making simplest room thermometer
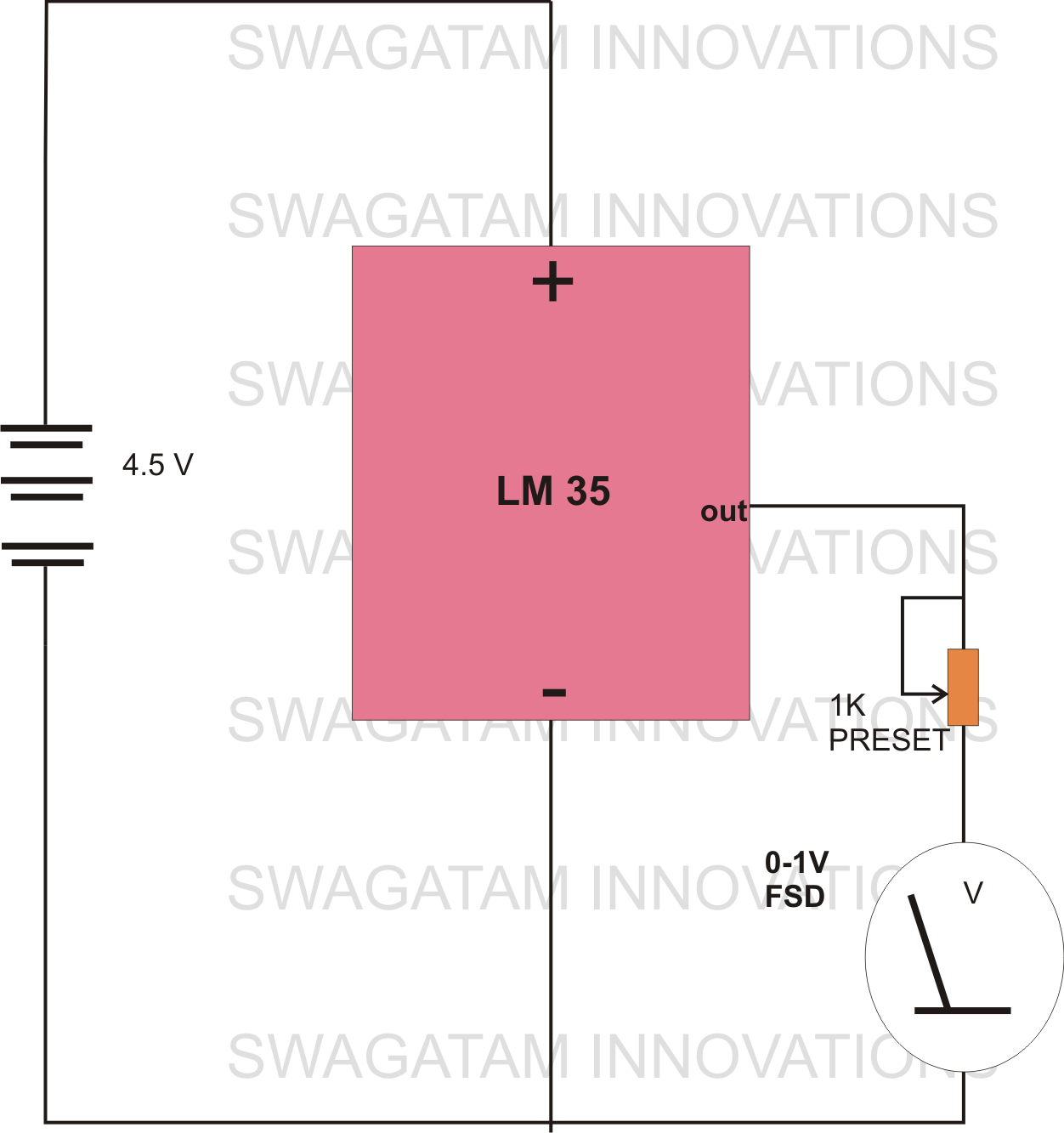
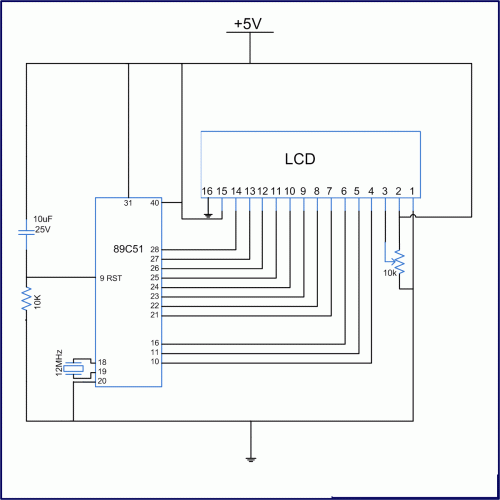
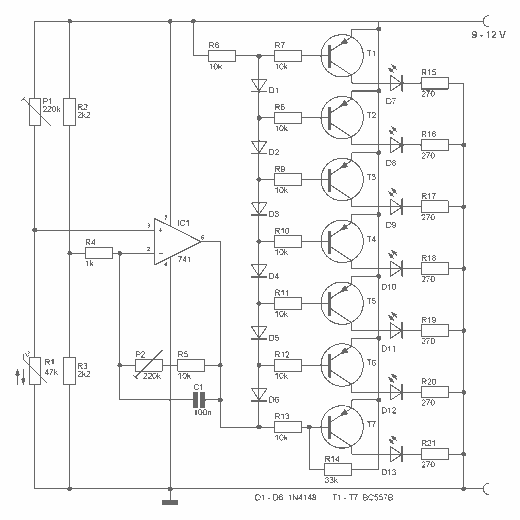
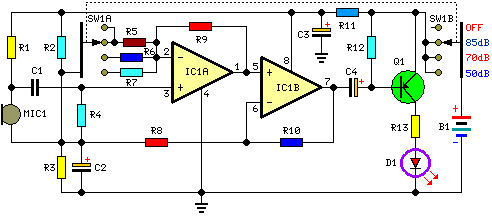
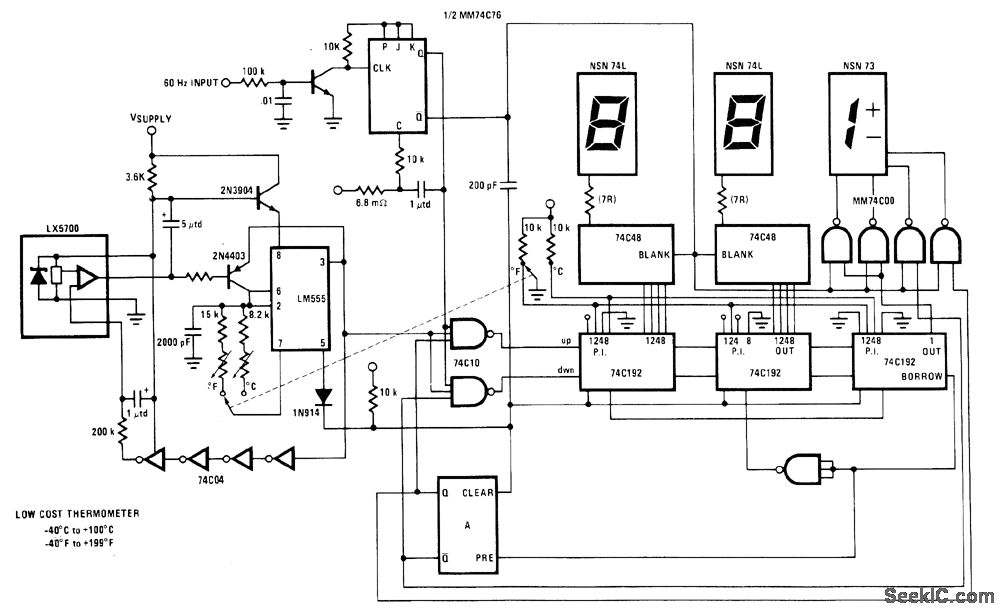
The circuit diagram provided illustrates a straightforward setup. There is no requirement for complex circuitry; simply connect a 0-1 V full-scale deflection (FSD) moving coil meter across the designated pins of the integrated circuit (IC). Adjust the potentiometer as needed, and the room temperature sensor circuit will be operational.
The described circuit utilizes a simple configuration to measure temperature through a moving coil meter, which provides an analog readout of the temperature in volts. The IC serves as the core component, likely functioning as a temperature sensor or signal conditioner.
In this setup, the moving coil meter is calibrated to operate within a 0-1 V range, allowing for direct interpretation of the voltage output as a temperature reading. The potentiometer plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the sensitivity and accuracy of the circuit, enabling the user to adjust the output voltage to correspond with the specific temperature range of interest.
The connections to the IC should be made with care to ensure proper functionality. The relevant pins for the meter connection must be identified in the circuit diagram, and attention should be given to the power supply requirements of the IC. It is advisable to use decoupling capacitors near the power pins to stabilize the voltage supply and minimize noise.
For enhanced performance, consider incorporating filtering components, such as capacitors, to smooth out any fluctuations in the output voltage. This will provide a more stable and accurate reading on the moving coil meter. The overall design is suitable for applications where a simple and effective temperature measurement solution is required, such as in HVAC systems, laboratory environments, or home automation projects.The circuit diagram shown below explains it all, no need of any complicated circuitry, just connect a 0-1 V FSD moving coil meter across the relevant pins of the IC, set the pot appropriately, and you are ready with your room temperature sensor circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a simple configuration to measure temperature through a moving coil meter, which provides an analog readout of the temperature in volts. The IC serves as the core component, likely functioning as a temperature sensor or signal conditioner.
In this setup, the moving coil meter is calibrated to operate within a 0-1 V range, allowing for direct interpretation of the voltage output as a temperature reading. The potentiometer plays a crucial role in fine-tuning the sensitivity and accuracy of the circuit, enabling the user to adjust the output voltage to correspond with the specific temperature range of interest.
The connections to the IC should be made with care to ensure proper functionality. The relevant pins for the meter connection must be identified in the circuit diagram, and attention should be given to the power supply requirements of the IC. It is advisable to use decoupling capacitors near the power pins to stabilize the voltage supply and minimize noise.
For enhanced performance, consider incorporating filtering components, such as capacitors, to smooth out any fluctuations in the output voltage. This will provide a more stable and accurate reading on the moving coil meter. The overall design is suitable for applications where a simple and effective temperature measurement solution is required, such as in HVAC systems, laboratory environments, or home automation projects.The circuit diagram shown below explains it all, no need of any complicated circuitry, just connect a 0-1 V FSD moving coil meter across the relevant pins of the IC, set the pot appropriately, and you are ready with your room temperature sensor circuit. 🔗 External reference