making 25w low power inverter circuit
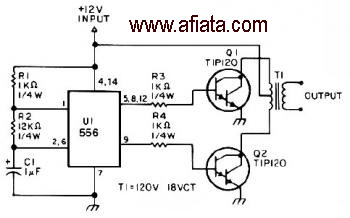
The first section of the 555 timer is configured as an astable oscillator, with R2 and C1 determining the frequency. The output is accessible at pin 5. The second section functions as a phase inverter, with its output available at pin 9. Resistors R3 and R4 prevent output transistors Q1 and Q2 from loading the oscillator.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In the astable mode, the timer continuously switches between high and low states, generating a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors R2 and capacitor C1, which set the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor.
The output from the astable oscillator is taken from pin 5, which provides a square wave signal. This output can drive other components or circuits directly, depending on the load requirements. The second section of the 555 timer acts as a phase inverter, which is crucial for applications requiring signal inversion or phase shifting. The output from this section is available at pin 9, allowing for further signal manipulation or interfacing with other circuit elements.
Resistors R3 and R4 play an essential role in maintaining the stability of the circuit. They are connected to the outputs of transistors Q1 and Q2, ensuring that these outputs do not excessively load the oscillator. This configuration helps maintain the integrity of the oscillation frequency while preventing distortion that could arise from improper loading conditions.
In summary, this configuration of the 555 timer as an astable oscillator with a phase inverter provides a reliable means of generating and manipulating pulse signals. The careful selection of component values and the inclusion of load-resisting elements ensure robust performance across various electronic applications.The first section of the 555 timer is wires as an astable oscillator with R2 and C1 setting the frequency. The output is available at pin 5. The second section is wired as a phase inverter. That output is available at pin 9. Resistor R3 and R4 keep output transistor Q1 and Q2 from loading down the oscillator. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In the astable mode, the timer continuously switches between high and low states, generating a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors R2 and capacitor C1, which set the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor.
The output from the astable oscillator is taken from pin 5, which provides a square wave signal. This output can drive other components or circuits directly, depending on the load requirements. The second section of the 555 timer acts as a phase inverter, which is crucial for applications requiring signal inversion or phase shifting. The output from this section is available at pin 9, allowing for further signal manipulation or interfacing with other circuit elements.
Resistors R3 and R4 play an essential role in maintaining the stability of the circuit. They are connected to the outputs of transistors Q1 and Q2, ensuring that these outputs do not excessively load the oscillator. This configuration helps maintain the integrity of the oscillation frequency while preventing distortion that could arise from improper loading conditions.
In summary, this configuration of the 555 timer as an astable oscillator with a phase inverter provides a reliable means of generating and manipulating pulse signals. The careful selection of component values and the inclusion of load-resisting elements ensure robust performance across various electronic applications.The first section of the 555 timer is wires as an astable oscillator with R2 and C1 setting the frequency. The output is available at pin 5. The second section is wired as a phase inverter. That output is available at pin 9. Resistor R3 and R4 keep output transistor Q1 and Q2 from loading down the oscillator. 🔗 External reference