Motion Detectors with Infrared Sensors
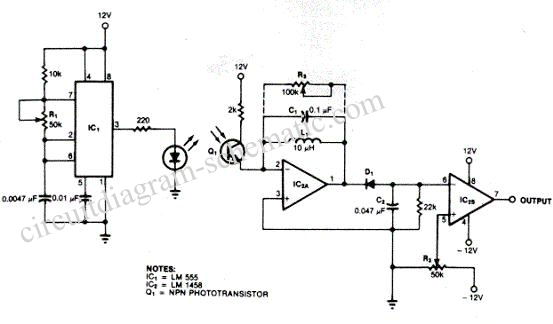
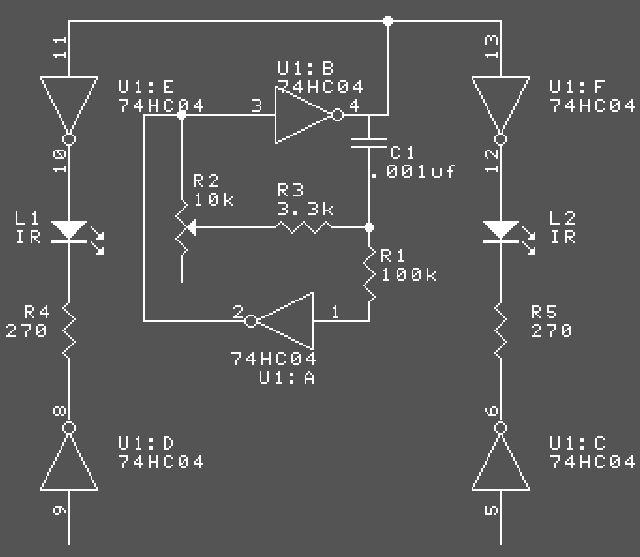
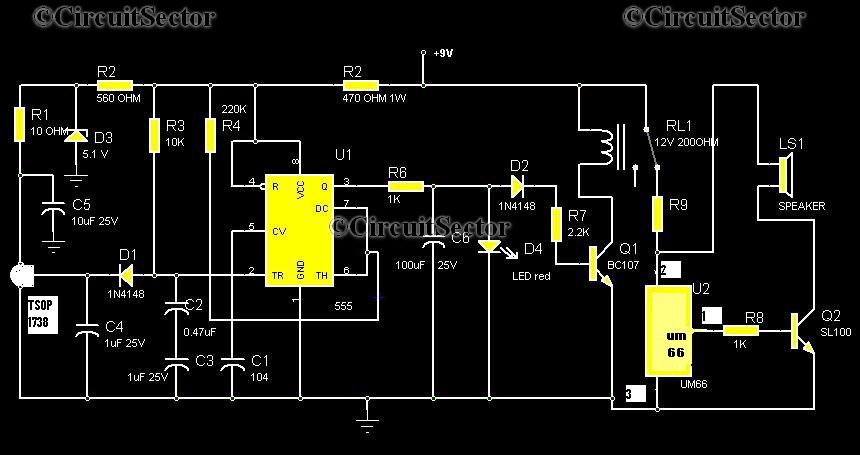
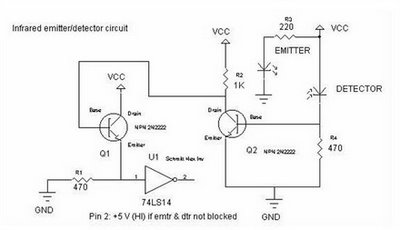
Motion detectors commonly utilize ultrasonic sensors due to their sensitivity and rapid response. However, a significant drawback of these sensors is their tendency to react to environmental vibrations, such as sounds from passing cars or planes, leading to unexpected false responses. This issue can be mitigated by employing active infrared sensors. The fundamental concept is akin to that of an ultrasonic sensor. In this system, a photodiode emits pulses of infrared light at a frequency of 5 kHz, which are then reflected by a reflector positioned in front of it and received by a phototransistor acting as the receiver. The object being detected is situated between the transmitter and receiver, along with the reflector. The schematic diagram illustrates the transmitter circuit on the left, which generates a 5 kHz modulated infrared pulse. The receiver circuit on the right features a resonance-tuned amplifier that can be adjusted to control bandwidth, thereby enabling the capture of the 5 kHz modulation from the transmitter. This bandwidth control also helps to minimize sensitivity to ambient light interference.
The motion detection circuit employing active infrared sensors operates based on the principle of modulated infrared light transmission and reception. The transmitter circuit consists of a photodiode configured to emit infrared light pulses at a precise frequency of 5 kHz. This modulation is crucial as it allows the system to distinguish between the transmitted signal and potential noise from other infrared sources in the environment.
The receiver circuit is designed to capture the reflected infrared light using a phototransistor. The resonance-tuned amplifier within the receiver circuit plays a pivotal role in filtering out unwanted signals and enhancing the detection of the specific 5 kHz signal from the transmitter. The adjustable bandwidth of the amplifier allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity, which is essential for reducing false triggers caused by ambient light or other infrared sources.
In practical applications, the transmitter and receiver must be strategically positioned to ensure optimal detection range and accuracy. The reflector is also a critical component, as it aids in directing the emitted infrared light back toward the receiver, enhancing the likelihood of detection when an object enters the sensing zone.
Overall, this active infrared sensor-based motion detection system provides a reliable solution for various applications, including security systems, automated lighting, and occupancy sensing, by minimizing the impact of environmental noise and ensuring accurate object detection.Motion detectors often we hear, is to use ultrasonic sensors, the advantages of this sensor is sensitive and rapid response. But the main problem is that sometimes these sensors also respond to vibration in the environment, such as a passing car or plane sound, which resulted in an error response that we did not expect.
This can be overcome by usi ng active infrared sensors. The basic concept is similar to an ultrasonic sensor as shown below: As transmitter Photodioda out pulses of infrared light with a certain frequency 5KHz, then reflected by the reflector in front of him. and received by the phototransistor as the receiver. The detected object is located in between the transmitter-receiver with a reflector. The following is a schematic drawing: Circuit on the left is the transmitter circuit that produces an infrared pulse modulation 5KHz.
On the right side (receiver circuit) there is resonance tuned amplifier that we can control bandwidth in order to capture the pulse modulation transmitter 5Khz. Bandwidth control also serves to reduce the sensitivity to the effects of light around him. 🔗 External reference
The motion detection circuit employing active infrared sensors operates based on the principle of modulated infrared light transmission and reception. The transmitter circuit consists of a photodiode configured to emit infrared light pulses at a precise frequency of 5 kHz. This modulation is crucial as it allows the system to distinguish between the transmitted signal and potential noise from other infrared sources in the environment.
The receiver circuit is designed to capture the reflected infrared light using a phototransistor. The resonance-tuned amplifier within the receiver circuit plays a pivotal role in filtering out unwanted signals and enhancing the detection of the specific 5 kHz signal from the transmitter. The adjustable bandwidth of the amplifier allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity, which is essential for reducing false triggers caused by ambient light or other infrared sources.
In practical applications, the transmitter and receiver must be strategically positioned to ensure optimal detection range and accuracy. The reflector is also a critical component, as it aids in directing the emitted infrared light back toward the receiver, enhancing the likelihood of detection when an object enters the sensing zone.
Overall, this active infrared sensor-based motion detection system provides a reliable solution for various applications, including security systems, automated lighting, and occupancy sensing, by minimizing the impact of environmental noise and ensuring accurate object detection.Motion detectors often we hear, is to use ultrasonic sensors, the advantages of this sensor is sensitive and rapid response. But the main problem is that sometimes these sensors also respond to vibration in the environment, such as a passing car or plane sound, which resulted in an error response that we did not expect.
This can be overcome by usi ng active infrared sensors. The basic concept is similar to an ultrasonic sensor as shown below: As transmitter Photodioda out pulses of infrared light with a certain frequency 5KHz, then reflected by the reflector in front of him. and received by the phototransistor as the receiver. The detected object is located in between the transmitter-receiver with a reflector. The following is a schematic drawing: Circuit on the left is the transmitter circuit that produces an infrared pulse modulation 5KHz.
On the right side (receiver circuit) there is resonance tuned amplifier that we can control bandwidth in order to capture the pulse modulation transmitter 5Khz. Bandwidth control also serves to reduce the sensitivity to the effects of light around him. 🔗 External reference