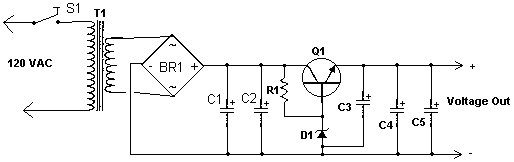
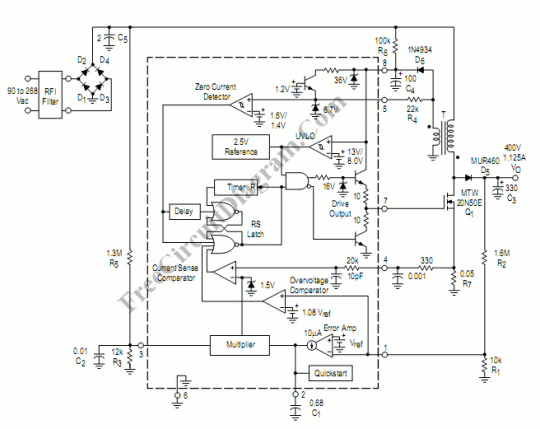
p channel power mosfets approach n channel performance
Utilizing the latest advancements in trench and polar power MOSFET technologies, both trench and polar P-Channel power MOSFETs have been developed that maintain all the characteristics of comparable N-Channel power MOSFETs, including rapid switching, voltage control, ease of paralleling, and excellent temperature stability. These devices are designed for applications that necessitate the convenience of reverse polarity operation. The n-type body region offers reduced resistivity and improved avalanche characteristics due to the lower likelihood of the parasitic PNP transistor turning on. When compared to N-channel power MOSFETs with similar design attributes, P-channel power MOSFETs exhibit enhanced Forward Bias Safe Operating Area (FBSOA) and are virtually immune to Single Event Burnout phenomena. A significant advantage of P-channel power MOSFETs is the simplified gate driving technique required for High-Side (HS) switch configurations.
The P-channel power MOSFETs are characterized by their unique structural design, which includes a n-type body region that contributes to enhanced electrical performance. This configuration minimizes the on-resistance (R_DS(on)) and improves the device's efficiency, particularly in high-frequency applications. The trench and polar technologies employed in their fabrication allow for reduced gate charge, leading to faster switching times, which is crucial for applications requiring quick response times.
The gate driving circuit for P-channel MOSFETs in high-side configurations can be simplified due to the inherent characteristics of these devices. Unlike N-channel MOSFETs, which require a gate voltage higher than the source voltage to turn on, P-channel MOSFETs can be turned on by applying a lower voltage to the gate, making them easier to drive in certain circuit topologies. This feature is particularly beneficial in battery-powered devices and other applications where efficiency and simplicity are paramount.
In terms of thermal performance, P-channel power MOSFETs exhibit superior thermal stability, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures without compromising reliability. This is particularly advantageous in automotive and industrial applications, where temperature fluctuations are common. The enhanced FBSOA ensures that these devices can handle transient conditions without risk of failure, further extending their applicability in demanding environments.
Overall, the development of trench and polar P-channel power MOSFETs represents a significant advancement in power semiconductor technology, offering enhanced performance, simplified circuit design, and increased reliability for a wide range of applications.Using the latest generation of trench and polar power MOSFET technologies, we have developed both trench and polar P-Channel power MOSFETs that retain all the features of comparable N-Channel power MOSFETs such as very fast switching, voltage control, ease of paralleling and excellent temperature stability. They are intended for applications that require the convenience of reverse polarity operation. They have an n-type body region that provides lower resistivity in the body region and good avalanche characteristics because the parasitic PNP transistor is less prone to turn-on.
Compared with N-channel power MOSFETs having similar design features, P-channel power MOSFETs have better FBSOA (Forward Bias Safe Operating Area) and are practically immune to Single Event Burnout phenomena . The most important advantage of P-channel Power MOSFETs is the simplified gate driving technique in the High-Side (HS) switch position..
🔗 External reference
The P-channel power MOSFETs are characterized by their unique structural design, which includes a n-type body region that contributes to enhanced electrical performance. This configuration minimizes the on-resistance (R_DS(on)) and improves the device's efficiency, particularly in high-frequency applications. The trench and polar technologies employed in their fabrication allow for reduced gate charge, leading to faster switching times, which is crucial for applications requiring quick response times.
The gate driving circuit for P-channel MOSFETs in high-side configurations can be simplified due to the inherent characteristics of these devices. Unlike N-channel MOSFETs, which require a gate voltage higher than the source voltage to turn on, P-channel MOSFETs can be turned on by applying a lower voltage to the gate, making them easier to drive in certain circuit topologies. This feature is particularly beneficial in battery-powered devices and other applications where efficiency and simplicity are paramount.
In terms of thermal performance, P-channel power MOSFETs exhibit superior thermal stability, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures without compromising reliability. This is particularly advantageous in automotive and industrial applications, where temperature fluctuations are common. The enhanced FBSOA ensures that these devices can handle transient conditions without risk of failure, further extending their applicability in demanding environments.
Overall, the development of trench and polar P-channel power MOSFETs represents a significant advancement in power semiconductor technology, offering enhanced performance, simplified circuit design, and increased reliability for a wide range of applications.Using the latest generation of trench and polar power MOSFET technologies, we have developed both trench and polar P-Channel power MOSFETs that retain all the features of comparable N-Channel power MOSFETs such as very fast switching, voltage control, ease of paralleling and excellent temperature stability. They are intended for applications that require the convenience of reverse polarity operation. They have an n-type body region that provides lower resistivity in the body region and good avalanche characteristics because the parasitic PNP transistor is less prone to turn-on.
Compared with N-channel power MOSFETs having similar design features, P-channel power MOSFETs have better FBSOA (Forward Bias Safe Operating Area) and are practically immune to Single Event Burnout phenomena . The most important advantage of P-channel Power MOSFETs is the simplified gate driving technique in the High-Side (HS) switch position..
🔗 External reference