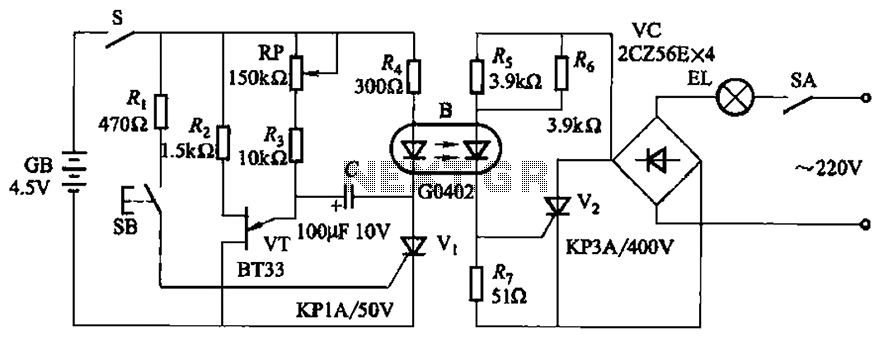
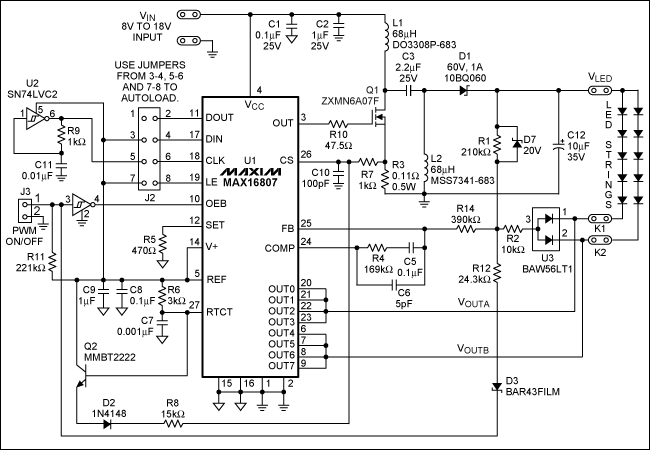
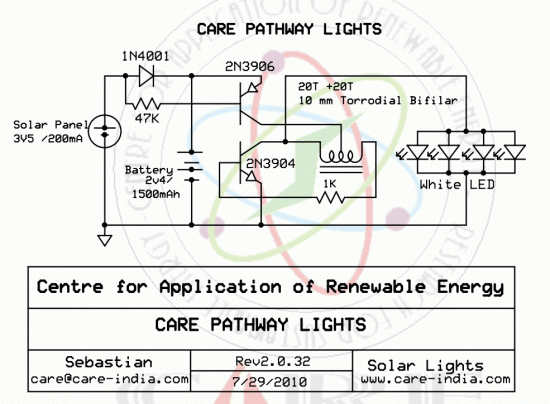
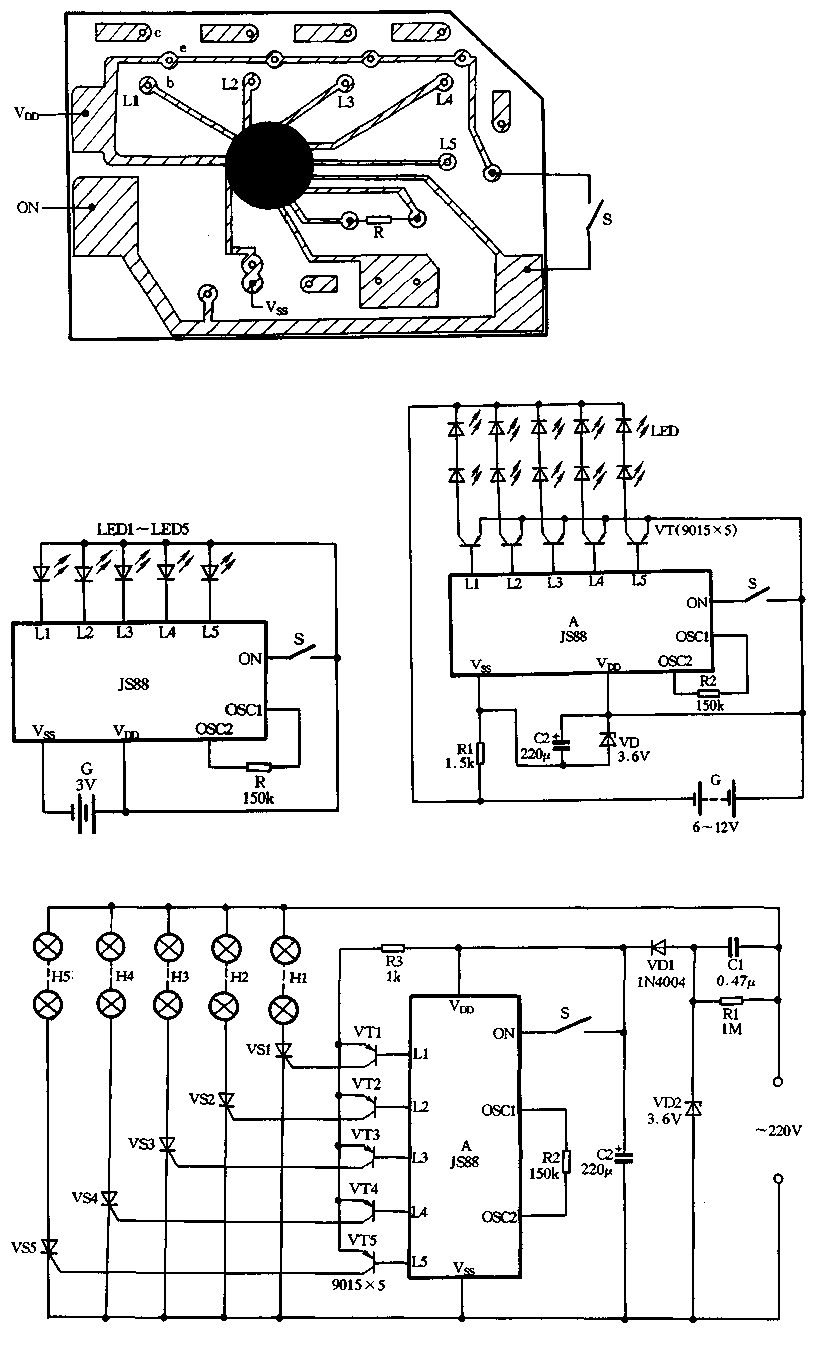
Music/Sound Controlled Disco Light

The mains supply can be conveniently reduced with no heat dissipation by the reactance of C1; then rectified by D1 (1N4007) and D2 (1N4007) and clamped to 24V.
The circuit operates by utilizing the reactance of capacitor C1 to reduce the mains voltage without generating excess heat, which is a significant advantage in terms of efficiency. The capacitor's reactance effectively limits the current flow, allowing for a safe voltage reduction. Following this, the reduced AC voltage is directed to diodes D1 and D2, both of which are 1N4007 components. These diodes serve to rectify the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage, ensuring that the output is suitable for further processing or usage in DC applications.
The output voltage is then clamped to 24V, which is achieved through the use of additional components, likely involving a voltage regulator or zener diode in conjunction with the rectification stage. This clamping mechanism ensures that the voltage does not exceed the desired level, providing a stable output that can be utilized for powering electronic devices or circuits that require a consistent voltage supply.
In summary, this circuit effectively reduces mains voltage through capacitive reactance, rectifies it using robust diodes, and clamps the output to a safe, usable level of 24V, ensuring both efficiency and reliability in operation.The mains supply can be conveniently reduced with no heat dissipation by the reactance of C1; then rectified by D1 (1N4007) and D2 (1N4007) and clamped to 24V.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the reactance of capacitor C1 to reduce the mains voltage without generating excess heat, which is a significant advantage in terms of efficiency. The capacitor's reactance effectively limits the current flow, allowing for a safe voltage reduction. Following this, the reduced AC voltage is directed to diodes D1 and D2, both of which are 1N4007 components. These diodes serve to rectify the AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage, ensuring that the output is suitable for further processing or usage in DC applications.
The output voltage is then clamped to 24V, which is achieved through the use of additional components, likely involving a voltage regulator or zener diode in conjunction with the rectification stage. This clamping mechanism ensures that the voltage does not exceed the desired level, providing a stable output that can be utilized for powering electronic devices or circuits that require a consistent voltage supply.
In summary, this circuit effectively reduces mains voltage through capacitive reactance, rectifies it using robust diodes, and clamps the output to a safe, usable level of 24V, ensuring both efficiency and reliability in operation.The mains supply can be conveniently reduced with no heat dissipation by the reactance of C1; then rectified by D1 (1N4007) and D2 (1N4007) and clamped to 24V.. 🔗 External reference