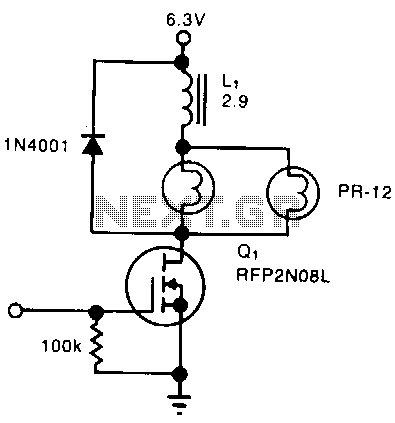
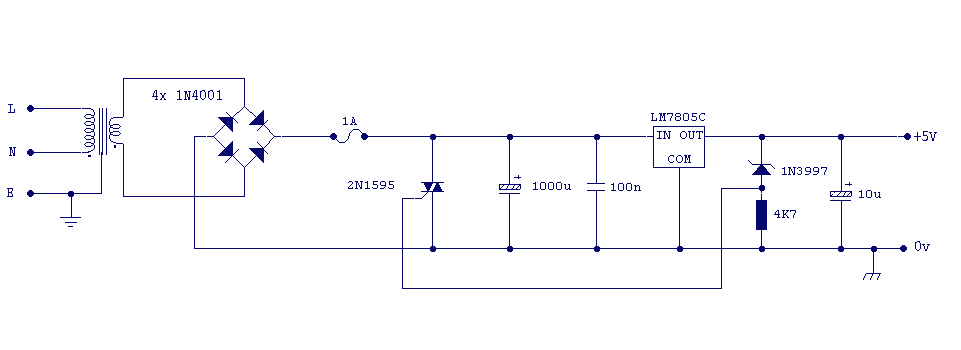
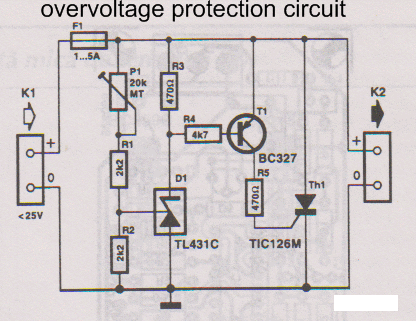
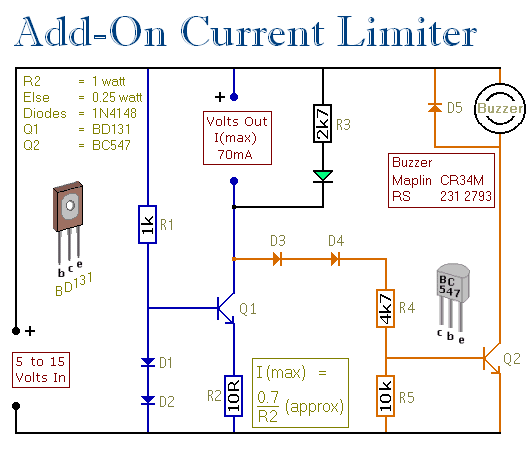
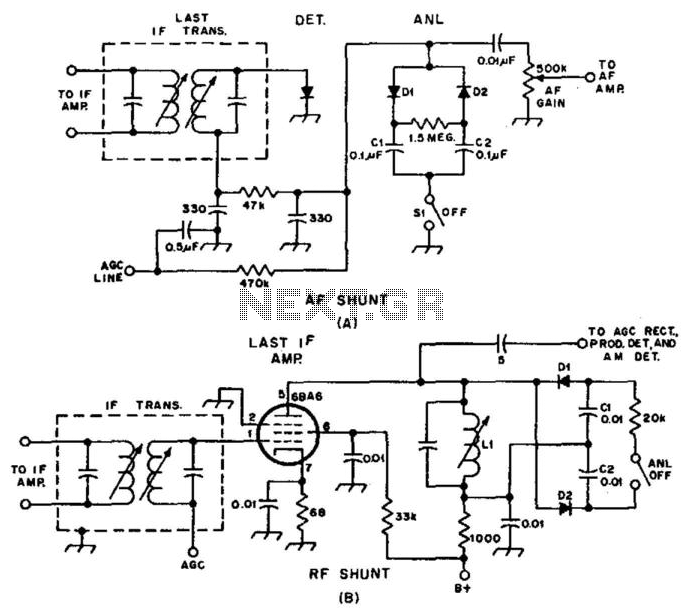
MAX6495 Overvoltage Limiter
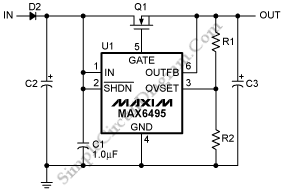
To protect downstream circuits from overvoltage conditions that occur during load-dump events or transients, the MAX6495, MAX6499, MAX6397, and MAX6398 can be utilized.
The MAX6495, MAX6499, MAX6397, and MAX6398 are integrated circuits designed for overvoltage protection in various electronic applications. These devices are particularly effective in automotive environments where load-dump events can lead to sudden voltage spikes that may damage sensitive components.
The MAX6495 and MAX6499 are voltage supervisors that monitor supply voltage levels and can quickly disconnect the load if the voltage exceeds a predefined threshold. This rapid response is crucial in protecting downstream circuitry from potential damage. The MAX6397 and MAX6398 serve a similar purpose but are optimized for different voltage ranges and applications.
In a typical application circuit, the overvoltage protection IC is connected in series with the load. The input voltage is continuously monitored, and if the voltage exceeds the specified limit, the IC activates a switch (often a MOSFET or a relay) to disconnect the load from the power source. The IC features a built-in delay to prevent false triggering from transient voltage spikes that might occur during normal operation.
Additionally, these devices may include features such as thermal shutdown, fault indication outputs, and the ability to reset automatically once the voltage returns to safe levels. The selection of appropriate components, including the correct resistor values for setting thresholds and the choice of MOSFET for load switching, is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, the MAX6495, MAX6499, MAX6397, and MAX6398 provide robust solutions for safeguarding electronic circuits against overvoltage conditions, enhancing the reliability and longevity of the devices they protect.To protect downstream circuits from overvoltage conditions that show up during load-dump events or transients, we can use the MAX6495MAX6499/MAX6397/MAX6398.. 🔗 External reference
The MAX6495, MAX6499, MAX6397, and MAX6398 are integrated circuits designed for overvoltage protection in various electronic applications. These devices are particularly effective in automotive environments where load-dump events can lead to sudden voltage spikes that may damage sensitive components.
The MAX6495 and MAX6499 are voltage supervisors that monitor supply voltage levels and can quickly disconnect the load if the voltage exceeds a predefined threshold. This rapid response is crucial in protecting downstream circuitry from potential damage. The MAX6397 and MAX6398 serve a similar purpose but are optimized for different voltage ranges and applications.
In a typical application circuit, the overvoltage protection IC is connected in series with the load. The input voltage is continuously monitored, and if the voltage exceeds the specified limit, the IC activates a switch (often a MOSFET or a relay) to disconnect the load from the power source. The IC features a built-in delay to prevent false triggering from transient voltage spikes that might occur during normal operation.
Additionally, these devices may include features such as thermal shutdown, fault indication outputs, and the ability to reset automatically once the voltage returns to safe levels. The selection of appropriate components, including the correct resistor values for setting thresholds and the choice of MOSFET for load switching, is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, the MAX6495, MAX6499, MAX6397, and MAX6398 provide robust solutions for safeguarding electronic circuits against overvoltage conditions, enhancing the reliability and longevity of the devices they protect.To protect downstream circuits from overvoltage conditions that show up during load-dump events or transients, we can use the MAX6495MAX6499/MAX6397/MAX6398.. 🔗 External reference