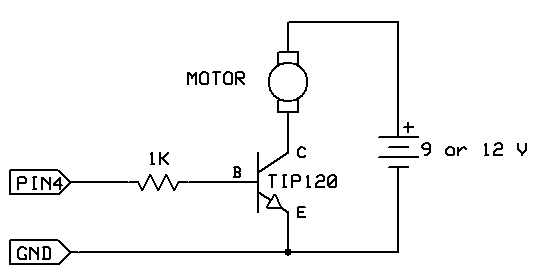
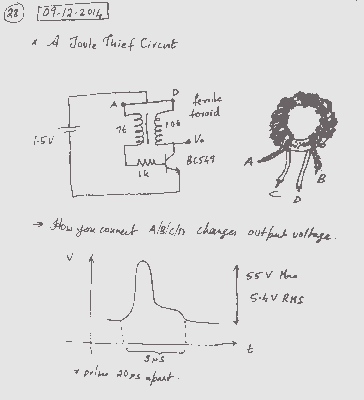
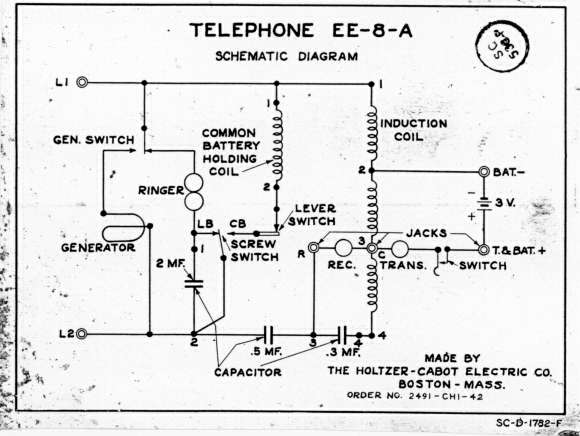
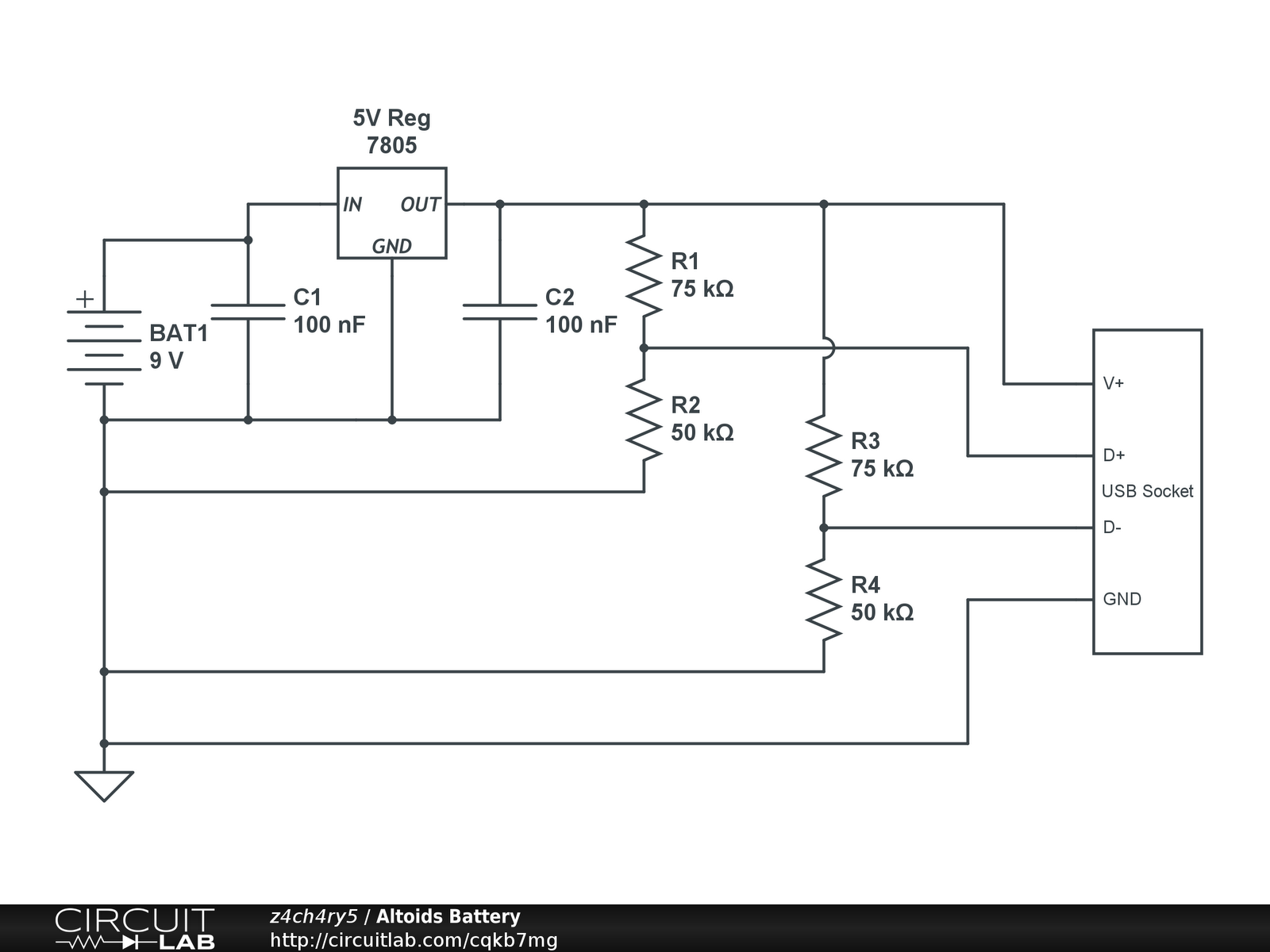
One infrared burglar alarm circuit
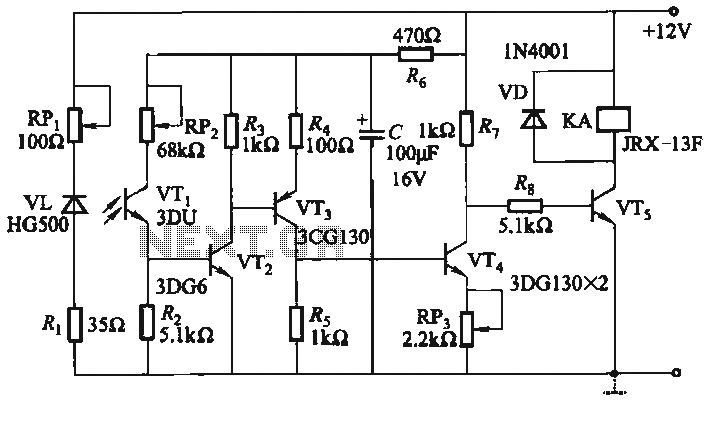
The infrared alarm system utilizes an infrared LED that emits invisible light. When this light is obstructed by an object, it triggers an alarm. The system comprises an infrared light-emitting circuit and a receiving circuit. The light-emitting diode (LED) is represented by VL, and the sensitive component is a three-pole tube denoted as VTi. The switch circuit is constructed using transistors VT2 and VTs, while the actuators are represented by relay KA.
The infrared alarm system operates on the principle of detecting interruptions in a beam of infrared light. The infrared LED (VL) emits a continuous stream of infrared light that is not visible to the human eye. This light travels toward a photodetector or a sensitive three-pole tube (VTi), which is designed to detect the presence of this infrared light.
When an object, such as a person, passes through the path of the emitted infrared light, it blocks the light from reaching the photodetector. This interruption is sensed by the receiving circuit, which includes the three-pole tube (VTi). The tube is configured to respond to the absence of light by sending a signal to the switching circuit.
The switching circuit is formed by two transistors, VT2 and VTs, which work in tandem to amplify the signal generated by the photodetector. When the beam is interrupted, the transistors are activated, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This action triggers the relay (KA), which serves as the actuator for the alarm system. The relay is responsible for closing or opening a circuit, thereby activating an alarm sound, visual indicator, or any other alert mechanism linked to the system.
Overall, the infrared alarm system is a reliable and efficient method for detecting unauthorized access or movement within a designated area. Its design is compact and can be easily integrated into various applications, such as security systems for homes, offices, and restricted areas. The simplicity of the components used, along with the effectiveness of infrared technology, makes this alarm system a popular choice for enhancing security measures.Infrared alarm system is the use of infrared LED emits invisible light, when the light is blocked by the body, namely the police. It consists of an infrared light emitting circuit and reception circuit (by the infrared light-emitting diode VL, sensitive three-pole tube VTi composition), the switch circuit (composed by the transistor VT2-VTs) and actuators - relay KA composition.
The infrared alarm system operates on the principle of detecting interruptions in a beam of infrared light. The infrared LED (VL) emits a continuous stream of infrared light that is not visible to the human eye. This light travels toward a photodetector or a sensitive three-pole tube (VTi), which is designed to detect the presence of this infrared light.
When an object, such as a person, passes through the path of the emitted infrared light, it blocks the light from reaching the photodetector. This interruption is sensed by the receiving circuit, which includes the three-pole tube (VTi). The tube is configured to respond to the absence of light by sending a signal to the switching circuit.
The switching circuit is formed by two transistors, VT2 and VTs, which work in tandem to amplify the signal generated by the photodetector. When the beam is interrupted, the transistors are activated, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This action triggers the relay (KA), which serves as the actuator for the alarm system. The relay is responsible for closing or opening a circuit, thereby activating an alarm sound, visual indicator, or any other alert mechanism linked to the system.
Overall, the infrared alarm system is a reliable and efficient method for detecting unauthorized access or movement within a designated area. Its design is compact and can be easily integrated into various applications, such as security systems for homes, offices, and restricted areas. The simplicity of the components used, along with the effectiveness of infrared technology, makes this alarm system a popular choice for enhancing security measures.Infrared alarm system is the use of infrared LED emits invisible light, when the light is blocked by the body, namely the police. It consists of an infrared light emitting circuit and reception circuit (by the infrared light-emitting diode VL, sensitive three-pole tube VTi composition), the switch circuit (composed by the transistor VT2-VTs) and actuators - relay KA composition.