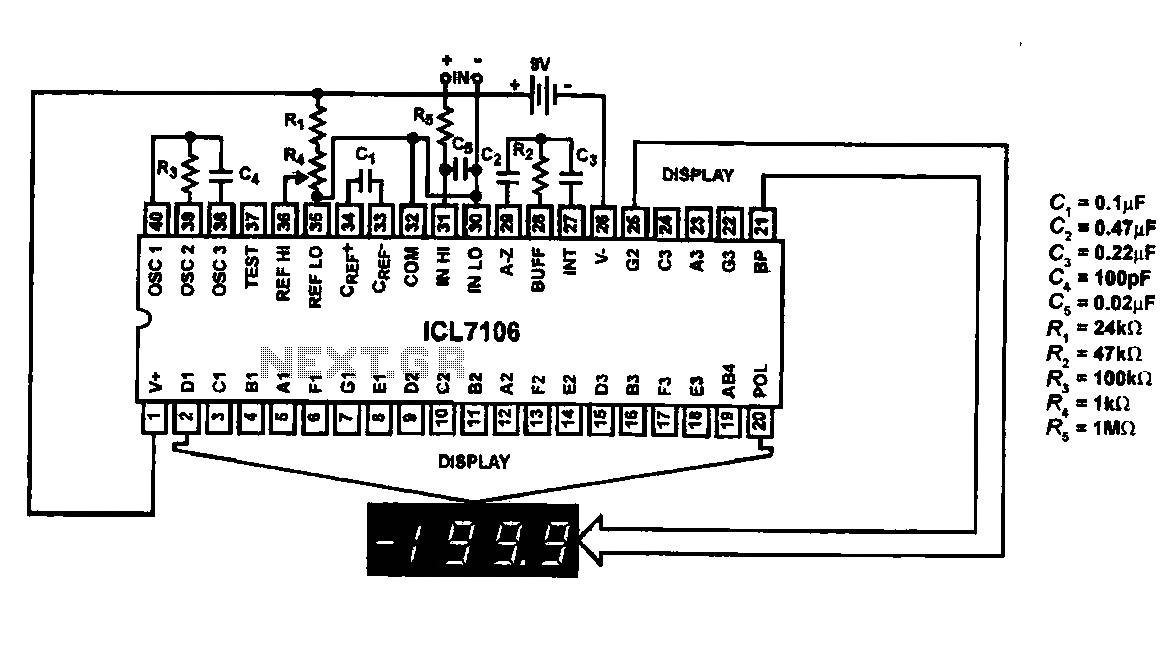
Motorcycle charging circuit diagram
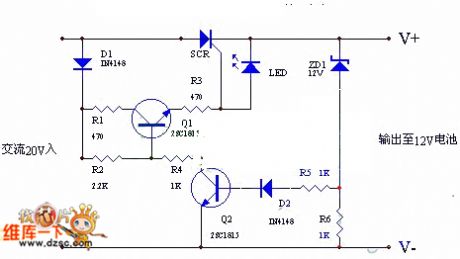
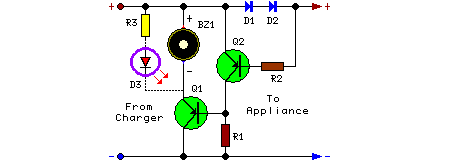
The circuit utilizes the positive half-cycle of an alternating current (AC) to charge a battery. It offers a rapid charging speed and has the potential to extend battery life. This charger is commonly used with standard motorcycles, demonstrating excellent performance and achieving a fuel savings of 5%. It is a practical charging circuit. The working principle involves applying AC voltage to the diode D1 and a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR). The circuit utilizes a half-wave rectifier configuration with D1 to...
The described circuit operates by harnessing the positive half-cycle of an AC voltage source to effectively charge a connected battery. The charging mechanism is primarily facilitated through a half-wave rectifier, which is implemented using diode D1. This diode allows current to flow during the positive half-cycle while blocking it during the negative half-cycle, thus converting the AC input into a pulsating DC output suitable for charging the battery.
The inclusion of the SCR in the circuit serves an important role in controlling the charging process. The SCR can be triggered to conduct during specific intervals of the AC cycle, allowing for regulated charging. This regulation can help prevent overcharging, thereby extending the overall life of the battery being charged. The fast charging speed is attributed to the efficient conversion of AC to DC, enabling quick replenishment of the battery's energy.
Moreover, the circuit's design is optimized for use in motorcycles, where space and efficiency are critical. The ability to save fuel by 5% is particularly notable, as it indicates that the charging circuit not only enhances battery performance but also contributes to overall fuel efficiency of the motorcycle. This dual benefit makes the charging circuit a valuable addition to motorcycle electrical systems.
In summary, the circuit's efficient use of the positive half-cycle of AC, combined with the strategic implementation of a half-wave rectifier and SCR, results in a practical solution for motorcycle battery charging that enhances performance and promotes fuel savings.The circuit uses ACpositive half cycle charge. Charging speed is fast and it can extend battery life. People use the charger on ordinary motorcycle. It has an excellent performance and saves 5% fuel. It is a practical charging circuit. Working principle: (shown as the figure)AC voltage is also added to the D1 and SCR. It passes the half-wave rectifier D1 to.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates by harnessing the positive half-cycle of an AC voltage source to effectively charge a connected battery. The charging mechanism is primarily facilitated through a half-wave rectifier, which is implemented using diode D1. This diode allows current to flow during the positive half-cycle while blocking it during the negative half-cycle, thus converting the AC input into a pulsating DC output suitable for charging the battery.
The inclusion of the SCR in the circuit serves an important role in controlling the charging process. The SCR can be triggered to conduct during specific intervals of the AC cycle, allowing for regulated charging. This regulation can help prevent overcharging, thereby extending the overall life of the battery being charged. The fast charging speed is attributed to the efficient conversion of AC to DC, enabling quick replenishment of the battery's energy.
Moreover, the circuit's design is optimized for use in motorcycles, where space and efficiency are critical. The ability to save fuel by 5% is particularly notable, as it indicates that the charging circuit not only enhances battery performance but also contributes to overall fuel efficiency of the motorcycle. This dual benefit makes the charging circuit a valuable addition to motorcycle electrical systems.
In summary, the circuit's efficient use of the positive half-cycle of AC, combined with the strategic implementation of a half-wave rectifier and SCR, results in a practical solution for motorcycle battery charging that enhances performance and promotes fuel savings.The circuit uses ACpositive half cycle charge. Charging speed is fast and it can extend battery life. People use the charger on ordinary motorcycle. It has an excellent performance and saves 5% fuel. It is a practical charging circuit. Working principle: (shown as the figure)AC voltage is also added to the D1 and SCR. It passes the half-wave rectifier D1 to.. 🔗 External reference