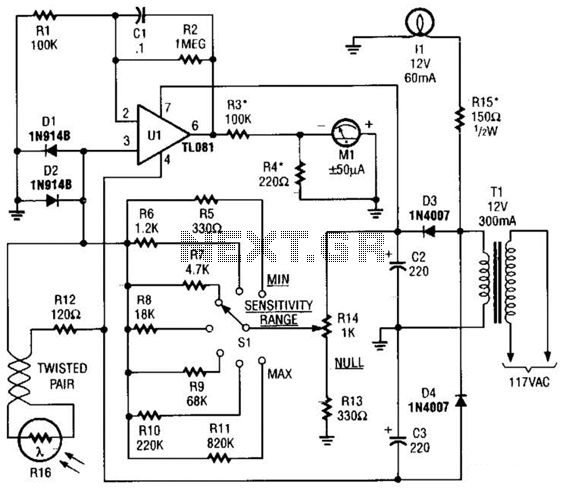
Micro Ampere Meter
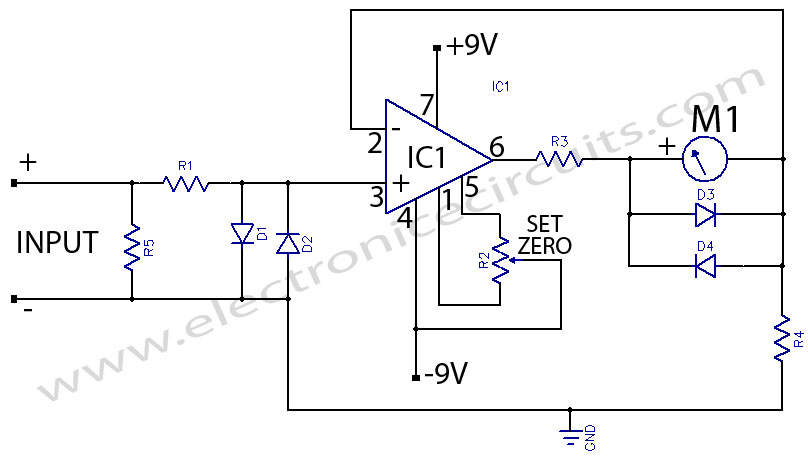
The microampere meter provides full-scale deflection for a 0.1 V input. The current to be measured flows through a known resistor.
The microampere meter is an essential instrument used for measuring very low currents in the microampere range. It operates on the principle that a known voltage across a resistor generates a proportional current, allowing the meter to indicate the current value accurately.
In practical applications, the microampere meter is typically connected in series with the circuit under test. A precision resistor, often referred to as a shunt resistor, is placed in line to convert the microampere level current into a measurable voltage drop. The value of this resistor is critical, as it must be chosen to ensure that the voltage drop does not exceed the meter's input specifications while still allowing for accurate current readings.
The full-scale deflection of the meter at 0.1 V means that when the voltage across the shunt resistor reaches this threshold, the meter needle or digital display will indicate the maximum value on its scale. This feature makes the microampere meter particularly useful in applications such as sensor circuits, where low currents are prevalent, and precise measurements are necessary for proper functionality.
In terms of circuit design, the microampere meter circuit typically includes an operational amplifier to buffer the input signal, ensuring that the meter does not load the circuit under measurement. Additionally, filtering components may be included to reduce noise and improve measurement accuracy.
Overall, the microampere meter is a vital tool for engineers and technicians working with low-current applications, providing reliable and precise measurements necessary for the successful operation of various electronic devices.The microampere meter The microampere meter gives full scale deflection for 0.1 V input. The current to be measured is passed through a known.. 🔗 External reference
The microampere meter is an essential instrument used for measuring very low currents in the microampere range. It operates on the principle that a known voltage across a resistor generates a proportional current, allowing the meter to indicate the current value accurately.
In practical applications, the microampere meter is typically connected in series with the circuit under test. A precision resistor, often referred to as a shunt resistor, is placed in line to convert the microampere level current into a measurable voltage drop. The value of this resistor is critical, as it must be chosen to ensure that the voltage drop does not exceed the meter's input specifications while still allowing for accurate current readings.
The full-scale deflection of the meter at 0.1 V means that when the voltage across the shunt resistor reaches this threshold, the meter needle or digital display will indicate the maximum value on its scale. This feature makes the microampere meter particularly useful in applications such as sensor circuits, where low currents are prevalent, and precise measurements are necessary for proper functionality.
In terms of circuit design, the microampere meter circuit typically includes an operational amplifier to buffer the input signal, ensuring that the meter does not load the circuit under measurement. Additionally, filtering components may be included to reduce noise and improve measurement accuracy.
Overall, the microampere meter is a vital tool for engineers and technicians working with low-current applications, providing reliable and precise measurements necessary for the successful operation of various electronic devices.The microampere meter The microampere meter gives full scale deflection for 0.1 V input. The current to be measured is passed through a known.. 🔗 External reference