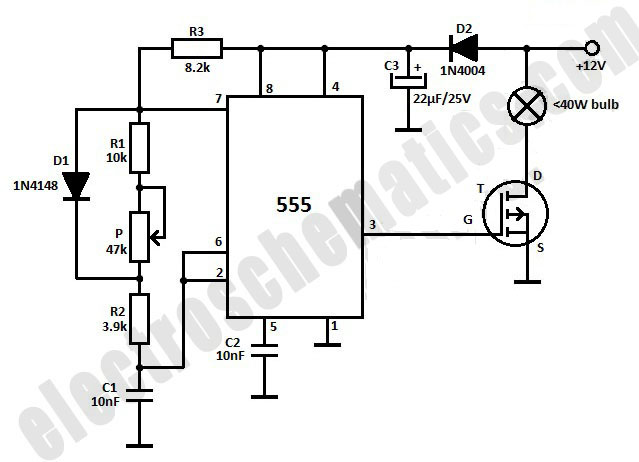
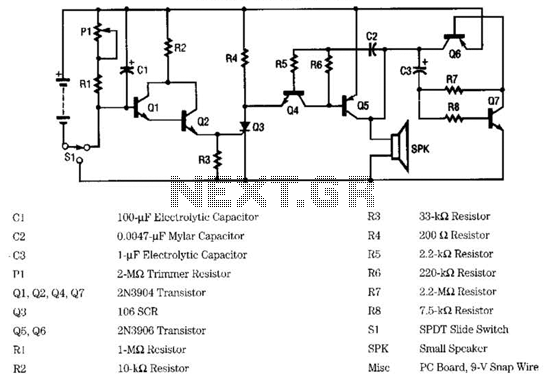
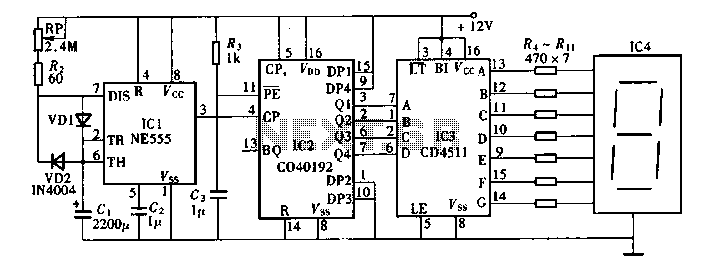
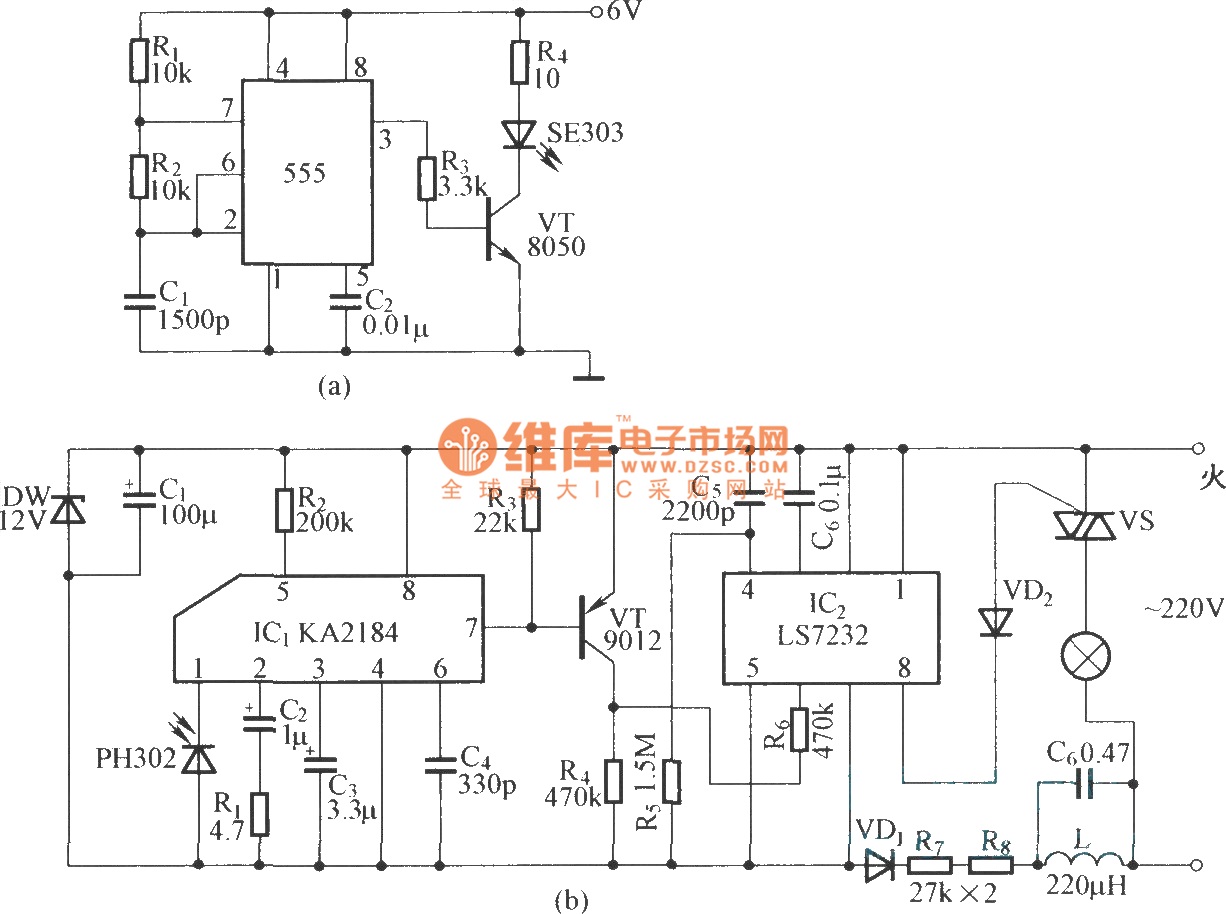
Polarity Protection Circuit
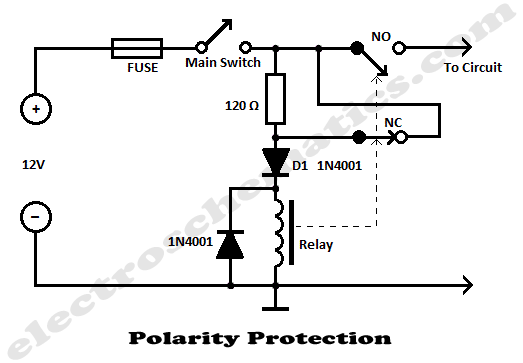
The simplest polarity protection technique is to connect a series diode to the power line input. The diode conducts only when the power supply is connected correctly.
A series diode is an effective method for preventing reverse polarity in electronic circuits. When a power supply is connected with the correct polarity, the diode allows current to flow through the circuit. However, if the power supply is connected in reverse, the diode becomes reverse-biased and blocks the current, thereby protecting sensitive components from damage.
In a typical implementation, a silicon diode, such as a 1N4001, is placed in series with the positive line of the power input. The anode of the diode is connected to the power source, while the cathode is connected to the load. This configuration ensures that under normal operating conditions, the diode conducts and the load receives the necessary voltage.
For applications requiring higher efficiency, Schottky diodes can be utilized due to their lower forward voltage drop compared to standard silicon diodes. This characteristic results in reduced power loss and improved overall efficiency of the circuit.
It is important to consider the current rating and reverse voltage rating of the diode to ensure it can handle the expected load and prevent breakdown during reverse polarity conditions. Additionally, the thermal management of the diode should be assessed, especially in high-current applications, to prevent overheating and potential failure.
In summary, the series diode configuration is a straightforward and reliable method for polarity protection in electronic circuits, safeguarding components from reverse voltage damage while maintaining operational integrity under normal conditions.The most simple polarity protection tehnique is to connect a series diode to the power line input. The diode conducts only when the power supply protection.. 🔗 External reference
A series diode is an effective method for preventing reverse polarity in electronic circuits. When a power supply is connected with the correct polarity, the diode allows current to flow through the circuit. However, if the power supply is connected in reverse, the diode becomes reverse-biased and blocks the current, thereby protecting sensitive components from damage.
In a typical implementation, a silicon diode, such as a 1N4001, is placed in series with the positive line of the power input. The anode of the diode is connected to the power source, while the cathode is connected to the load. This configuration ensures that under normal operating conditions, the diode conducts and the load receives the necessary voltage.
For applications requiring higher efficiency, Schottky diodes can be utilized due to their lower forward voltage drop compared to standard silicon diodes. This characteristic results in reduced power loss and improved overall efficiency of the circuit.
It is important to consider the current rating and reverse voltage rating of the diode to ensure it can handle the expected load and prevent breakdown during reverse polarity conditions. Additionally, the thermal management of the diode should be assessed, especially in high-current applications, to prevent overheating and potential failure.
In summary, the series diode configuration is a straightforward and reliable method for polarity protection in electronic circuits, safeguarding components from reverse voltage damage while maintaining operational integrity under normal conditions.The most simple polarity protection tehnique is to connect a series diode to the power line input. The diode conducts only when the power supply protection.. 🔗 External reference