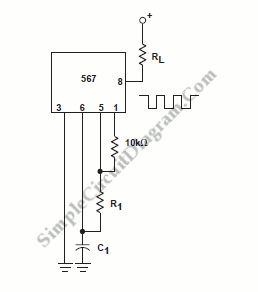
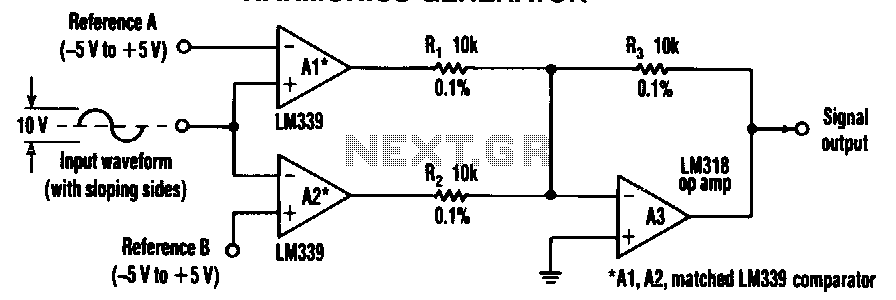
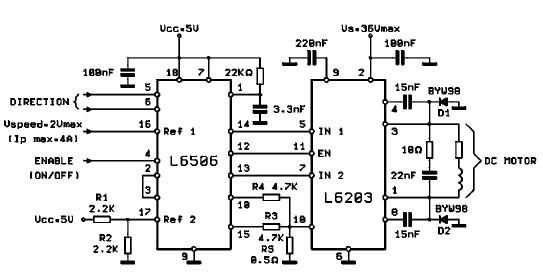
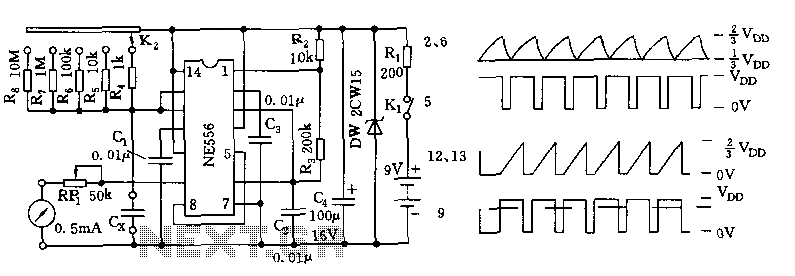
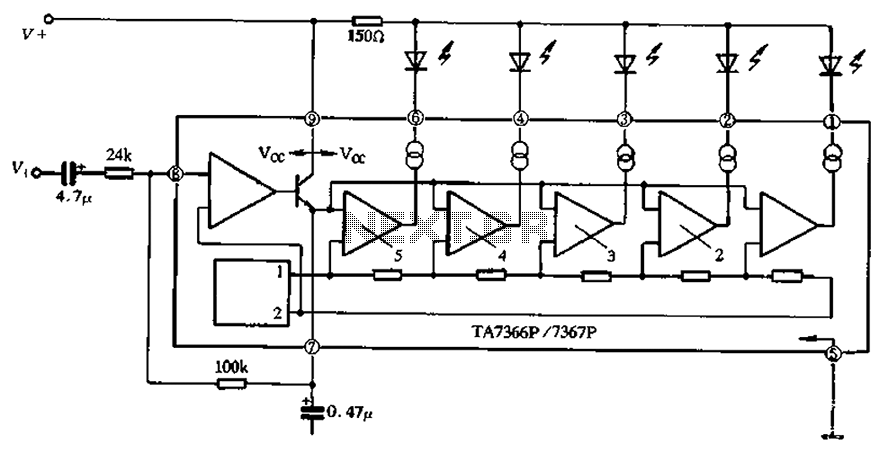
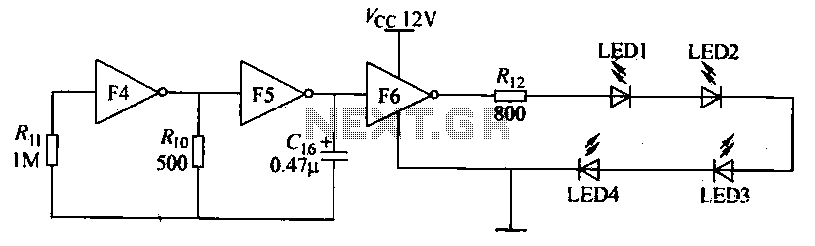
Pattern Generator For Radio Direction Finding Circuit
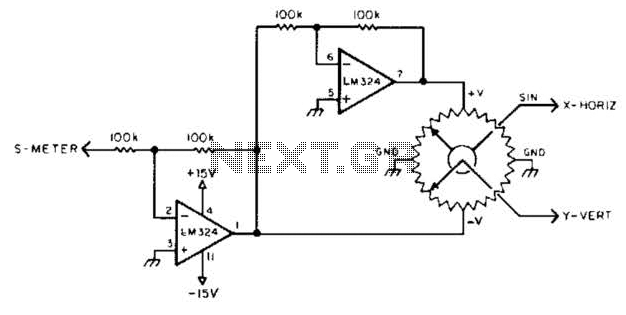
To display polar quantities, which include both the magnitude and direction of a received radio signal, a sine and cosine voltage proportional to an angle corresponding to the antenna direction is required. This setup utilizes a sine-cosine potentiometer connected to a directional antenna, along with a sample voltage that is proportional to the received signal, to illustrate the relative magnitude and direction of the signal.
In this system, the sine-cosine potentiometer serves as a critical component that translates the angular position of the antenna into corresponding sine and cosine voltages. As the antenna is rotated to various positions, the potentiometer outputs vary, producing two voltage signals: one representing the sine of the angle and the other representing the cosine of the angle. These voltages are essential for determining the phase and amplitude of the incoming radio signal.
The directional antenna captures the radio waves, and the voltage sample derived from the received signal is processed to determine its magnitude. This voltage is usually scaled to ensure that it can be accurately compared with the outputs from the sine-cosine potentiometer. The combined information from the potentiometer and the received signal allows for a comprehensive representation of the signal's characteristics.
The display mechanism, which could be an analog or digital interface, presents the polar quantities visually, enabling users to assess both the strength and direction of the signal easily. This setup is particularly useful in applications such as radio direction finding, where understanding the orientation and intensity of signals is crucial for effective navigation and communication. In order to display polar quantities (magnitude and direction of a received radio signal), a sine and cosine voltage proportional to an angle (antenna direction) is needed. In this case, a sine-cosine potentiometer coupled to a directional antenna and a sample of a voltage proportional to received signal is used to display
relative magnitude and direction of a received signal. 🔗 External reference
In this system, the sine-cosine potentiometer serves as a critical component that translates the angular position of the antenna into corresponding sine and cosine voltages. As the antenna is rotated to various positions, the potentiometer outputs vary, producing two voltage signals: one representing the sine of the angle and the other representing the cosine of the angle. These voltages are essential for determining the phase and amplitude of the incoming radio signal.
The directional antenna captures the radio waves, and the voltage sample derived from the received signal is processed to determine its magnitude. This voltage is usually scaled to ensure that it can be accurately compared with the outputs from the sine-cosine potentiometer. The combined information from the potentiometer and the received signal allows for a comprehensive representation of the signal's characteristics.
The display mechanism, which could be an analog or digital interface, presents the polar quantities visually, enabling users to assess both the strength and direction of the signal easily. This setup is particularly useful in applications such as radio direction finding, where understanding the orientation and intensity of signals is crucial for effective navigation and communication. In order to display polar quantities (magnitude and direction of a received radio signal), a sine and cosine voltage proportional to an angle (antenna direction) is needed. In this case, a sine-cosine potentiometer coupled to a directional antenna and a sample of a voltage proportional to received signal is used to display
relative magnitude and direction of a received signal. 🔗 External reference