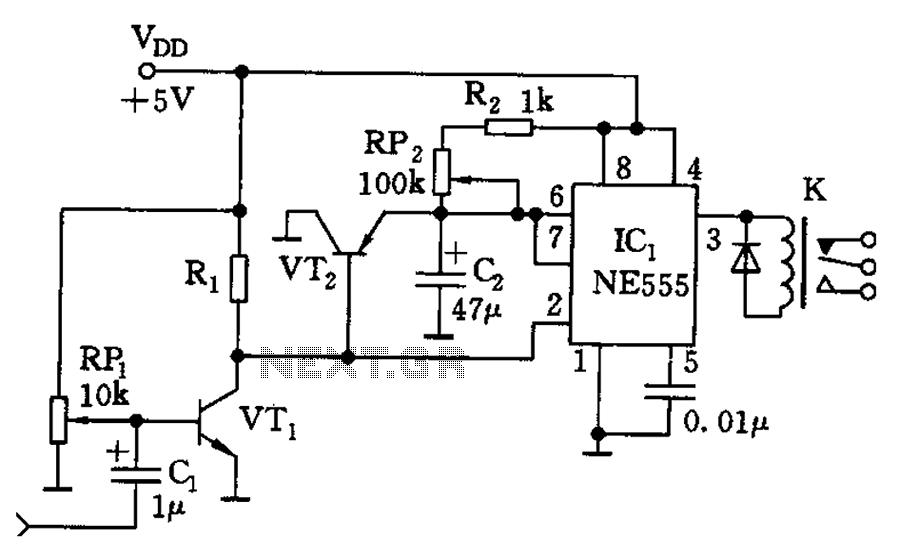
PIC16F84A Controlled Relay Driver
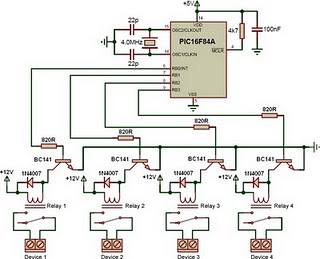
This is a relay driver based on a PIC16F84A microcontroller. The board includes four relays, allowing control of four distinct outputs.
The relay driver circuit utilizing the PIC16F84A microcontroller is designed for controlling multiple devices or systems through relay activation. The PIC16F84A is an 8-bit microcontroller featuring 13-bit instruction architecture and a 14-bit program memory. It is well-suited for applications requiring logic control and output interfacing.
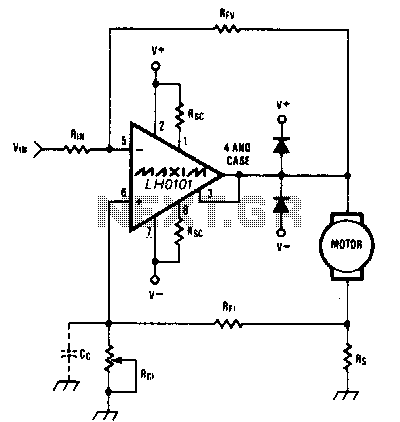
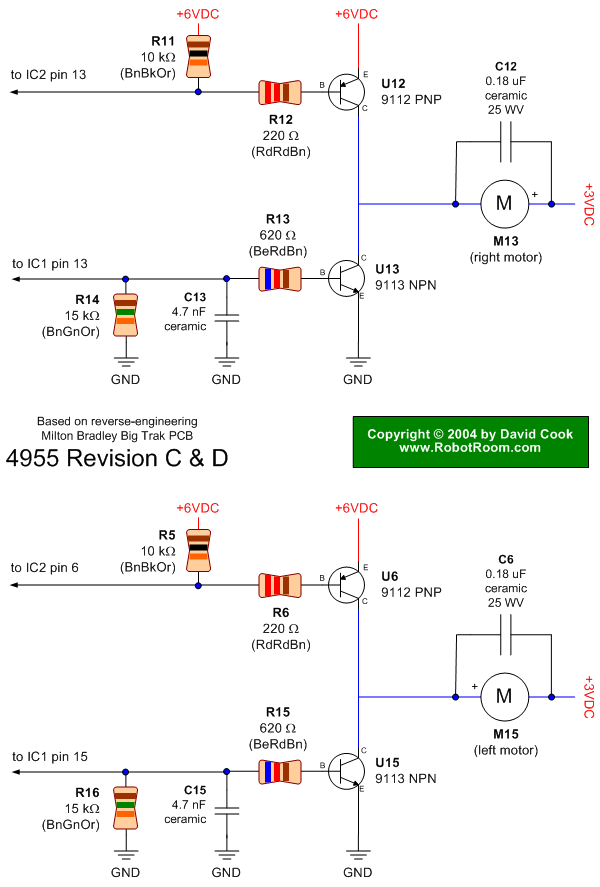
In this schematic, the microcontroller interfaces directly with four relays, which are typically electromechanical switches. Each relay is connected to a specific output pin of the microcontroller, allowing for individual control. The relays are powered through a suitable power supply, ensuring that the voltage and current ratings meet the requirements of the devices being controlled.
To drive the relays, the circuit incorporates transistor drivers. Each output pin from the PIC16F84A connects to the base of a transistor through a current-limiting resistor. When the microcontroller sends a high signal to the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, energizing the relay coil. A flyback diode is placed in parallel with the relay coil to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is de-energized.
The design may also include additional components such as pull-down resistors to ensure stable operation of the microcontroller inputs and capacitors for filtering power supply noise. The board layout should be optimized for minimizing interference and ensuring reliable operation, particularly if the relays are controlling inductive loads.
Programming the PIC16F84A involves writing firmware that defines how the microcontroller responds to inputs, manages timing for relay activation, and ensures safe operation of the connected devices. The firmware should also include debounce logic if mechanical switches are used as inputs to prevent false triggering of relays.
This relay driver circuit is applicable in various automation projects, including home automation, industrial control systems, and remote device management, providing a robust solution for controlling multiple outputs efficiently.This is a relay driver that is based on a PIC16F84A microcontroller. The board includes four relays so this lets us to control four distinct .. 🔗 External reference
The relay driver circuit utilizing the PIC16F84A microcontroller is designed for controlling multiple devices or systems through relay activation. The PIC16F84A is an 8-bit microcontroller featuring 13-bit instruction architecture and a 14-bit program memory. It is well-suited for applications requiring logic control and output interfacing.
In this schematic, the microcontroller interfaces directly with four relays, which are typically electromechanical switches. Each relay is connected to a specific output pin of the microcontroller, allowing for individual control. The relays are powered through a suitable power supply, ensuring that the voltage and current ratings meet the requirements of the devices being controlled.
To drive the relays, the circuit incorporates transistor drivers. Each output pin from the PIC16F84A connects to the base of a transistor through a current-limiting resistor. When the microcontroller sends a high signal to the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, energizing the relay coil. A flyback diode is placed in parallel with the relay coil to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay is de-energized.
The design may also include additional components such as pull-down resistors to ensure stable operation of the microcontroller inputs and capacitors for filtering power supply noise. The board layout should be optimized for minimizing interference and ensuring reliable operation, particularly if the relays are controlling inductive loads.
Programming the PIC16F84A involves writing firmware that defines how the microcontroller responds to inputs, manages timing for relay activation, and ensures safe operation of the connected devices. The firmware should also include debounce logic if mechanical switches are used as inputs to prevent false triggering of relays.
This relay driver circuit is applicable in various automation projects, including home automation, industrial control systems, and remote device management, providing a robust solution for controlling multiple outputs efficiently.This is a relay driver that is based on a PIC16F84A microcontroller. The board includes four relays so this lets us to control four distinct .. 🔗 External reference