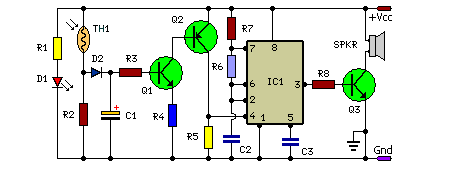
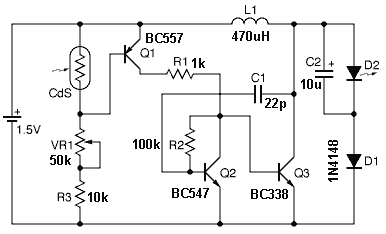
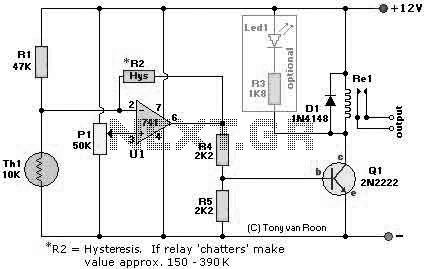
Photo detector using LED

Here's a circuit that takes advantage of the photo-voltaic voltage of an ordinary LED. The LED voltage is buffered by a junction FET transistor and then applied to the inverting input of an op-amp with a gain of about 20. This produces a change of about 5 volts at the output from darkness to bright light. More: The 100K potentiometer can be set so that the output is around 7 volts in darkness and falls to about 2 volts in bright light.
The described circuit utilizes a light-dependent voltage generation mechanism through the photo-voltaic effect exhibited by an LED. When exposed to light, the LED generates a small voltage, which is then buffered using a junction field-effect transistor (JFET). The purpose of the JFET in this configuration is to provide high input impedance, minimizing the load on the LED and ensuring that the voltage produced is not significantly affected by the circuit's input characteristics.
The buffered voltage from the JFET is fed into the inverting input of an operational amplifier (op-amp). The op-amp is configured with a gain of approximately 20, which amplifies the input voltage signal from the LED. This configuration allows for a significant output voltage swing in response to changes in ambient light levels. Specifically, the output voltage can vary from around 7 volts in low-light conditions (darkness) to approximately 2 volts in bright light conditions, demonstrating a dynamic range that can be effectively utilized in light-sensing applications.
A 100K potentiometer is incorporated into the circuit to adjust the sensitivity and output voltage levels. By varying the resistance of the potentiometer, the user can calibrate the circuit to achieve the desired output range, thereby allowing for flexibility in different lighting environments. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as automatic lighting systems or light-sensitive alarms, where precise voltage output corresponding to light levels is critical.
Overall, this circuit design showcases an efficient method of converting light intensity into a measurable voltage output, utilizing readily available components such as an LED, JFET, and op-amp, making it a practical solution for various electronic applications.Here's a circuit that takes advantage of the photo-voltaic voltage of an ordinary LED. The LED voltage is buffered by a junction FET transistor and then applied to the inverting input of an op-amp with a gain of about 20. This produces a change of about 5 volts at the output from darkness to bright light. The 100K potentiometer can be set so that the output is around 7 volts in darkness and falls to about 2 volts in bright light. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a light-dependent voltage generation mechanism through the photo-voltaic effect exhibited by an LED. When exposed to light, the LED generates a small voltage, which is then buffered using a junction field-effect transistor (JFET). The purpose of the JFET in this configuration is to provide high input impedance, minimizing the load on the LED and ensuring that the voltage produced is not significantly affected by the circuit's input characteristics.
The buffered voltage from the JFET is fed into the inverting input of an operational amplifier (op-amp). The op-amp is configured with a gain of approximately 20, which amplifies the input voltage signal from the LED. This configuration allows for a significant output voltage swing in response to changes in ambient light levels. Specifically, the output voltage can vary from around 7 volts in low-light conditions (darkness) to approximately 2 volts in bright light conditions, demonstrating a dynamic range that can be effectively utilized in light-sensing applications.
A 100K potentiometer is incorporated into the circuit to adjust the sensitivity and output voltage levels. By varying the resistance of the potentiometer, the user can calibrate the circuit to achieve the desired output range, thereby allowing for flexibility in different lighting environments. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as automatic lighting systems or light-sensitive alarms, where precise voltage output corresponding to light levels is critical.
Overall, this circuit design showcases an efficient method of converting light intensity into a measurable voltage output, utilizing readily available components such as an LED, JFET, and op-amp, making it a practical solution for various electronic applications.Here's a circuit that takes advantage of the photo-voltaic voltage of an ordinary LED. The LED voltage is buffered by a junction FET transistor and then applied to the inverting input of an op-amp with a gain of about 20. This produces a change of about 5 volts at the output from darkness to bright light. The 100K potentiometer can be set so that the output is around 7 volts in darkness and falls to about 2 volts in bright light. 🔗 External reference