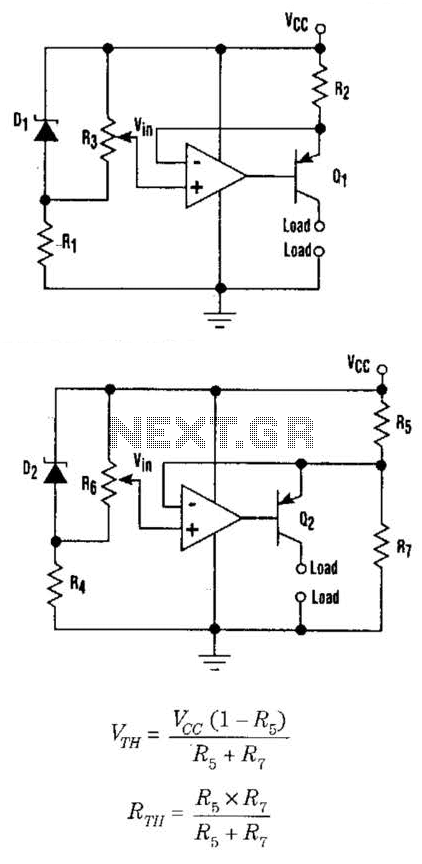
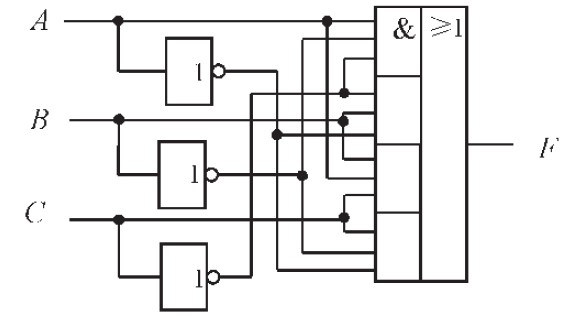
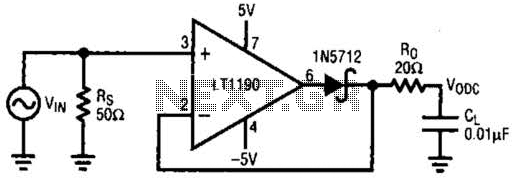
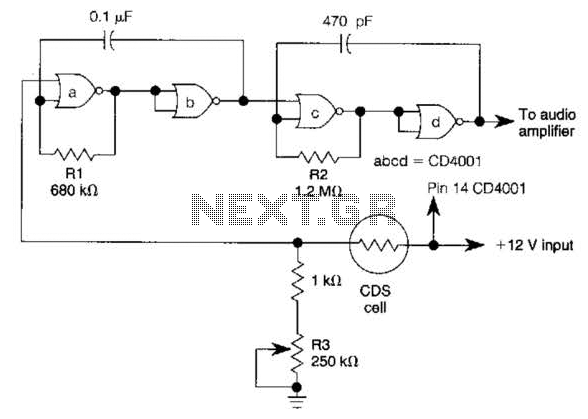
plant soil moisture tester circuit
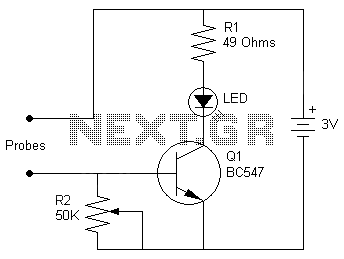
This project involves a straightforward soil moisture detection circuit that utilizes only four components and operates with a 3-volt battery. The circuit is designed to identify the presence of moisture in the soil of any plant and activate an LED indicator. A potentiometer, labeled R2, is incorporated into the design to allow users to adjust the moisture level threshold required to turn on the LED.
The soil moisture detection circuit consists of the following components: a moisture sensor, a potentiometer (R2), an LED, and a resistor. The moisture sensor is typically a pair of conductive electrodes that are inserted into the soil. When the soil is moist, the conductivity between the electrodes increases, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
The potentiometer R2 serves as a variable resistor that adjusts the sensitivity of the moisture sensor. By changing the resistance value, the user can set the moisture level at which the LED will illuminate. This feature provides flexibility, enabling the circuit to cater to different types of plants with varying moisture requirements.
The LED acts as a visual indicator; it will light up when the moisture level exceeds the set threshold. This simple yet effective design allows for easy monitoring of soil moisture, helping to prevent overwatering or underwatering of plants. The entire circuit can be powered by a 3-volt battery, ensuring portability and ease of use in various gardening applications.
Overall, this soil moisture circuit is an excellent tool for gardening enthusiasts, combining simplicity, functionality, and efficiency in plant care.A very simple and useful project of soil moisture circuit. The circuit is using only four components and a 3 volt battery. The circuit will detect if there is water in the soil of any plant and light up the LED. The resistor R2 is a potentiometer to adjust the level on which you want to make the LED on. 🔗 External reference
The soil moisture detection circuit consists of the following components: a moisture sensor, a potentiometer (R2), an LED, and a resistor. The moisture sensor is typically a pair of conductive electrodes that are inserted into the soil. When the soil is moist, the conductivity between the electrodes increases, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
The potentiometer R2 serves as a variable resistor that adjusts the sensitivity of the moisture sensor. By changing the resistance value, the user can set the moisture level at which the LED will illuminate. This feature provides flexibility, enabling the circuit to cater to different types of plants with varying moisture requirements.
The LED acts as a visual indicator; it will light up when the moisture level exceeds the set threshold. This simple yet effective design allows for easy monitoring of soil moisture, helping to prevent overwatering or underwatering of plants. The entire circuit can be powered by a 3-volt battery, ensuring portability and ease of use in various gardening applications.
Overall, this soil moisture circuit is an excellent tool for gardening enthusiasts, combining simplicity, functionality, and efficiency in plant care.A very simple and useful project of soil moisture circuit. The circuit is using only four components and a 3 volt battery. The circuit will detect if there is water in the soil of any plant and light up the LED. The resistor R2 is a potentiometer to adjust the level on which you want to make the LED on. 🔗 External reference