LOW frequency square wave oscillator circuit
Warning: Undefined array key "extension" in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 477
Deprecated: strtolower(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($string) of type string is deprecated in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 477
A simple circuit that can generate an inverted square wave similar to the one used by the inventor on his function generator.
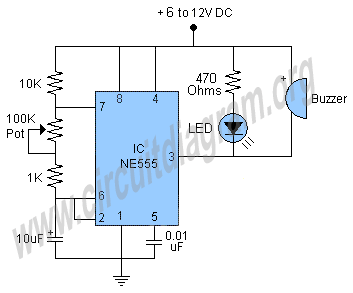
To construct a circuit that produces an inverted square wave, a basic approach involves using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output. For inversion, the output can be fed through a transistor or an inverter gate.
The circuit setup begins with the 555 timer connected in astable mode. Resistor R1 and resistor R2, along with capacitor C1, determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The values of R1 and R2 can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency of the output square wave.
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances in ohms.
- \( C1 \) is the capacitance in farads.
For the inversion, the output from the 555 timer (pin 3) is connected to the base of an NPN transistor through a current-limiting resistor. The emitter is grounded, while the collector is connected to a positive voltage supply through a load resistor. When the output from the 555 timer goes high, the transistor turns on, pulling the output low, and when the timer output goes low, the transistor turns off, allowing the output to go high. This configuration effectively inverts the square wave produced by the timer.
Alternatively, a logic inverter (such as a 74HC14) can be used to achieve the same effect. The output from the 555 timer is connected to the input of the inverter, and the output of the inverter will provide the inverted square wave.
This simple circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and with the appropriate component selection, it can be fine-tuned for specific frequency requirements.A real simple circuit that I can make that will give me the same inverted square wave the inventor is using The inventor calls out the setup he used on his funtion generator. 🔗 External reference
To construct a circuit that produces an inverted square wave, a basic approach involves using a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output. For inversion, the output can be fed through a transistor or an inverter gate.
The circuit setup begins with the 555 timer connected in astable mode. Resistor R1 and resistor R2, along with capacitor C1, determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The values of R1 and R2 can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency of the output square wave.
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances in ohms.
- \( C1 \) is the capacitance in farads.
For the inversion, the output from the 555 timer (pin 3) is connected to the base of an NPN transistor through a current-limiting resistor. The emitter is grounded, while the collector is connected to a positive voltage supply through a load resistor. When the output from the 555 timer goes high, the transistor turns on, pulling the output low, and when the timer output goes low, the transistor turns off, allowing the output to go high. This configuration effectively inverts the square wave produced by the timer.
Alternatively, a logic inverter (such as a 74HC14) can be used to achieve the same effect. The output from the 555 timer is connected to the input of the inverter, and the output of the inverter will provide the inverted square wave.
This simple circuit can be powered by a standard DC power supply, and with the appropriate component selection, it can be fine-tuned for specific frequency requirements.A real simple circuit that I can make that will give me the same inverted square wave the inventor is using The inventor calls out the setup he used on his funtion generator. 🔗 External reference