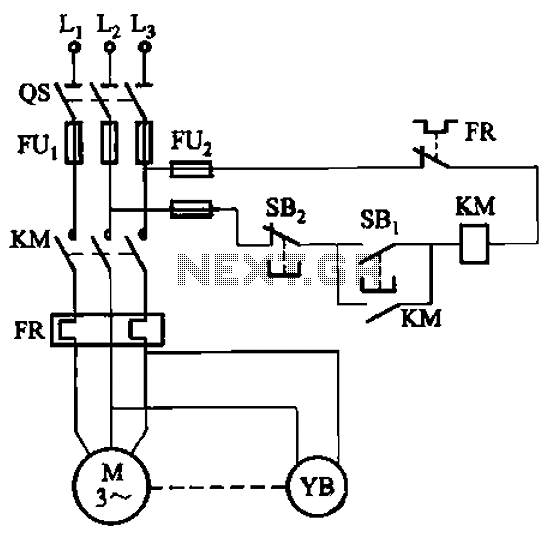
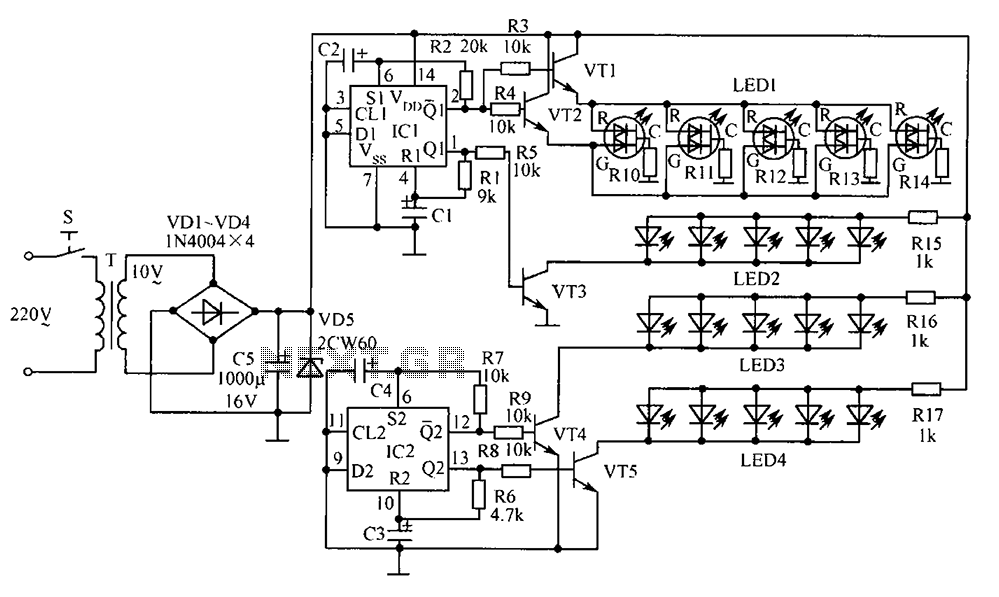
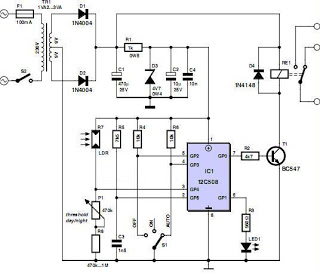
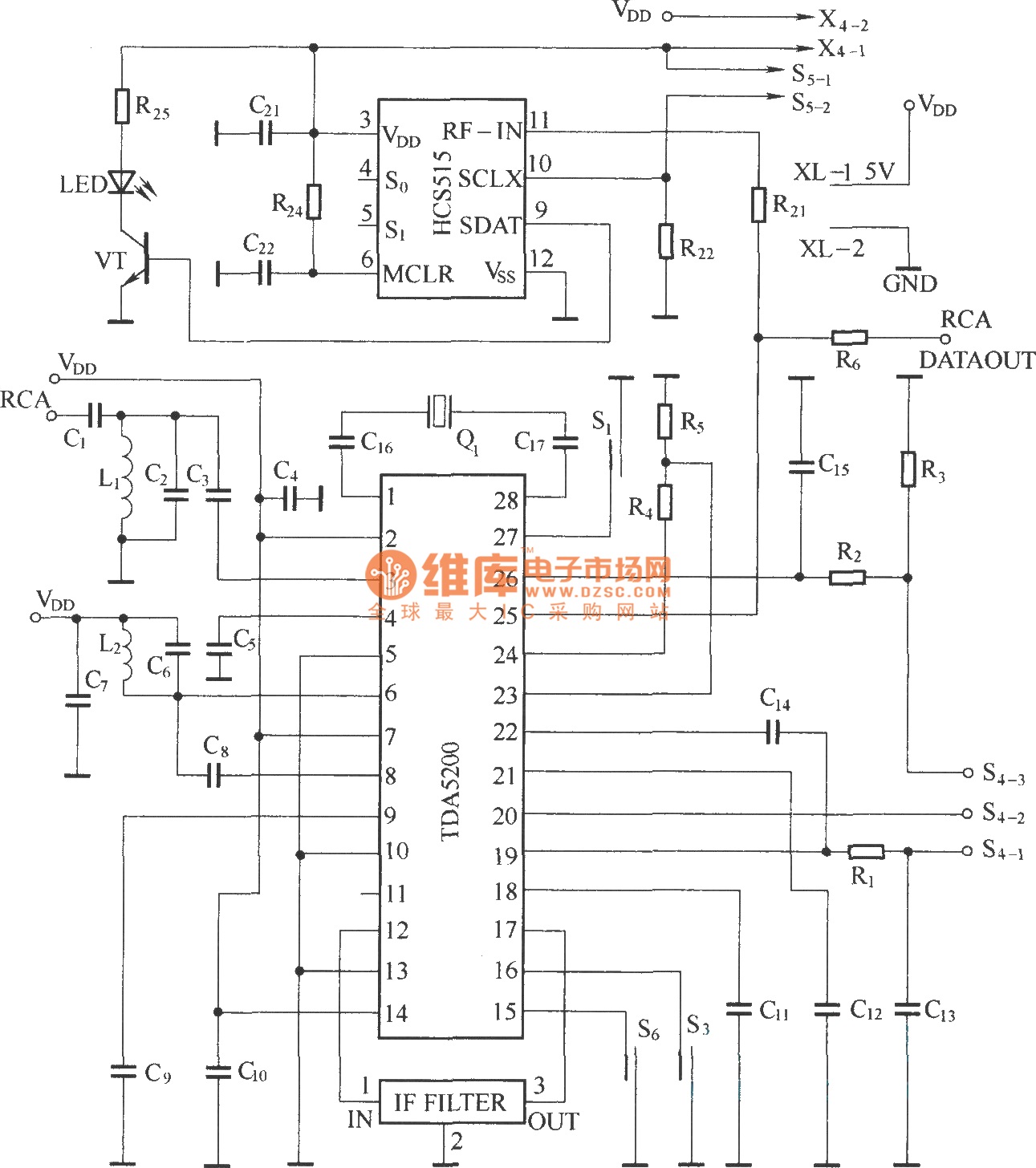
Ramp generator circuit diagram
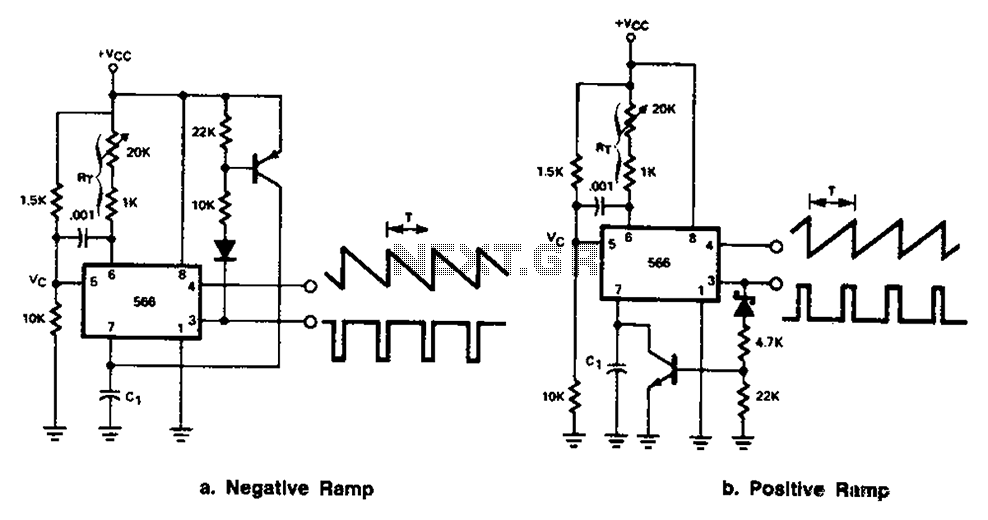
The 566 can be connected to either a positive or negative ramp generator. For a positive ramp generator, an external transistor is driven by the output pin 3. At the end of charging, C1 discharges quickly, allowing for immediate recharging.
The 566 integrated circuit (IC) is a versatile component frequently used in applications requiring ramp signal generation. It can be configured to work with both positive and negative ramp generators, making it adaptable to various circuit designs. In a typical application involving a positive ramp generator, the 566's output pin 3 is utilized to drive an external transistor. This transistor acts as a switch that controls the charging and discharging of a capacitor, commonly designated as C1.
During the charging phase, the 566 generates a linear voltage ramp, which is applied to C1. The voltage across C1 increases gradually, creating a smooth ramp signal. Once the voltage reaches a predetermined level, the output pin 3 activates the external transistor, which rapidly discharges C1. This quick discharge is crucial as it allows the circuit to reset and prepare for the next charging cycle without significant delay.
The design of this circuit can be optimized by selecting appropriate values for C1 and the associated resistors, which determine the charging time constant and the ramp-up rate. Additionally, the choice of the external transistor influences the discharge speed, which is vital for high-frequency applications where rapid transitions are required. Overall, the 566 IC's ability to generate precise ramp signals makes it an essential component in various electronic applications, including waveform generators, timing circuits, and analog-to-digital converters. Circuit Description: The 566 can be connected to either positive or negative ramp generator. For positive ramp generator, the external transistor driven by the output pin 3, at the end of charging, quick to discharge C1, so you can immediately start charging again.
The 566 integrated circuit (IC) is a versatile component frequently used in applications requiring ramp signal generation. It can be configured to work with both positive and negative ramp generators, making it adaptable to various circuit designs. In a typical application involving a positive ramp generator, the 566's output pin 3 is utilized to drive an external transistor. This transistor acts as a switch that controls the charging and discharging of a capacitor, commonly designated as C1.
During the charging phase, the 566 generates a linear voltage ramp, which is applied to C1. The voltage across C1 increases gradually, creating a smooth ramp signal. Once the voltage reaches a predetermined level, the output pin 3 activates the external transistor, which rapidly discharges C1. This quick discharge is crucial as it allows the circuit to reset and prepare for the next charging cycle without significant delay.
The design of this circuit can be optimized by selecting appropriate values for C1 and the associated resistors, which determine the charging time constant and the ramp-up rate. Additionally, the choice of the external transistor influences the discharge speed, which is vital for high-frequency applications where rapid transitions are required. Overall, the 566 IC's ability to generate precise ramp signals makes it an essential component in various electronic applications, including waveform generators, timing circuits, and analog-to-digital converters. Circuit Description: The 566 can be connected to either positive or negative ramp generator. For positive ramp generator, the external transistor driven by the output pin 3, at the end of charging, quick to discharge C1, so you can immediately start charging again.