Low Cost Universal Battery Charger Schematic

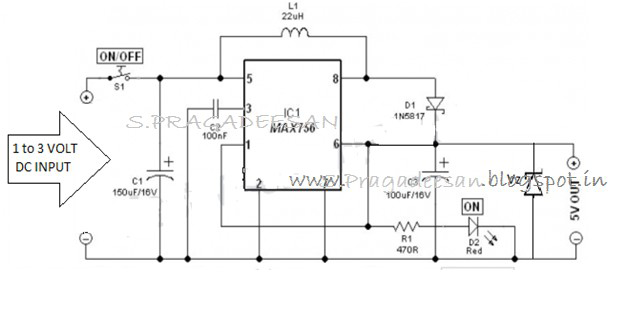
This is a simple and low-cost NiCd and NiMH battery charger. The schematic diagram indicates that the charging current (I) should be set to 1/10 of the battery's rated capacity. For instance, if the battery has a rated capacity of 1700mA, then I should be 170mA. Additionally, the input voltage must be at least three times the battery's nominal voltage.
The schematic for the NiCd and NiMH battery charger typically includes a transformer, rectifier, and voltage regulation components to ensure a stable charging current. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a suitable level for charging. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to DC voltage, which is necessary for charging the battery.
The charging circuit may also incorporate a resistor to limit the charging current to the specified value of I (1/10 of the battery capacity). This resistor is crucial for preventing damage to the battery from excessive current. The use of a potentiometer can allow for fine-tuning of the charging current, accommodating batteries with different capacities.
Furthermore, a diode may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which can occur when the charger is disconnected from the battery. This feature protects the charger and prolongs the lifespan of the battery.
For safety and efficiency, it is essential that the input voltage is adequately regulated and filtered to ensure that the charger operates within safe limits. The design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat, which may affect the performance and safety of the components involved.
Overall, this simple NiCd and NiMH battery charger circuit is an effective solution for charging batteries efficiently while minimizing costs. It is suitable for hobbyists and applications where cost and simplicity are paramount.Here the simple and low cost NiCd and NiMH battery charger: Schematic diagram: Note: I is 1/10 of the batterys charging capacity. For example if battery has a rated capacity of 1700mA then ?=170. The input voltage must be at least 3 times.. 🔗 External reference
The schematic for the NiCd and NiMH battery charger typically includes a transformer, rectifier, and voltage regulation components to ensure a stable charging current. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a suitable level for charging. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to DC voltage, which is necessary for charging the battery.
The charging circuit may also incorporate a resistor to limit the charging current to the specified value of I (1/10 of the battery capacity). This resistor is crucial for preventing damage to the battery from excessive current. The use of a potentiometer can allow for fine-tuning of the charging current, accommodating batteries with different capacities.
Furthermore, a diode may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which can occur when the charger is disconnected from the battery. This feature protects the charger and prolongs the lifespan of the battery.
For safety and efficiency, it is essential that the input voltage is adequately regulated and filtered to ensure that the charger operates within safe limits. The design should also consider thermal management, as charging can generate heat, which may affect the performance and safety of the components involved.
Overall, this simple NiCd and NiMH battery charger circuit is an effective solution for charging batteries efficiently while minimizing costs. It is suitable for hobbyists and applications where cost and simplicity are paramount.Here the simple and low cost NiCd and NiMH battery charger: Schematic diagram: Note: I is 1/10 of the batterys charging capacity. For example if battery has a rated capacity of 1700mA then ?=170. The input voltage must be at least 3 times.. 🔗 External reference