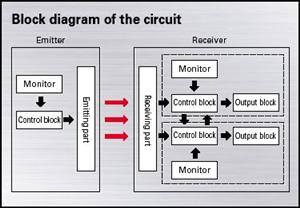
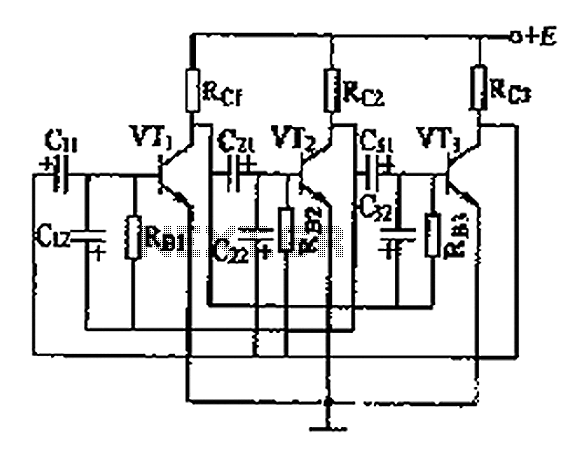
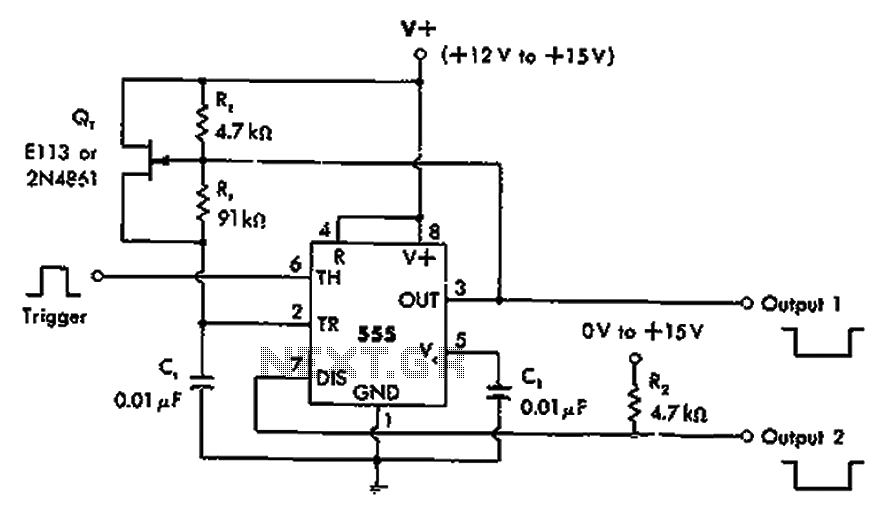
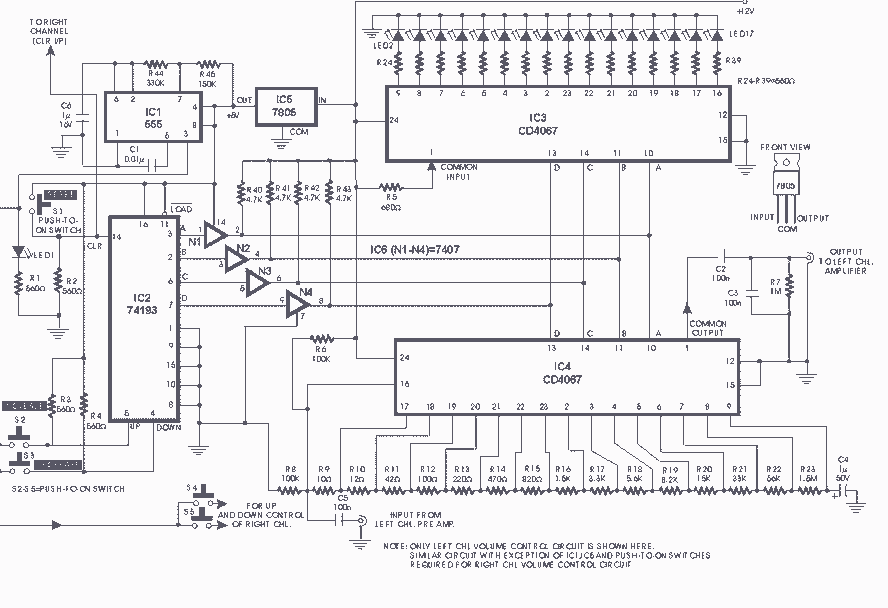
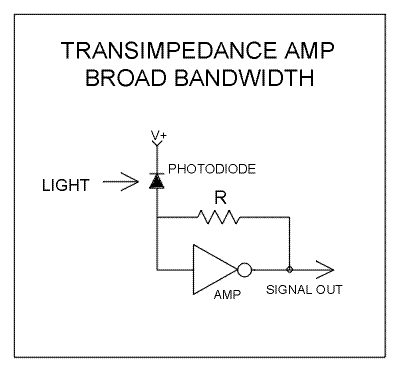
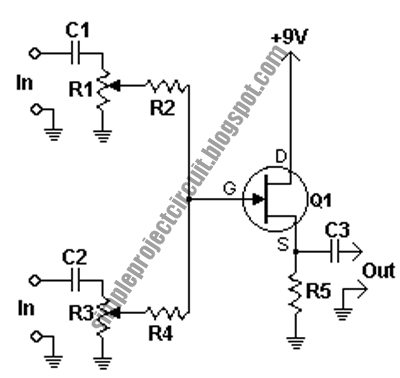
Photo Strobe Circuit
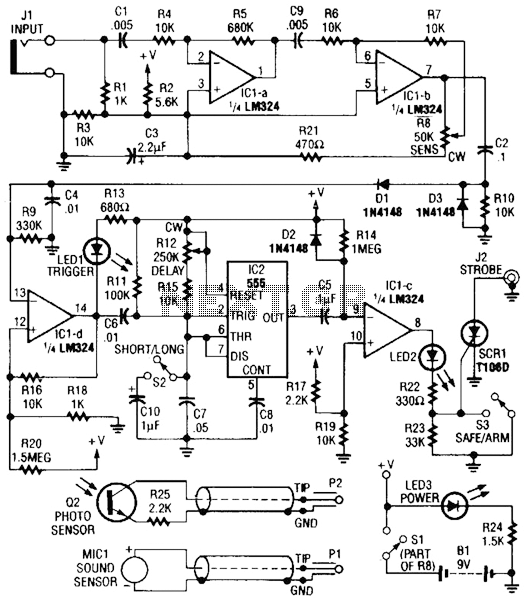
Sound or light sensors connected to J2 produce a voltage that is amplified by IC1-a and IC1-b. A positive trigger voltage developed by D1 and R3, and amplified by IC1-d, drives IC2 and IC1 to trigger SCR1. SCR1 is connected to a strobe. This device is useful for photographic purposes to capture images of events that involve sound, such as impacts, etc.
The circuit consists of several key components that work together to detect sound or light and trigger a strobe light for photographic purposes. The sound or light sensors connected to connector J2 generate an initial voltage signal in response to environmental stimuli. This voltage is then fed into two operational amplifiers, IC1-a and IC1-b, which serve to amplify the signal to a usable level.
The amplified signal is processed further to generate a positive trigger voltage. This is achieved through the diode D1 and resistor R3, which work in conjunction with operational amplifier IC1-d. The role of IC1-d is to further amplify the trigger voltage, ensuring that it is strong enough to drive subsequent components in the circuit.
The output from IC1-d is connected to two additional integrated circuits, IC2 and IC1, which are configured to control the triggering mechanism of the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR1). SCR1 acts as a switch that controls the power to the strobe light. When the trigger voltage reaches a certain threshold, SCR1 is activated, allowing current to flow to the strobe, thereby producing a flash of light.
This circuit is particularly advantageous for capturing images of dynamic events that are difficult to photograph using conventional methods. The ability to synchronize the strobe with sound or light events enables photographers to capture precise moments, such as impacts or other rapid occurrences, making it a valuable tool in various photographic applications. Sound or light sensors corniected to J2 produce a voltage that is amplified by ICl-a and ICl-b. A positive trigger voltage that is developed by D1 and 1)3 and amplified by ICl-d, drives 1C2 and 1C1 to trigger SCR1. SCR1 is connected to a strobe. This device is handy for photographic purposes to take pictures of events that involve sound, such as impacts, ctc.
The circuit consists of several key components that work together to detect sound or light and trigger a strobe light for photographic purposes. The sound or light sensors connected to connector J2 generate an initial voltage signal in response to environmental stimuli. This voltage is then fed into two operational amplifiers, IC1-a and IC1-b, which serve to amplify the signal to a usable level.
The amplified signal is processed further to generate a positive trigger voltage. This is achieved through the diode D1 and resistor R3, which work in conjunction with operational amplifier IC1-d. The role of IC1-d is to further amplify the trigger voltage, ensuring that it is strong enough to drive subsequent components in the circuit.
The output from IC1-d is connected to two additional integrated circuits, IC2 and IC1, which are configured to control the triggering mechanism of the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR1). SCR1 acts as a switch that controls the power to the strobe light. When the trigger voltage reaches a certain threshold, SCR1 is activated, allowing current to flow to the strobe, thereby producing a flash of light.
This circuit is particularly advantageous for capturing images of dynamic events that are difficult to photograph using conventional methods. The ability to synchronize the strobe with sound or light events enables photographers to capture precise moments, such as impacts or other rapid occurrences, making it a valuable tool in various photographic applications. Sound or light sensors corniected to J2 produce a voltage that is amplified by ICl-a and ICl-b. A positive trigger voltage that is developed by D1 and 1)3 and amplified by ICl-d, drives 1C2 and 1C1 to trigger SCR1. SCR1 is connected to a strobe. This device is handy for photographic purposes to take pictures of events that involve sound, such as impacts, ctc.