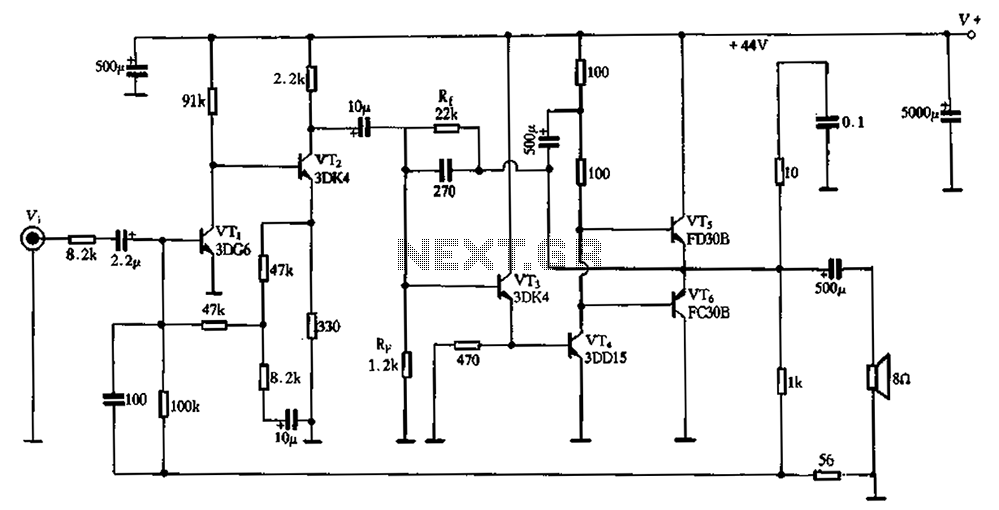
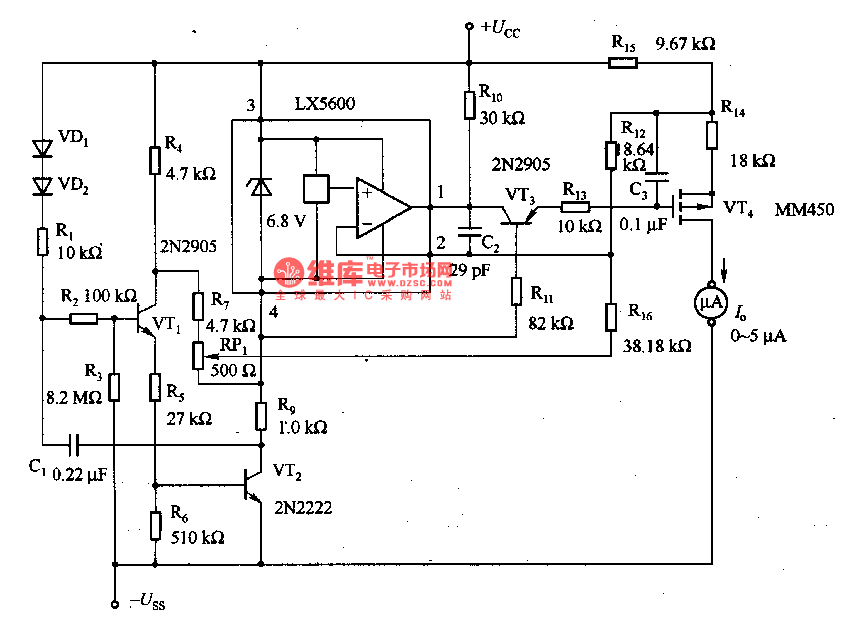
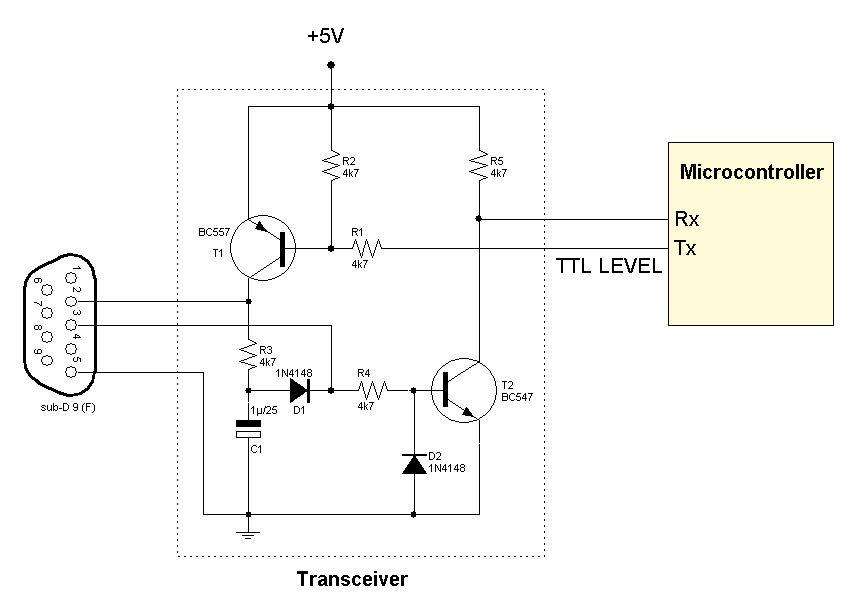
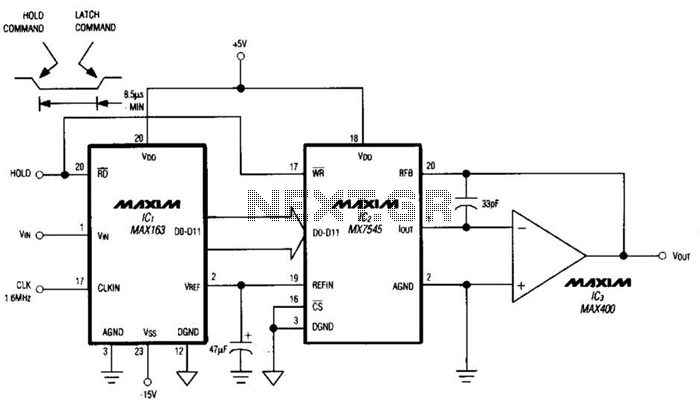
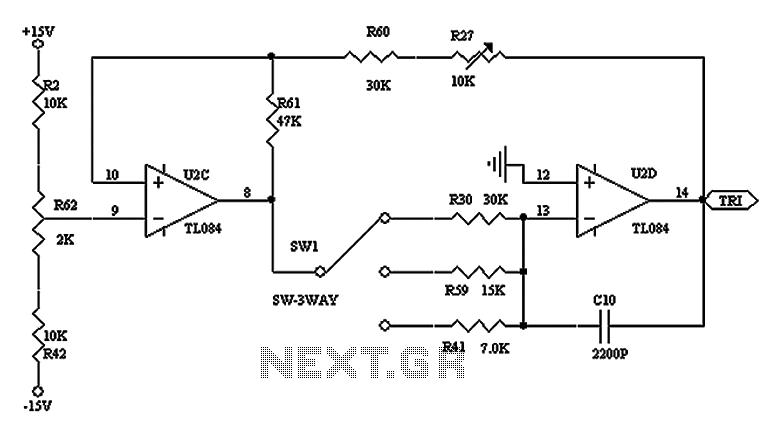
Power operational amplifier integrated circuit
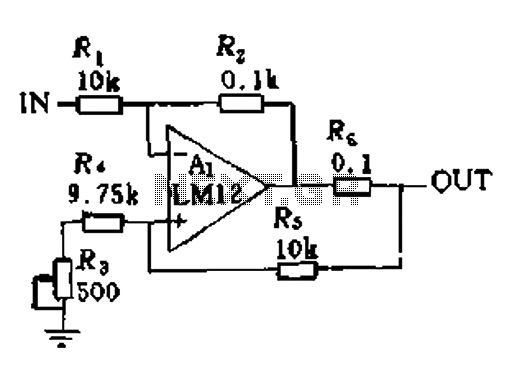
In a servo system, the current drive connection is frequently utilized. The output current (IOUT) is proportional to the input channel number (y). Using the current drive mode can mitigate issues caused by the motor's large inductance, which induces a phase shift and aids in stabilizing the servo loop.
In the context of servo systems, the implementation of a current drive connection serves a critical role in enhancing performance and stability. The relationship between the output current (IOUT) and the input channel number (y) is a fundamental aspect of this configuration, as it establishes a direct proportionality that is essential for accurate control of the servo mechanism.
The current drive mode is particularly advantageous when dealing with motors that exhibit significant inductance. Inductive components can introduce phase shifts that complicate the control dynamics of the servo loop. By employing a current drive approach, these phase shifts can be effectively countered, leading to improved stability and responsiveness of the servo system. This stabilization is vital for applications that demand precise positioning and speed control, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated systems.
In a typical schematic for a servo system utilizing current drive, key components include a current sensor, a feedback loop, and control circuitry. The current sensor monitors the output current (IOUT), providing real-time data to the control circuitry. This feedback is crucial for adjusting the input signal based on the current draw of the motor, ensuring that the system operates within desired parameters.
The control circuitry typically employs a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which processes the input from the current sensor and adjusts the drive signal accordingly. By fine-tuning the PID parameters, the system can achieve optimal performance, minimizing overshoot and settling time while maintaining stability despite the challenges posed by inductive loads.
Overall, the implementation of a current drive connection in servo systems represents a sophisticated approach to managing the complexities of motor control, particularly in high-performance applications where precision and stability are paramount.When used in the servo system, often using the current drive connection. Figure 11-1, the output current IOUT and the input channel number y.. It is proportional. Current drive mode can be reduced because the motor has a large inductance causes a phase shift, help stabilize the servo loop.
In the context of servo systems, the implementation of a current drive connection serves a critical role in enhancing performance and stability. The relationship between the output current (IOUT) and the input channel number (y) is a fundamental aspect of this configuration, as it establishes a direct proportionality that is essential for accurate control of the servo mechanism.
The current drive mode is particularly advantageous when dealing with motors that exhibit significant inductance. Inductive components can introduce phase shifts that complicate the control dynamics of the servo loop. By employing a current drive approach, these phase shifts can be effectively countered, leading to improved stability and responsiveness of the servo system. This stabilization is vital for applications that demand precise positioning and speed control, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated systems.
In a typical schematic for a servo system utilizing current drive, key components include a current sensor, a feedback loop, and control circuitry. The current sensor monitors the output current (IOUT), providing real-time data to the control circuitry. This feedback is crucial for adjusting the input signal based on the current draw of the motor, ensuring that the system operates within desired parameters.
The control circuitry typically employs a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which processes the input from the current sensor and adjusts the drive signal accordingly. By fine-tuning the PID parameters, the system can achieve optimal performance, minimizing overshoot and settling time while maintaining stability despite the challenges posed by inductive loads.
Overall, the implementation of a current drive connection in servo systems represents a sophisticated approach to managing the complexities of motor control, particularly in high-performance applications where precision and stability are paramount.When used in the servo system, often using the current drive connection. Figure 11-1, the output current IOUT and the input channel number y.. It is proportional. Current drive mode can be reduced because the motor has a large inductance causes a phase shift, help stabilize the servo loop.