magnetic stripe reader circuit
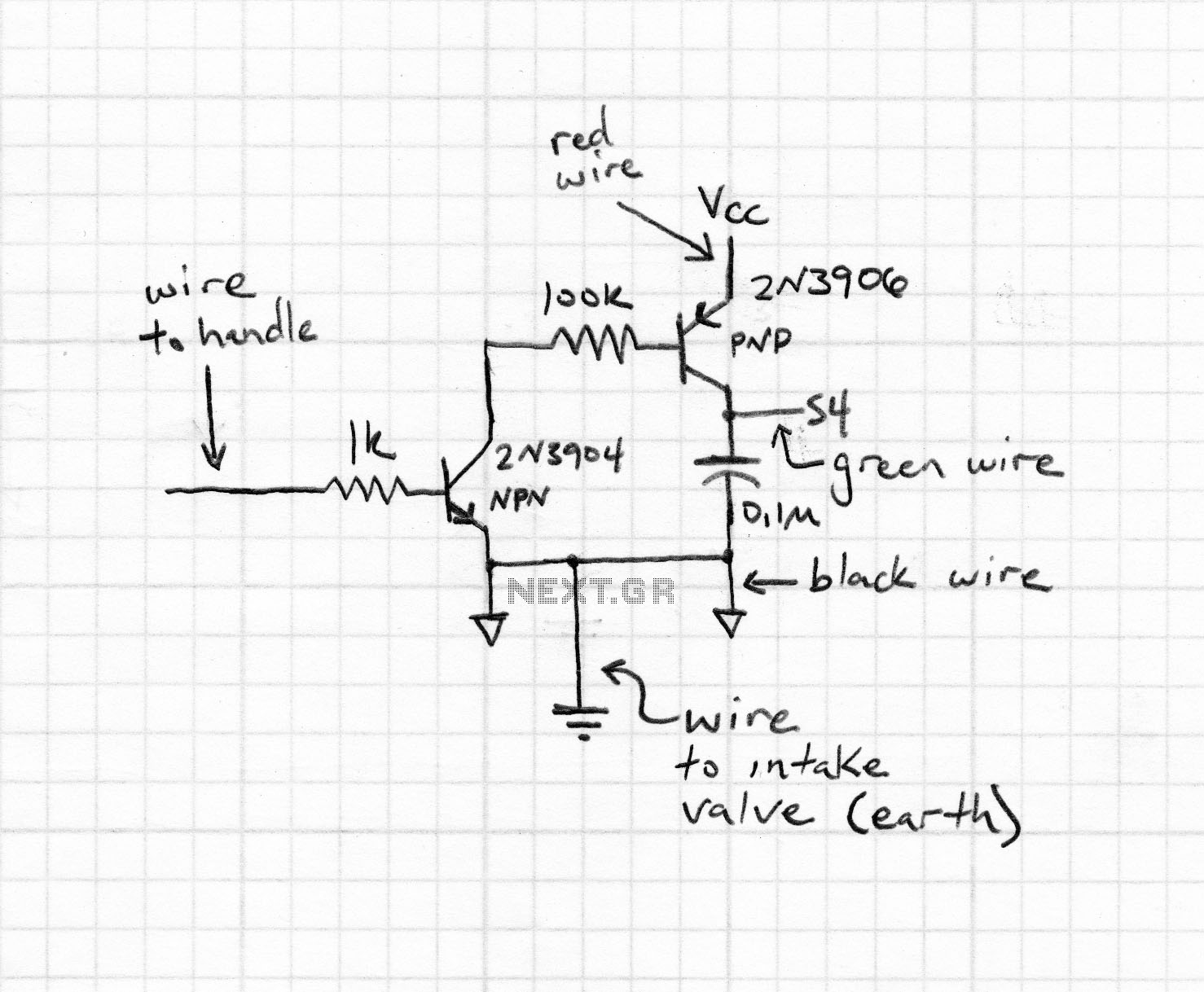
Magnetic stripe reader, electric circuit theory, logic operation. The wiring diagram does not connect the transistor in the circuit. The collector pin of the transistor connects to the tip pin of the jack. The base pin of the transistor connects to the junction of the 120,000-ohm resistor and the 470-nanofarad capacitor.
In a magnetic stripe reader circuit, the proper configuration of components is critical for accurate operation. The circuit typically includes a magnetic sensor, a signal processing unit, and an output interface. The transistor plays a vital role in amplifying the signal received from the magnetic stripe reader.
In this particular wiring diagram, the transistor's collector is connected to the tip pin of the jack, which serves as the output connection to the next stage of the circuit or to an external device. This connection is essential for transferring the amplified signal generated by the transistor.
The base pin of the transistor is connected to the junction of a 120,000-ohm resistor and a 470-nanofarad capacitor. This configuration forms a biasing network that controls the transistor's operation. The resistor limits the current flowing into the base, while the capacitor couples the AC signal from the magnetic stripe reader to the base of the transistor. This allows the transistor to switch on and off in response to the magnetic stripe's information, effectively converting the analog signal into a digital format that can be processed further.
It is crucial to ensure that the transistor is correctly wired in the circuit to avoid malfunction. The absence of a connection to the transistor may lead to a failure in signal amplification, rendering the magnetic stripe reader ineffective. Proper attention to the component values and connections will facilitate a reliable and efficient operation of the magnetic stripe reader circuit.magnetic stripe reader, electric circuit theory, logic operation: Your wiring diagram does not connect the transistor in the circuit. The collector pin of the transistor connects to the tip pin of the Jack. The base pin of the transistor connect to the junction of the 120,000 ohm resistor and the 470 nanofarad capacitor..
🔗 External reference
In a magnetic stripe reader circuit, the proper configuration of components is critical for accurate operation. The circuit typically includes a magnetic sensor, a signal processing unit, and an output interface. The transistor plays a vital role in amplifying the signal received from the magnetic stripe reader.
In this particular wiring diagram, the transistor's collector is connected to the tip pin of the jack, which serves as the output connection to the next stage of the circuit or to an external device. This connection is essential for transferring the amplified signal generated by the transistor.
The base pin of the transistor is connected to the junction of a 120,000-ohm resistor and a 470-nanofarad capacitor. This configuration forms a biasing network that controls the transistor's operation. The resistor limits the current flowing into the base, while the capacitor couples the AC signal from the magnetic stripe reader to the base of the transistor. This allows the transistor to switch on and off in response to the magnetic stripe's information, effectively converting the analog signal into a digital format that can be processed further.
It is crucial to ensure that the transistor is correctly wired in the circuit to avoid malfunction. The absence of a connection to the transistor may lead to a failure in signal amplification, rendering the magnetic stripe reader ineffective. Proper attention to the component values and connections will facilitate a reliable and efficient operation of the magnetic stripe reader circuit.magnetic stripe reader, electric circuit theory, logic operation: Your wiring diagram does not connect the transistor in the circuit. The collector pin of the transistor connects to the tip pin of the Jack. The base pin of the transistor connect to the junction of the 120,000 ohm resistor and the 470 nanofarad capacitor..
🔗 External reference