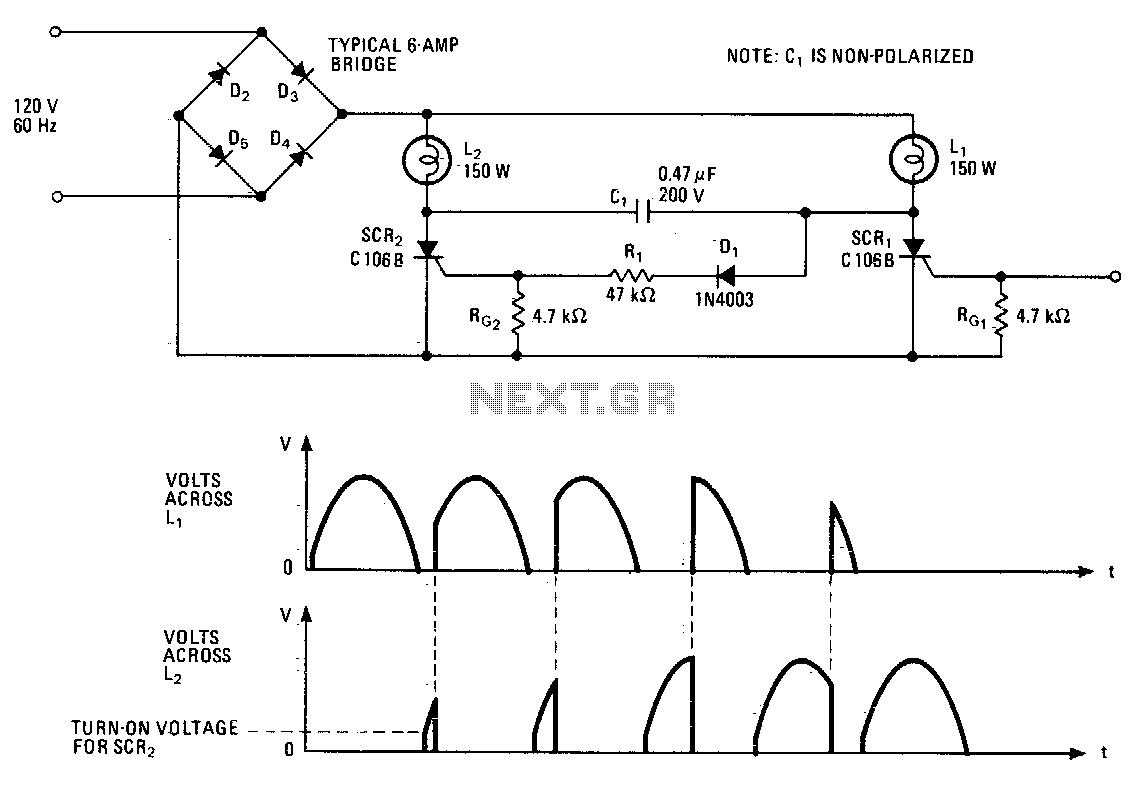
photo sensor control relay
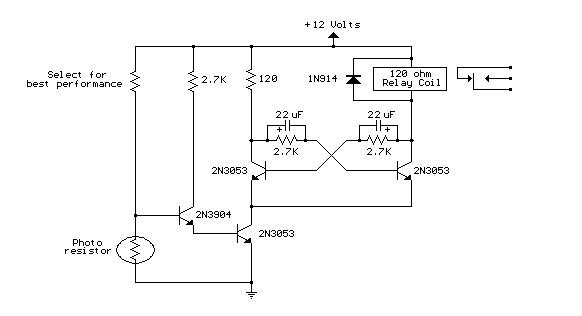
A photo-activated normally open relay is employed in a circuit that interacts with light. In this configuration, a photodiode is utilized to detect light levels. The photodiode exhibits high resistance in the absence of light. It is connected in a reverse-biased state, where the only current that flows through it is due to minority carriers. When light strikes the photodiode, the increase in minority carrier concentration results in a decrease in resistance. However, the voltage across the diode remains insufficient to forward-bias transistor Q1, causing it to reset. In darkness, the photodiode's resistance increases, and the voltage across it becomes adequate to forward-bias transistor Q1, activating the relay. Diode D2 functions as a protective device to guard against switching transients generated by the relay. This configuration allows for the load connected to the relay contacts to be turned on and off in response to light detected by the photodiode.
The circuit described utilizes a photodiode as a light sensor to control a normally open relay. The photodiode is typically a semiconductor device that operates based on the principle of light-induced electron-hole pair generation. In the absence of light, the photodiode is reverse-biased, which results in a high resistance state, allowing minimal leakage current to flow. This condition is critical for the operation of the relay, as it ensures that the circuit remains inactive until light is detected.
When light illuminates the photodiode, it generates electron-hole pairs, effectively reducing the resistance of the photodiode. This transition allows a small current to flow through the photodiode, but it is not sufficient to forward-bias transistor Q1. The transistor remains in its off state, preventing the relay from activating.
In contrast, when the ambient light level decreases, the photodiode's resistance increases significantly. This increase in resistance raises the voltage across the photodiode to a level that is adequate to forward-bias transistor Q1. As a result, transistor Q1 turns on, allowing current to flow through the relay coil, which activates the relay contacts. This action connects the load to the power supply, effectively turning it on.
Diode D2 is included in the circuit to protect transistor Q1 from voltage spikes that may occur when the relay coil is de-energized. These voltage transients, known as back EMF, can damage the transistor if not properly managed. The inclusion of D2 in parallel with the relay coil provides a safe path for the back EMF, allowing it to dissipate without affecting the transistor's operation.
This photo-activated relay circuit provides a reliable means to control electrical loads based on light levels, making it suitable for applications such as automatic lighting systems, light-sensitive alarms, or remote control systems where manual intervention is minimized. The design ensures that the relay operates efficiently while protecting sensitive components from potential damage caused by switching transients.A photo or slightly activated relay normally open relay in the closed circuit / contact with the light. In this circuit, a photodiode is used to sense light. The photodiode has a high resistance in the absence of light strikes. The photodiode is connected to the reverse biased state. The only current flowing through it will be due to minority carr iers. When light falls on it, the minority current carriers in the wake of increasing the diode provides a low resistance. Because the voltage across the diode will not be sufficient to bias transistor Q1 and will be reset. Where there is darkness, the resistance increases photodiode and the voltage across it will be enough to move forward bias the transistor Q1 of the relay ON.
The diode D2 is used as a diode to protect transistor switching transients produced relay. In this way, the load on the relay contacts can be switched on and off using light strikes the photodiode. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes a photodiode as a light sensor to control a normally open relay. The photodiode is typically a semiconductor device that operates based on the principle of light-induced electron-hole pair generation. In the absence of light, the photodiode is reverse-biased, which results in a high resistance state, allowing minimal leakage current to flow. This condition is critical for the operation of the relay, as it ensures that the circuit remains inactive until light is detected.
When light illuminates the photodiode, it generates electron-hole pairs, effectively reducing the resistance of the photodiode. This transition allows a small current to flow through the photodiode, but it is not sufficient to forward-bias transistor Q1. The transistor remains in its off state, preventing the relay from activating.
In contrast, when the ambient light level decreases, the photodiode's resistance increases significantly. This increase in resistance raises the voltage across the photodiode to a level that is adequate to forward-bias transistor Q1. As a result, transistor Q1 turns on, allowing current to flow through the relay coil, which activates the relay contacts. This action connects the load to the power supply, effectively turning it on.
Diode D2 is included in the circuit to protect transistor Q1 from voltage spikes that may occur when the relay coil is de-energized. These voltage transients, known as back EMF, can damage the transistor if not properly managed. The inclusion of D2 in parallel with the relay coil provides a safe path for the back EMF, allowing it to dissipate without affecting the transistor's operation.
This photo-activated relay circuit provides a reliable means to control electrical loads based on light levels, making it suitable for applications such as automatic lighting systems, light-sensitive alarms, or remote control systems where manual intervention is minimized. The design ensures that the relay operates efficiently while protecting sensitive components from potential damage caused by switching transients.A photo or slightly activated relay normally open relay in the closed circuit / contact with the light. In this circuit, a photodiode is used to sense light. The photodiode has a high resistance in the absence of light strikes. The photodiode is connected to the reverse biased state. The only current flowing through it will be due to minority carr iers. When light falls on it, the minority current carriers in the wake of increasing the diode provides a low resistance. Because the voltage across the diode will not be sufficient to bias transistor Q1 and will be reset. Where there is darkness, the resistance increases photodiode and the voltage across it will be enough to move forward bias the transistor Q1 of the relay ON.
The diode D2 is used as a diode to protect transistor switching transients produced relay. In this way, the load on the relay contacts can be switched on and off using light strikes the photodiode. 🔗 External reference