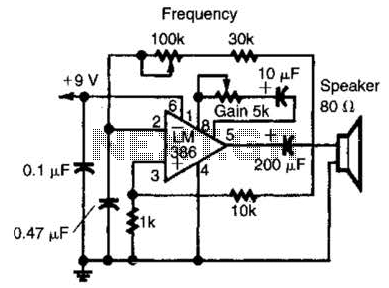
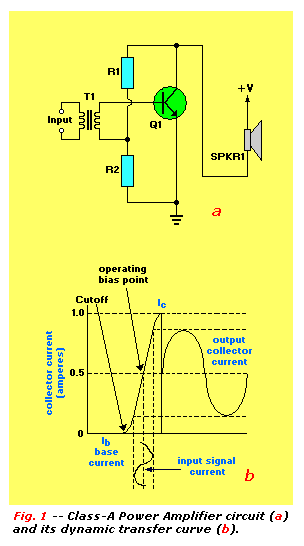
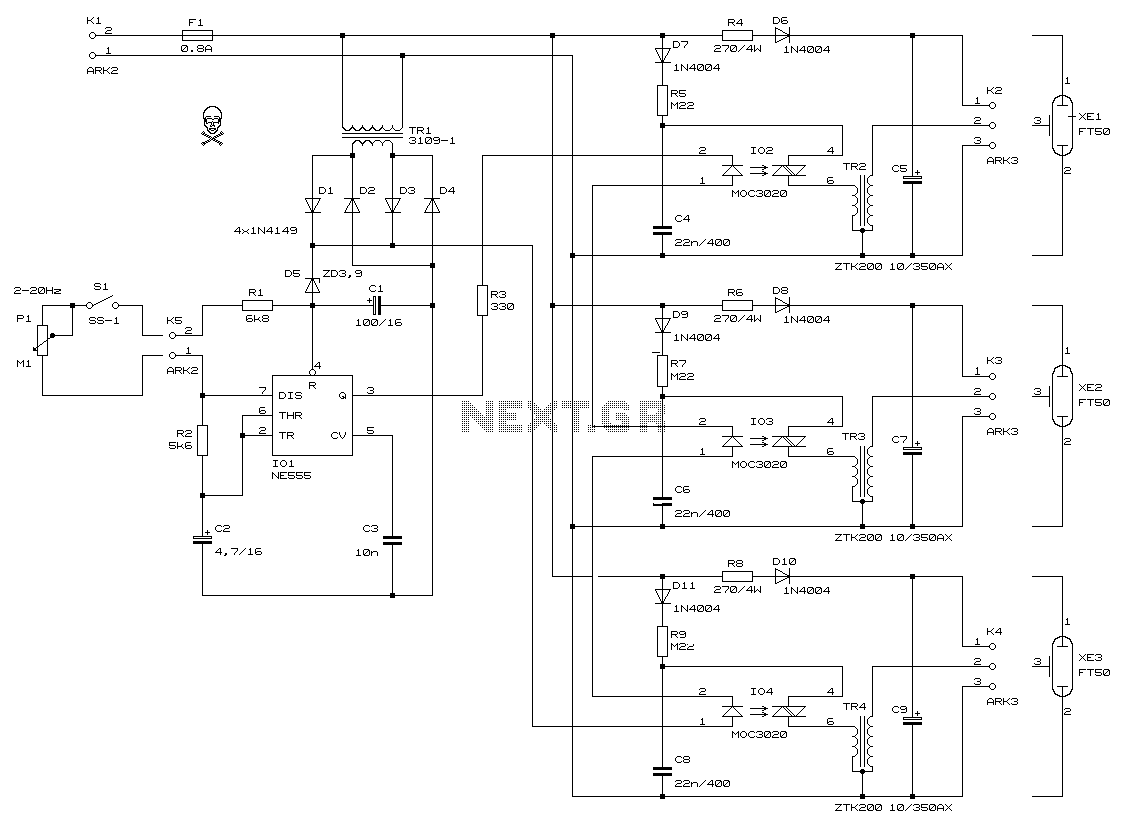
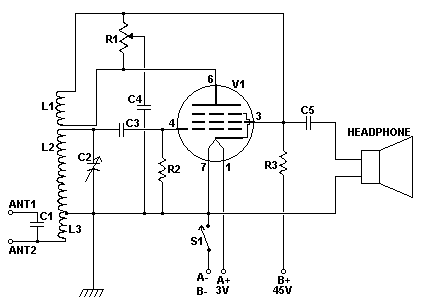
microcontroller How does this power supply circuit work? (MCU + LM317)

The filter consisting of resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1 integrates the PWM waveform. The purpose of the operational amplifier appears to be that of a non-inverting amplifier, with the gain determined by resistors R6 and R7. However, the need for amplifying the integrated DC voltage is unclear. There may be a misunderstanding regarding the operation of the LM317 in relation to the microcontroller (MCU). It is understood that the LM317 provides a reference voltage of 1.25V between the OUT and ADJ pins, which should be measured across resistor R5 in the circuit. The output voltage (Vout) is defined by the equation Vout = 1.25(1 + R2/R5) + I(adj) * R2, as per the datasheet. Given that the only variable in this equation is I(adj), it is suggested that the integrated DC voltage influences the current, which in turn affects the output voltage.
The circuit described involves a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal that is filtered by the combination of resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1. This filtering process smooths out the PWM waveform to produce a more stable DC voltage. The operational amplifier, configured as a non-inverting amplifier, serves to amplify this integrated DC voltage. The gain of the op-amp is set by the resistors R6 and R7, which defines how much the input signal is amplified before being sent to the next stage of the circuit.
The LM317 voltage regulator plays a critical role in this configuration. It maintains a constant output voltage by providing a reference voltage of 1.25V between its output (OUT) and adjust (ADJ) pins. The output voltage is adjustable and depends on the ratio of resistors R2 and R5, as illustrated in the provided equation. The term I(adj) represents the adjustment pin current, which is typically very small but can influence the output voltage slightly. The relationship between the integrated DC voltage and the output voltage indicates that changes in the current through the adjustment pin directly affect the output voltage. This understanding is crucial for ensuring that the LM317 operates effectively within the circuit, particularly when interfacing with the microcontroller, which may require specific voltage levels for accurate operation.
In summary, the circuit's operation hinges on the interplay between the PWM filtering, the amplification by the op-amp, and the regulation provided by the LM317. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the desired output voltage is achieved and maintained, enabling reliable performance of the overall system.The filter R1, R2 and C1 integrate the PWM waveform. But what is the point of the op-amp It looks like a non-inverting amplifier to me, with the gain set by R6 and R7 - if I`m not mistaken. But why does the integrated DC voltage need amplification Perhaps, I don`t understand that part because I don`t understand how the Lm317 is working in conjunction with the MCU.
I understand that LM317 drops a reference 1. 25V between the OUT and ADJ pin (which should be across R5 in reference to the circuit) and the Vout is defined as 1. 25(1 + R2/R5) + I(adj. ) * R2. (from datasheet) Since the only variable is I(adj) in the above equation, am I correct in my understanding that the integrated DC voltage is actually changes the current and hence the output voltage
🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal that is filtered by the combination of resistors R1, R2, and capacitor C1. This filtering process smooths out the PWM waveform to produce a more stable DC voltage. The operational amplifier, configured as a non-inverting amplifier, serves to amplify this integrated DC voltage. The gain of the op-amp is set by the resistors R6 and R7, which defines how much the input signal is amplified before being sent to the next stage of the circuit.
The LM317 voltage regulator plays a critical role in this configuration. It maintains a constant output voltage by providing a reference voltage of 1.25V between its output (OUT) and adjust (ADJ) pins. The output voltage is adjustable and depends on the ratio of resistors R2 and R5, as illustrated in the provided equation. The term I(adj) represents the adjustment pin current, which is typically very small but can influence the output voltage slightly. The relationship between the integrated DC voltage and the output voltage indicates that changes in the current through the adjustment pin directly affect the output voltage. This understanding is crucial for ensuring that the LM317 operates effectively within the circuit, particularly when interfacing with the microcontroller, which may require specific voltage levels for accurate operation.
In summary, the circuit's operation hinges on the interplay between the PWM filtering, the amplification by the op-amp, and the regulation provided by the LM317. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the desired output voltage is achieved and maintained, enabling reliable performance of the overall system.The filter R1, R2 and C1 integrate the PWM waveform. But what is the point of the op-amp It looks like a non-inverting amplifier to me, with the gain set by R6 and R7 - if I`m not mistaken. But why does the integrated DC voltage need amplification Perhaps, I don`t understand that part because I don`t understand how the Lm317 is working in conjunction with the MCU.
I understand that LM317 drops a reference 1. 25V between the OUT and ADJ pin (which should be across R5 in reference to the circuit) and the Vout is defined as 1. 25(1 + R2/R5) + I(adj. ) * R2. (from datasheet) Since the only variable is I(adj) in the above equation, am I correct in my understanding that the integrated DC voltage is actually changes the current and hence the output voltage
🔗 External reference