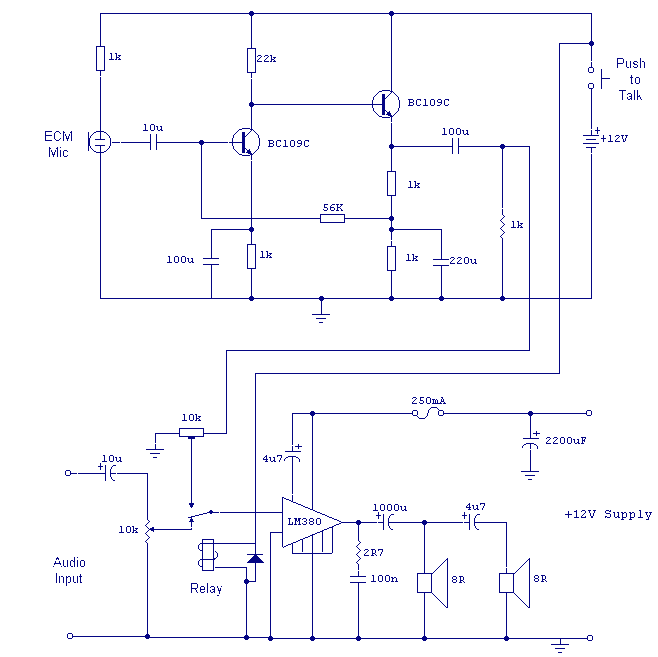
Low-Power 32kHz Oscillator Operates Over Wide Supply Range
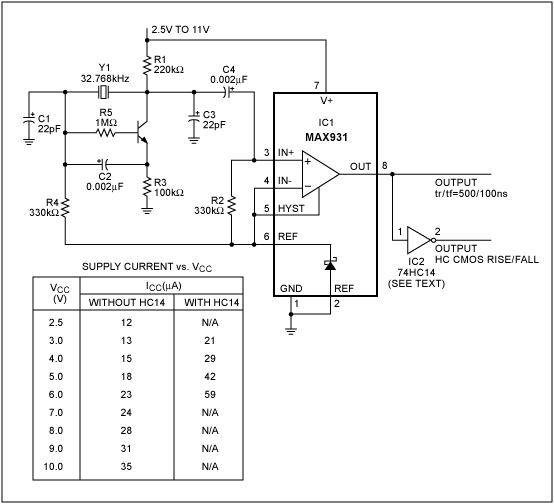
Design a 32kHz wide supply range oscillator with a low-power comparator, a reference, and crystal oscillator.
The circuit design involves creating a 32kHz oscillator that operates efficiently across a wide supply voltage range. The core components include a low-power comparator, a stable reference voltage source, and a crystal oscillator to ensure precise frequency generation.
The crystal oscillator is selected to operate at 32kHz, providing a stable frequency output that is critical for timing applications. The crystal's characteristics, including its load capacitance and series resistance, must be considered to ensure compatibility with the circuit design.
A low-power comparator is utilized to convert the analog signal from the oscillator into a digital signal. This component plays a crucial role in maintaining the oscillator's performance, especially at varying supply voltages. The comparator's input thresholds must be carefully set to ensure reliable switching at the desired frequency.
The reference voltage source provides a stable voltage level against which the comparator operates. This reference is essential for maintaining the oscillator's frequency stability and minimizing drift over temperature variations and supply voltage changes.
The overall design should also incorporate bypass capacitors to filter out noise from the power supply, ensuring that the oscillator operates reliably under different load conditions. Additionally, layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could affect the oscillator's performance.
In summary, the design of a 32kHz oscillator with a low-power comparator, a reference voltage source, and a crystal oscillator requires careful selection of components and thoughtful circuit layout to achieve stable and efficient performance across a wide supply range.Design a 32kHz wide supply range oscillator with a low-power comparator, a reference and crystal oscillator.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design involves creating a 32kHz oscillator that operates efficiently across a wide supply voltage range. The core components include a low-power comparator, a stable reference voltage source, and a crystal oscillator to ensure precise frequency generation.
The crystal oscillator is selected to operate at 32kHz, providing a stable frequency output that is critical for timing applications. The crystal's characteristics, including its load capacitance and series resistance, must be considered to ensure compatibility with the circuit design.
A low-power comparator is utilized to convert the analog signal from the oscillator into a digital signal. This component plays a crucial role in maintaining the oscillator's performance, especially at varying supply voltages. The comparator's input thresholds must be carefully set to ensure reliable switching at the desired frequency.
The reference voltage source provides a stable voltage level against which the comparator operates. This reference is essential for maintaining the oscillator's frequency stability and minimizing drift over temperature variations and supply voltage changes.
The overall design should also incorporate bypass capacitors to filter out noise from the power supply, ensuring that the oscillator operates reliably under different load conditions. Additionally, layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could affect the oscillator's performance.
In summary, the design of a 32kHz oscillator with a low-power comparator, a reference voltage source, and a crystal oscillator requires careful selection of components and thoughtful circuit layout to achieve stable and efficient performance across a wide supply range.Design a 32kHz wide supply range oscillator with a low-power comparator, a reference and crystal oscillator.. 🔗 External reference
.jpg)