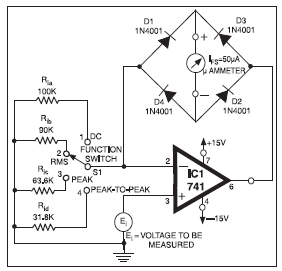
Single Input to Differential Input Adapter for Digital Voltmeter

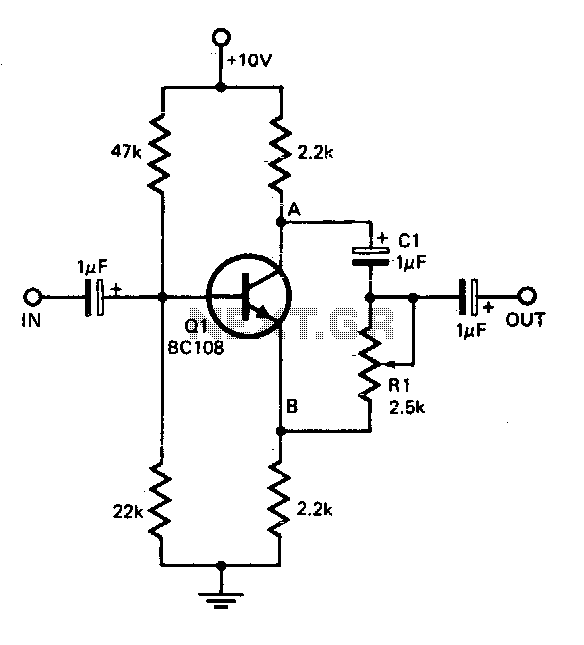
In some cases, a differential input is needed for voltage measurement. By using a single operational amplifier, it is possible to construct an adapter that provides a floating voltage reference.
To achieve a differential input for voltage measurement using an operational amplifier (op-amp), a specific circuit configuration can be utilized. The basic principle involves using the op-amp in a differential amplifier configuration, which allows for the measurement of the voltage difference between two input signals while rejecting common-mode noise.
The circuit typically consists of the following components:
1. **Operational Amplifier**: A single op-amp is used to amplify the difference between the two input voltages. Common choices for op-amps include the LM358 or the TL081, depending on the application requirements such as bandwidth and power supply voltage.
2. **Resistors**: Four precision resistors are used to set the gain of the op-amp and to ensure accurate differential measurement. The resistors are usually arranged in a configuration where two resistors (R1 and R2) are connected to the inverting input and the other two resistors (R3 and R4) to the non-inverting input. The values of these resistors determine the gain of the amplifier and should be selected to match closely for optimal performance.
3. **Power Supply**: The op-amp requires a dual power supply (positive and negative) to function correctly, which allows it to handle both positive and negative input voltages.
4. **Input Connections**: The two input voltages (V1 and V2) are connected to the non-inverting and inverting terminals of the op-amp respectively. The output voltage (Vout) will be proportional to the difference between these two input voltages.
5. **Floating Reference**: The circuit can be designed to provide a floating voltage reference, which means that the output voltage is not referenced to ground. This is particularly useful in applications where the input voltages may be at different ground potentials.
The final output from the op-amp can be further processed or utilized in various measurement systems, such as data acquisition systems or instrumentation amplifiers, where accurate voltage measurement is critical. Proper PCB layout and component placement are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the differential amplifier circuit.I some cases, a differential input is needed for voltage measurement. Using the only one operational amplifier, you can build an adapter to provide a floating. 🔗 External reference
To achieve a differential input for voltage measurement using an operational amplifier (op-amp), a specific circuit configuration can be utilized. The basic principle involves using the op-amp in a differential amplifier configuration, which allows for the measurement of the voltage difference between two input signals while rejecting common-mode noise.
The circuit typically consists of the following components:
1. **Operational Amplifier**: A single op-amp is used to amplify the difference between the two input voltages. Common choices for op-amps include the LM358 or the TL081, depending on the application requirements such as bandwidth and power supply voltage.
2. **Resistors**: Four precision resistors are used to set the gain of the op-amp and to ensure accurate differential measurement. The resistors are usually arranged in a configuration where two resistors (R1 and R2) are connected to the inverting input and the other two resistors (R3 and R4) to the non-inverting input. The values of these resistors determine the gain of the amplifier and should be selected to match closely for optimal performance.
3. **Power Supply**: The op-amp requires a dual power supply (positive and negative) to function correctly, which allows it to handle both positive and negative input voltages.
4. **Input Connections**: The two input voltages (V1 and V2) are connected to the non-inverting and inverting terminals of the op-amp respectively. The output voltage (Vout) will be proportional to the difference between these two input voltages.
5. **Floating Reference**: The circuit can be designed to provide a floating voltage reference, which means that the output voltage is not referenced to ground. This is particularly useful in applications where the input voltages may be at different ground potentials.
The final output from the op-amp can be further processed or utilized in various measurement systems, such as data acquisition systems or instrumentation amplifiers, where accurate voltage measurement is critical. Proper PCB layout and component placement are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the differential amplifier circuit.I some cases, a differential input is needed for voltage measurement. Using the only one operational amplifier, you can build an adapter to provide a floating. 🔗 External reference