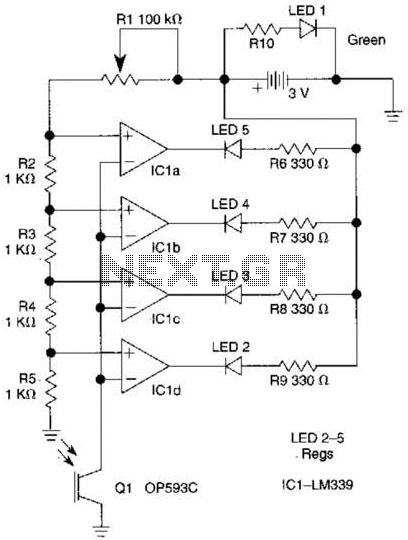
This circuit is a motion detection sensor that utilizes a light source and detector as an infrared motion detector. It incorporates components such as a light-emitting diode (LED), a phototransistor, a transmitter, a receiver, an NE555 timer configured as an astable multivibrator, and an LM1458 operational amplifier on a printed circuit board (PCB).
This motion detection circuit operates by emitting infrared light through the LED, which is then detected by the phototransistor. When an object moves within the detection range, it disrupts the infrared light beam, causing a change in the output signal of the phototransistor. This change is processed by the NE555 timer, which is configured in an astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output can be adjusted by varying the resistors and capacitors connected to the NE555 timer.
The LM1458 operational amplifier is utilized to amplify the output signal from the phototransistor, ensuring that even minor changes in the infrared light intensity are detected effectively. The amplified signal can be used to drive additional components, such as an alarm or a visual indicator (e.g., an LED), to alert users when motion is detected.
The PCB design for this circuit should ensure proper placement of components to minimize interference and optimize performance. It is essential to consider the power supply requirements for the NE555 timer and the LM1458 operational amplifier, as well as the appropriate biasing for the phototransistor to ensure sensitivity to motion. Overall, this infrared motion detection circuit is suitable for various applications, including security systems, automated lighting, and energy-saving devices.This circuit is a motion detection sensor, this circuit uses a light source and detector as a sensor infrared motion detector. motion detection, detection sensor, sensor, infrared, LED, phototransistor, transmitter, receiver, NE555, astable multivibrator, LM1458, PCB, circuit board,.
🔗 External reference
This motion detection circuit operates by emitting infrared light through the LED, which is then detected by the phototransistor. When an object moves within the detection range, it disrupts the infrared light beam, causing a change in the output signal of the phototransistor. This change is processed by the NE555 timer, which is configured in an astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output can be adjusted by varying the resistors and capacitors connected to the NE555 timer.
The LM1458 operational amplifier is utilized to amplify the output signal from the phototransistor, ensuring that even minor changes in the infrared light intensity are detected effectively. The amplified signal can be used to drive additional components, such as an alarm or a visual indicator (e.g., an LED), to alert users when motion is detected.
The PCB design for this circuit should ensure proper placement of components to minimize interference and optimize performance. It is essential to consider the power supply requirements for the NE555 timer and the LM1458 operational amplifier, as well as the appropriate biasing for the phototransistor to ensure sensitivity to motion. Overall, this infrared motion detection circuit is suitable for various applications, including security systems, automated lighting, and energy-saving devices.This circuit is a motion detection sensor, this circuit uses a light source and detector as a sensor infrared motion detector. motion detection, detection sensor, sensor, infrared, LED, phototransistor, transmitter, receiver, NE555, astable multivibrator, LM1458, PCB, circuit board,.
🔗 External reference