microcontroller driving relay

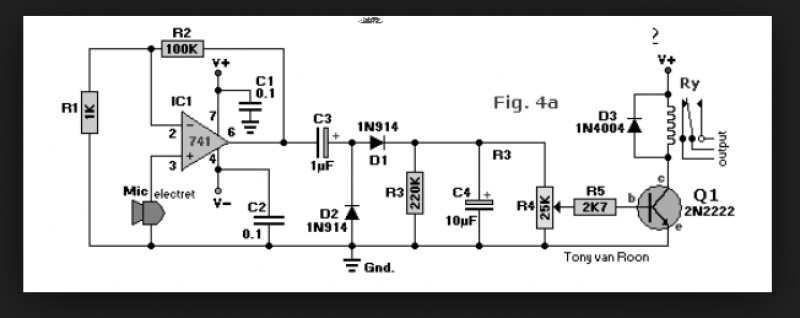
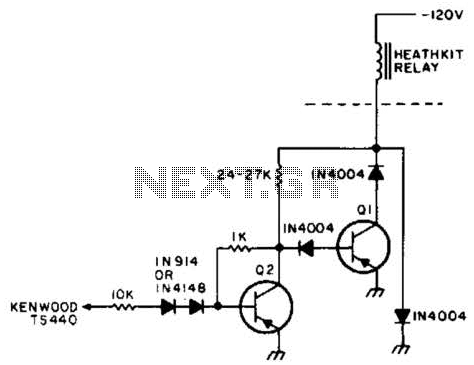
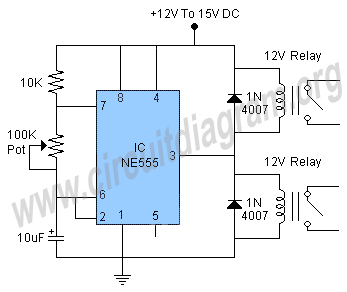
An NPN bipolar transistor is typically utilized for relay switching, particularly with 12V coil-rated relays, as it helps maintain circuit separation. A diode is also added to prevent issues. The necessity of driving the relay with a transistor depends on the coil resistance; if it is low (around 125 ohms), two pins can be used to provide 40mA. It is important to connect between the pins and 5V, as the pins can sink more current than they can source. A 100 ohm series resistor is necessary only if the supply voltage exceeds the coil's rating. Additionally, the schematic should include a back EMF protection diode.
An NPN bipolar transistor is a suitable choice for controlling a relay with a 12V coil, as it allows for isolation between the control circuit and the relay, ensuring that any noise or voltage spikes from the relay do not affect the control circuitry. When designing such a circuit, it is crucial to consider the coil resistance of the relay. For instance, with a coil resistance of approximately 125 ohms, the current drawn can be calculated using Ohm's law (I = V/R). In this case, the relay would require about 96mA (12V / 125Ω), which exceeds the maximum current that a microcontroller pin can safely supply. Therefore, utilizing a transistor to switch the relay is advisable.
The transistor should be connected in such a way that its collector is connected to one terminal of the relay coil, while the other terminal is connected to the positive supply voltage (12V). The emitter of the transistor is connected to ground. The base of the transistor is driven by a microcontroller pin through a current-limiting resistor. The value of this resistor can be calculated based on the desired base current, which should be sufficient to saturate the transistor when the relay is activated.
To ensure reliable operation, a diode must be placed in parallel with the relay coil, oriented to allow current to flow only when the relay is de-energized. This diode serves as a back EMF protection diode, preventing voltage spikes generated by the collapsing magnetic field of the relay coil from damaging the transistor or the microcontroller.
In scenarios where the supply voltage is higher than what the relay coil can handle, a series resistor (e.g., 100 ohms) may be necessary to limit the current through the coil to a safe level. However, this should be calculated carefully to avoid under-driving the relay. The overall schematic should clearly depict these connections, ensuring that all components are rated appropriately for the voltages and currents involved.I usually use an NPN Bipolar transistor to do the relay switching, mainly because my relays are 12v coil rated, but it also keeps everything nice and seperated. and yes i add a diode. with no problem. ( do I or did I need to drive it with a transistor ) but it seam like radio shack is getting out of the parts business.
I`ve got to place a order wit h digikey and though I mite find something better and cheaper. If you know the coil resistance it`s easy to calculate if you need a transistor. If it`s too low (say 125 ©) then you can use two pins to provide 40mA. Make sure you connect between the pins and 5V as the pins can sink more than source. The 100R series resistor is only required if the supply voltage is too high for the coil. The schematic also lacks the all-important back EMF protection diode. 🔗 External reference
An NPN bipolar transistor is a suitable choice for controlling a relay with a 12V coil, as it allows for isolation between the control circuit and the relay, ensuring that any noise or voltage spikes from the relay do not affect the control circuitry. When designing such a circuit, it is crucial to consider the coil resistance of the relay. For instance, with a coil resistance of approximately 125 ohms, the current drawn can be calculated using Ohm's law (I = V/R). In this case, the relay would require about 96mA (12V / 125Ω), which exceeds the maximum current that a microcontroller pin can safely supply. Therefore, utilizing a transistor to switch the relay is advisable.
The transistor should be connected in such a way that its collector is connected to one terminal of the relay coil, while the other terminal is connected to the positive supply voltage (12V). The emitter of the transistor is connected to ground. The base of the transistor is driven by a microcontroller pin through a current-limiting resistor. The value of this resistor can be calculated based on the desired base current, which should be sufficient to saturate the transistor when the relay is activated.
To ensure reliable operation, a diode must be placed in parallel with the relay coil, oriented to allow current to flow only when the relay is de-energized. This diode serves as a back EMF protection diode, preventing voltage spikes generated by the collapsing magnetic field of the relay coil from damaging the transistor or the microcontroller.
In scenarios where the supply voltage is higher than what the relay coil can handle, a series resistor (e.g., 100 ohms) may be necessary to limit the current through the coil to a safe level. However, this should be calculated carefully to avoid under-driving the relay. The overall schematic should clearly depict these connections, ensuring that all components are rated appropriately for the voltages and currents involved.I usually use an NPN Bipolar transistor to do the relay switching, mainly because my relays are 12v coil rated, but it also keeps everything nice and seperated. and yes i add a diode. with no problem. ( do I or did I need to drive it with a transistor ) but it seam like radio shack is getting out of the parts business.
I`ve got to place a order wit h digikey and though I mite find something better and cheaper. If you know the coil resistance it`s easy to calculate if you need a transistor. If it`s too low (say 125 ©) then you can use two pins to provide 40mA. Make sure you connect between the pins and 5V as the pins can sink more than source. The 100R series resistor is only required if the supply voltage is too high for the coil. The schematic also lacks the all-important back EMF protection diode. 🔗 External reference