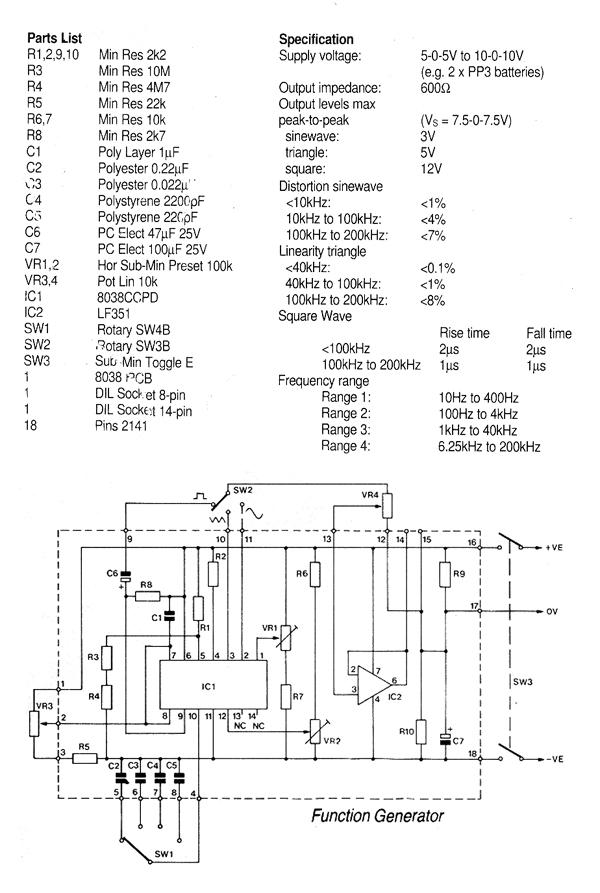
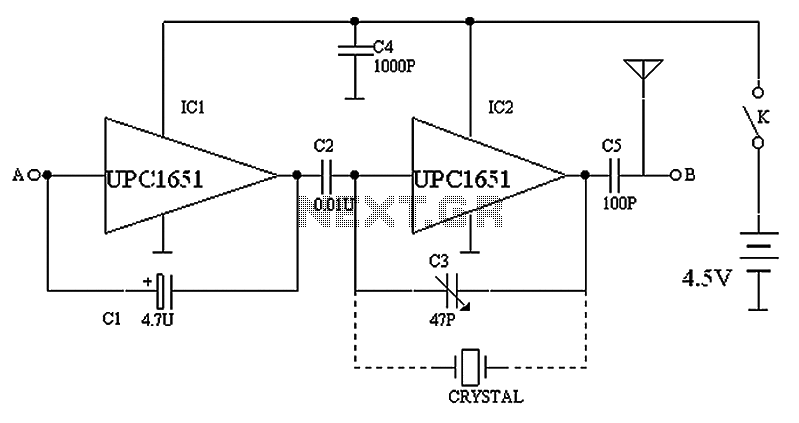
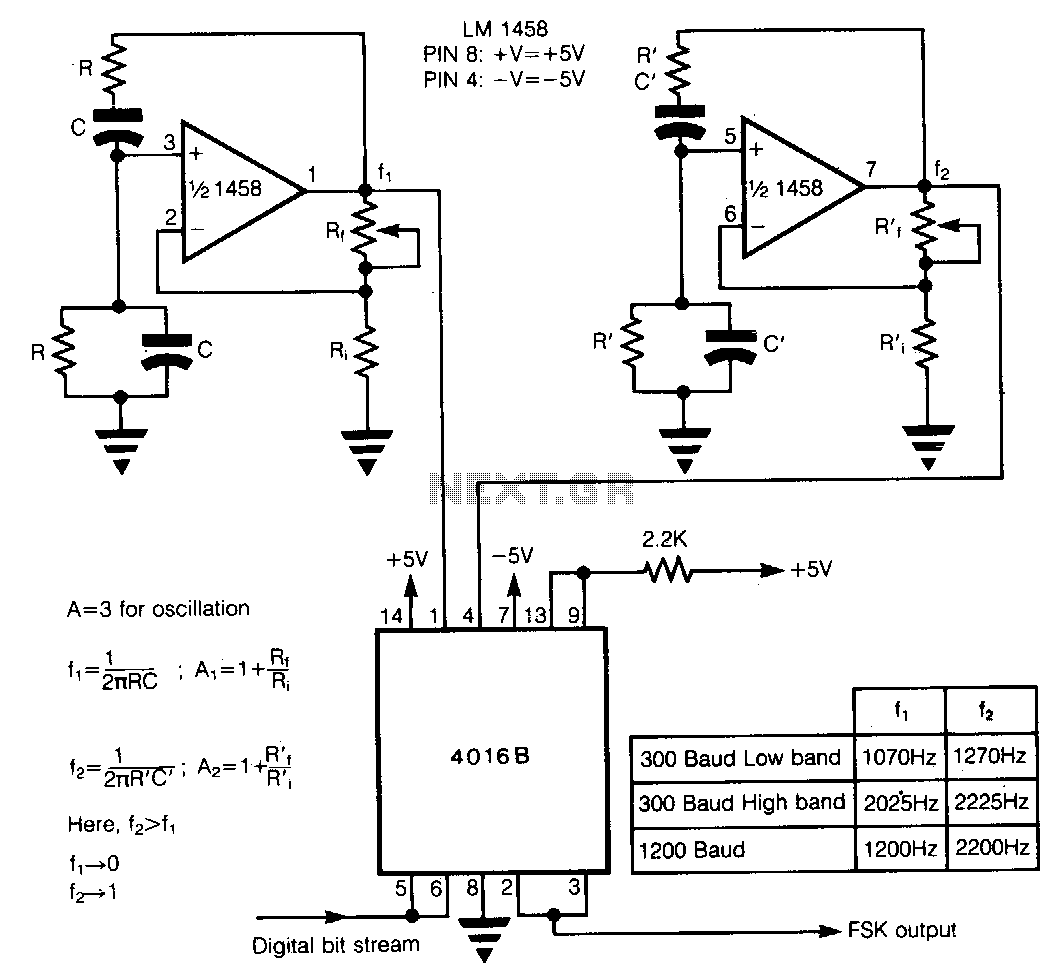
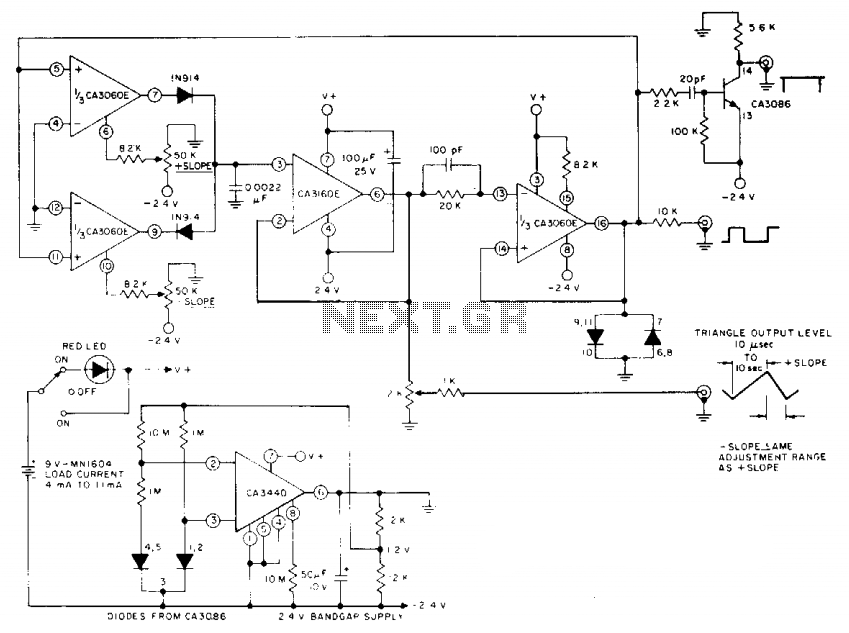
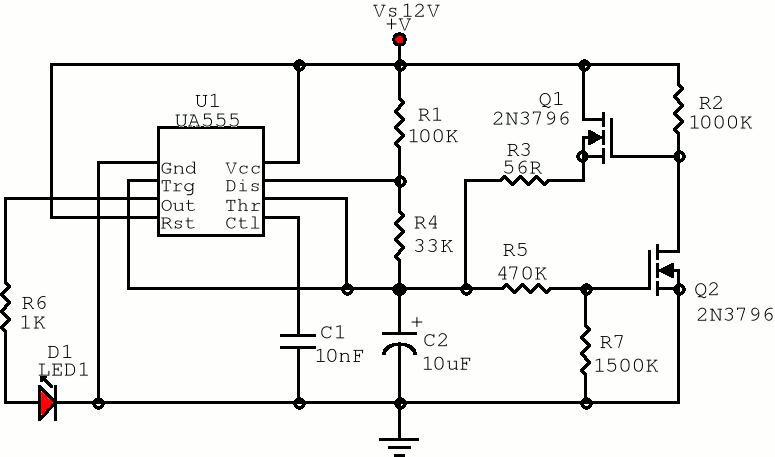
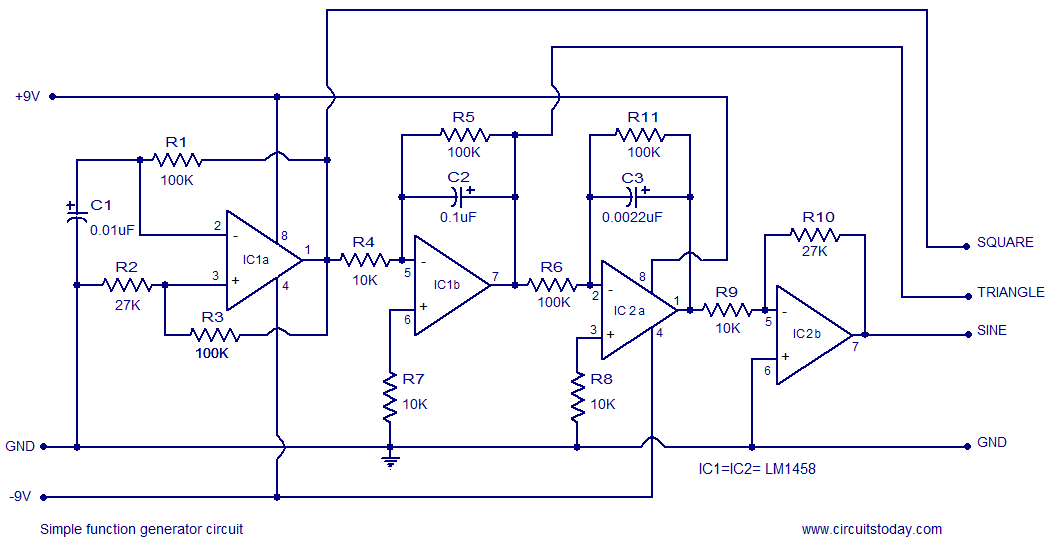
Musical chime generator
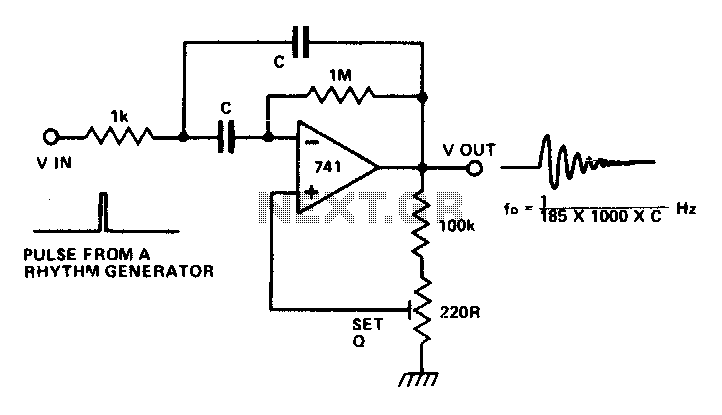
The circuit is a multiple feedback bandpass filter. A brief click (pulse) causes it to resonate at its natural frequency. The oscillations diminish exponentially, closely resembling various naturally occurring percussive or plucked sounds. The higher the quality factor (Q), the longer the decay time constant. High-frequency resonances resemble chimes, while lower frequencies sound like claves or bongos. Multiple circuits, each with different tuning, driven by pulses from a rhythm generator, can create an intriguing pattern of sounds.
The multiple feedback bandpass filter circuit utilizes a combination of resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to achieve its unique frequency-selective characteristics. At its core, the design includes a feedback loop that allows for both positive and negative feedback, enabling the circuit to selectively amplify signals within a specific frequency range while attenuating those outside of this range.
The natural resonance frequency of the circuit is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the design. By adjusting these component values, the filter can be tuned to resonate at various frequencies, allowing for a wide range of sound generation. The quality factor (Q) of the filter is a critical parameter that influences the sharpness of the resonance peak. A higher Q indicates a narrower bandwidth and longer decay time, resulting in a more pronounced ringing effect after the initial pulse.
The interaction of multiple bandpass filters, each tuned to different frequencies, can produce complex sound patterns when driven by a rhythm generator. This setup allows for the creation of layered sounds that can mimic acoustic instruments, such as chimes, claves, or bongos, depending on the tuning of each filter. The rhythmic pulses from the generator act as triggers, causing the filters to resonate in response, thus generating a rich tapestry of auditory textures.
In practical applications, such circuits are often employed in synthesizers and sound design tools to create percussive sounds or to add depth to musical compositions. The ability to adjust the tuning and quality factor of each filter provides a versatile platform for experimentation and creativity in sound synthesis.The circuit is that of a multiple feedback bandpass filter. A short click (pulse), makes it ring with a frequency which is its natural resonance frequency. Oscillations die away exponentially and closely resemble many naturally occuring percussive or plucked sounds. The higher the Q the longer the decay time constant Highfrequency resonances resemble chimes, lower frequencies sound like claves or bongos. Several circuits, all with different tuning, driven by pulses from a rhythm generator can produce an interesting pattern of sounds.
The multiple feedback bandpass filter circuit utilizes a combination of resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers to achieve its unique frequency-selective characteristics. At its core, the design includes a feedback loop that allows for both positive and negative feedback, enabling the circuit to selectively amplify signals within a specific frequency range while attenuating those outside of this range.
The natural resonance frequency of the circuit is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the design. By adjusting these component values, the filter can be tuned to resonate at various frequencies, allowing for a wide range of sound generation. The quality factor (Q) of the filter is a critical parameter that influences the sharpness of the resonance peak. A higher Q indicates a narrower bandwidth and longer decay time, resulting in a more pronounced ringing effect after the initial pulse.
The interaction of multiple bandpass filters, each tuned to different frequencies, can produce complex sound patterns when driven by a rhythm generator. This setup allows for the creation of layered sounds that can mimic acoustic instruments, such as chimes, claves, or bongos, depending on the tuning of each filter. The rhythmic pulses from the generator act as triggers, causing the filters to resonate in response, thus generating a rich tapestry of auditory textures.
In practical applications, such circuits are often employed in synthesizers and sound design tools to create percussive sounds or to add depth to musical compositions. The ability to adjust the tuning and quality factor of each filter provides a versatile platform for experimentation and creativity in sound synthesis.The circuit is that of a multiple feedback bandpass filter. A short click (pulse), makes it ring with a frequency which is its natural resonance frequency. Oscillations die away exponentially and closely resemble many naturally occuring percussive or plucked sounds. The higher the Q the longer the decay time constant Highfrequency resonances resemble chimes, lower frequencies sound like claves or bongos. Several circuits, all with different tuning, driven by pulses from a rhythm generator can produce an interesting pattern of sounds.