simple function generator circuit
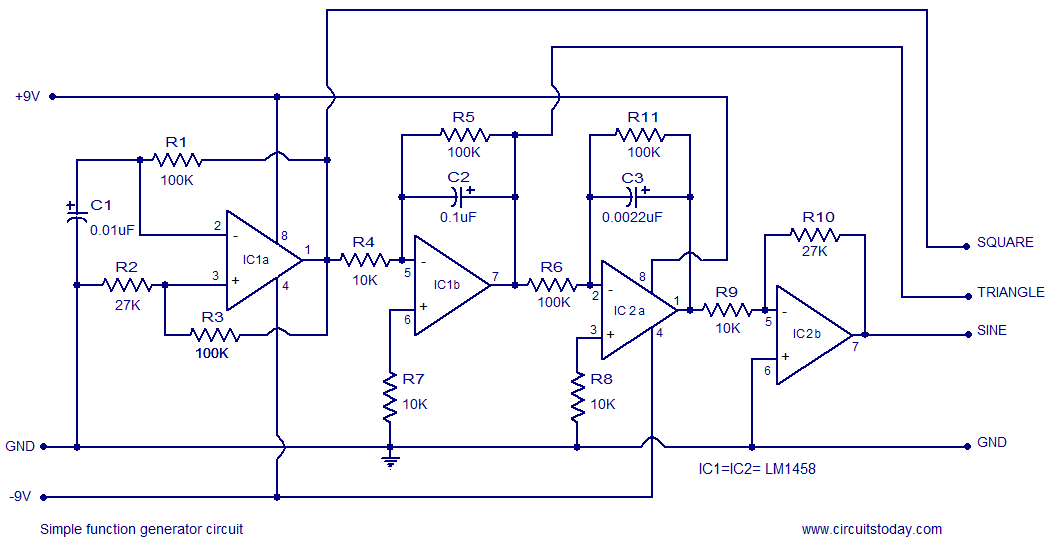
A simple function generator circuit utilizing the LM1458 is presented here. The LM1458 is a dual general-purpose operational amplifier. The two op-amps within the LM1458 share a common bias network and power supply line, yet operate independently.
The function generator circuit based on the LM1458 operational amplifier can generate various waveform outputs, including sine, square, and triangle waves. This versatility is achieved through the configuration of external resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency and amplitude of the output signals.
In a typical configuration, one op-amp is used for generating the triangle wave, while the second op-amp is employed for producing the square wave. The triangle wave is created by integrating a square wave signal, which can be generated using a feedback network consisting of resistors and capacitors. The integration process causes the output to ramp up and down, producing a triangular waveform.
The square wave can be derived from the triangle wave by employing a comparator configuration within the second op-amp. This comparator switches the output state based on the threshold levels set by the reference voltages. By adjusting the resistors in the feedback loop, the duty cycle of the square wave can also be modified.
Power supply requirements for the LM1458 are typically ±15V, which allows for a wide range of output swing and ensures the operational amplifiers function effectively across various applications. The design must also consider the bandwidth and slew rate of the op-amps to ensure that the generated signals are clean and free from distortion.
In summary, the LM1458-based function generator circuit is a robust solution for generating different types of waveforms, suitable for various applications in testing and signal processing. Proper selection of external components and configurations is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics.A simple function generator circuit using LM1458 is known here. LM1458 is a dual general purpose operational amplifier. The two opamps inside LM1458 has a common bias network, power supply line and are independent of each other in operation.. 🔗 External reference
The function generator circuit based on the LM1458 operational amplifier can generate various waveform outputs, including sine, square, and triangle waves. This versatility is achieved through the configuration of external resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency and amplitude of the output signals.
In a typical configuration, one op-amp is used for generating the triangle wave, while the second op-amp is employed for producing the square wave. The triangle wave is created by integrating a square wave signal, which can be generated using a feedback network consisting of resistors and capacitors. The integration process causes the output to ramp up and down, producing a triangular waveform.
The square wave can be derived from the triangle wave by employing a comparator configuration within the second op-amp. This comparator switches the output state based on the threshold levels set by the reference voltages. By adjusting the resistors in the feedback loop, the duty cycle of the square wave can also be modified.
Power supply requirements for the LM1458 are typically ±15V, which allows for a wide range of output swing and ensures the operational amplifiers function effectively across various applications. The design must also consider the bandwidth and slew rate of the op-amps to ensure that the generated signals are clean and free from distortion.
In summary, the LM1458-based function generator circuit is a robust solution for generating different types of waveforms, suitable for various applications in testing and signal processing. Proper selection of external components and configurations is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics.A simple function generator circuit using LM1458 is known here. LM1458 is a dual general purpose operational amplifier. The two opamps inside LM1458 has a common bias network, power supply line and are independent of each other in operation.. 🔗 External reference