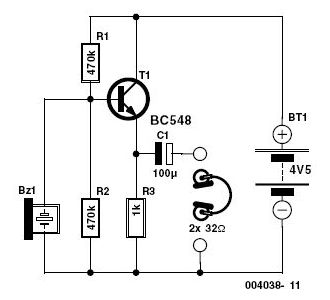
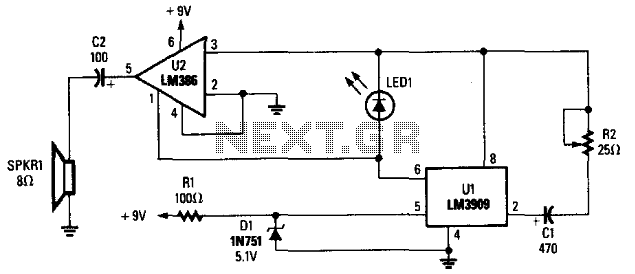
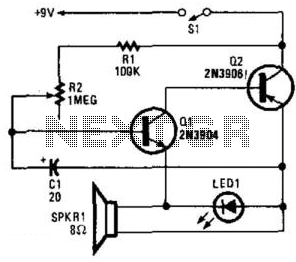
metronome
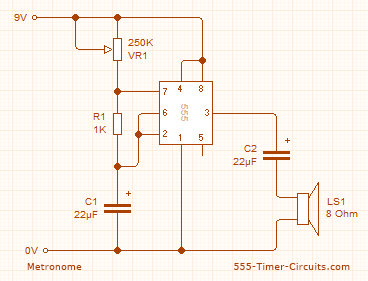
This circuit employs the 555 timer configured in astable mode to produce a continuous square wave output from Pin 3. The output is subsequently filtered through a 22.5 µF electrolytic capacitor to generate a smooth oscillation, resulting in a 'toc-toc' sound. The frequency of the output is adjustable via a 250K potentiometer (VR1).
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In astable mode, it operates as an oscillator without requiring any external triggering. The frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistance and capacitance values in the circuit.
In this particular configuration, the 250K potentiometer (VR1) is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and the threshold pin (Pin 6) of the 555 timer. The wiper of the potentiometer is connected to the timing capacitor (22.5 µF), which is also connected to ground. The capacitor charges and discharges through the resistive path provided by the potentiometer and a fixed resistor, if present, thereby controlling the frequency of the oscillation.
The output square wave at Pin 3 can be connected to various loads, such as a small speaker or a buzzer, to produce sound. The 22.5 µF electrolytic capacitor smooths the output waveform, which helps in achieving a more pleasant sound quality by filtering out high-frequency components.
It is essential to ensure that the capacitor is correctly polarized, as electrolytic capacitors are sensitive to reverse voltage. The circuit's design allows for easy adjustment of the sound frequency, making it suitable for applications where sound generation is required, such as alarms, timers, or simple musical devices. Proper power supply decoupling should also be considered to enhance the stability of the 555 timer's operation.This circuit uses the 555 timer in an Astable operating mode and generates a continuous output via Pin 3 in the form of a square wave. This is then passed through the 22 ½F electrolytic capacitor to create a smooth oscillation which then creates the `toc-toc` sound.
The speed of the output is controlled by the 250K Potentiometer (VR1). 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In astable mode, it operates as an oscillator without requiring any external triggering. The frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistance and capacitance values in the circuit.
In this particular configuration, the 250K potentiometer (VR1) is connected between the discharge pin (Pin 7) and the threshold pin (Pin 6) of the 555 timer. The wiper of the potentiometer is connected to the timing capacitor (22.5 µF), which is also connected to ground. The capacitor charges and discharges through the resistive path provided by the potentiometer and a fixed resistor, if present, thereby controlling the frequency of the oscillation.
The output square wave at Pin 3 can be connected to various loads, such as a small speaker or a buzzer, to produce sound. The 22.5 µF electrolytic capacitor smooths the output waveform, which helps in achieving a more pleasant sound quality by filtering out high-frequency components.
It is essential to ensure that the capacitor is correctly polarized, as electrolytic capacitors are sensitive to reverse voltage. The circuit's design allows for easy adjustment of the sound frequency, making it suitable for applications where sound generation is required, such as alarms, timers, or simple musical devices. Proper power supply decoupling should also be considered to enhance the stability of the 555 timer's operation.This circuit uses the 555 timer in an Astable operating mode and generates a continuous output via Pin 3 in the form of a square wave. This is then passed through the 22 ½F electrolytic capacitor to create a smooth oscillation which then creates the `toc-toc` sound.
The speed of the output is controlled by the 250K Potentiometer (VR1). 🔗 External reference