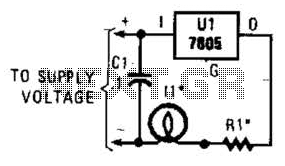
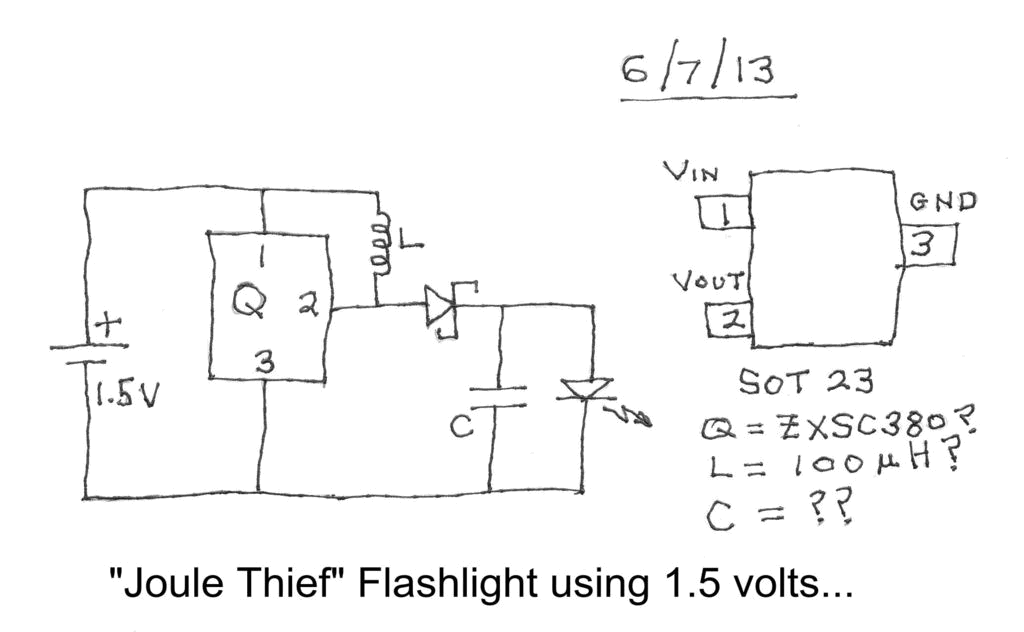
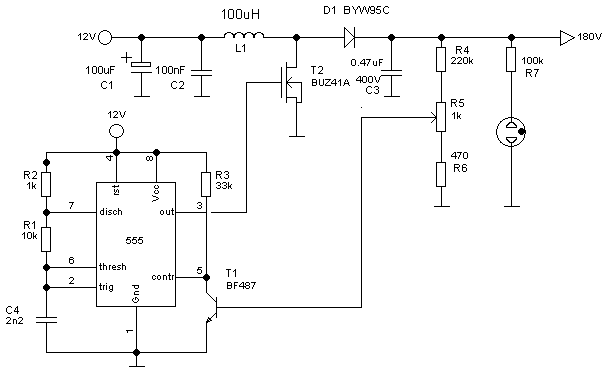
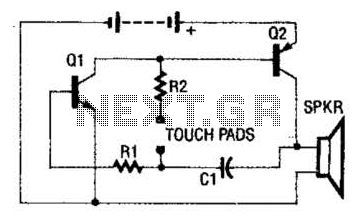
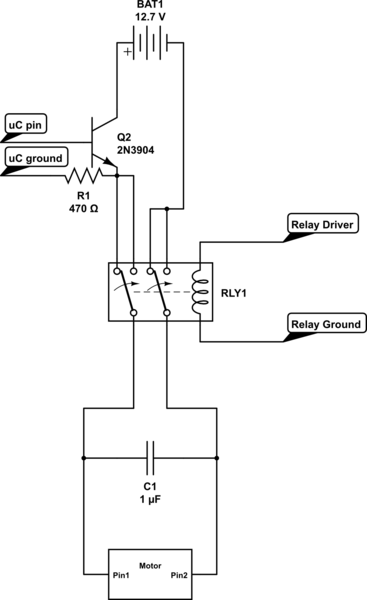
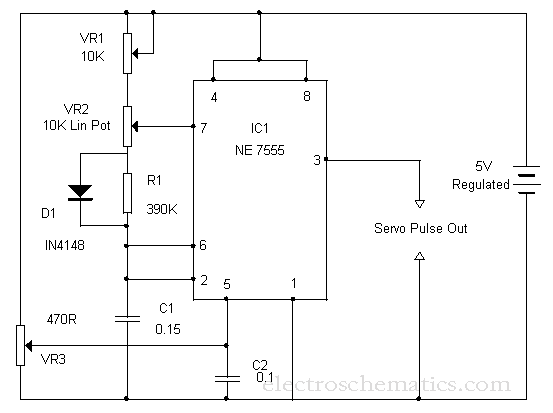Sample-And-Hold Circuit Ii Circuit
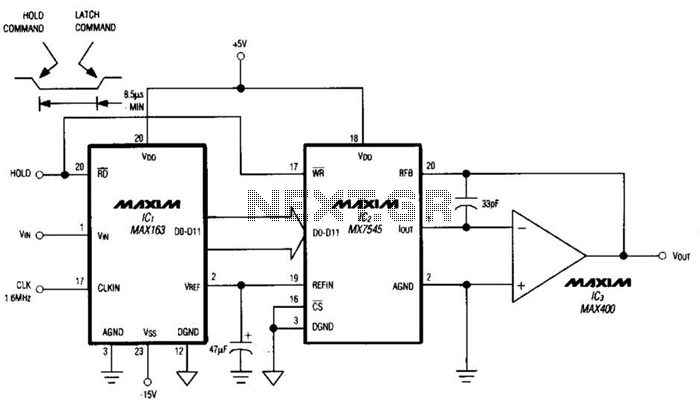
Driving a D/A converter using an A/D converter provides an overall analog-hold function. Although this function has limitations in output resolution, it offers zero voltage droop and infinite hold time. The A/D converter depicted (IC1) features a 12-bit compatible track/hold at its input. This track/hold has a full-power bandwidth of 6 MHz, an aperture delay of 30 ns, and an aperture jitter of 50 ps. The direct connections illustrated enable the D/A converter to reconstruct signal levels within the input range of 0 to 5 V.
The described circuit utilizes an A/D converter (IC1) that incorporates a 12-bit track/hold mechanism, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity during the sampling process. The track/hold function allows the circuit to capture the analog signal at a specific moment in time, holding that value steady while the D/A converter processes it. This is particularly important in applications requiring precise signal reconstruction, as it minimizes the effects of voltage droop that can occur during the conversion process.
The specifications of the A/D converter indicate a full-power bandwidth of 6 MHz, meaning it can accurately sample signals up to this frequency without significant distortion. The 30 ns aperture delay specifies the time it takes for the track/hold circuit to switch from tracking to holding mode, while the 50 ps aperture jitter indicates the stability of the sampling moment, which is essential for high-resolution applications.
The D/A converter is directly connected to the A/D converter, allowing it to reconstruct output signal levels that fall within the specified range of 0 to 5 V. This connection ensures that the digital representation of the analog input is accurately translated back into an analog signal, facilitating various applications such as audio processing, signal conditioning, and control systems. The combination of these components provides a robust solution for analog signal processing, ensuring high fidelity and stability in the output signal. Driving a D/A converter with an A/D converter provides an overall analog-hold function, which though limited in output resolution, offers zero voltage droop and infinite hold time. The A/D converter shown (IC1) includes a 12-bit compatible track/hold at its input. The track/hold specifies a 6-MHz full-power bandwidth, a 30-ns aperture delay, and a 50-ps aperture jitter.
The direct connections shown allow the D/A converter to reconstruct signal levels within the input range of 0 to 5 V.
The described circuit utilizes an A/D converter (IC1) that incorporates a 12-bit track/hold mechanism, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity during the sampling process. The track/hold function allows the circuit to capture the analog signal at a specific moment in time, holding that value steady while the D/A converter processes it. This is particularly important in applications requiring precise signal reconstruction, as it minimizes the effects of voltage droop that can occur during the conversion process.
The specifications of the A/D converter indicate a full-power bandwidth of 6 MHz, meaning it can accurately sample signals up to this frequency without significant distortion. The 30 ns aperture delay specifies the time it takes for the track/hold circuit to switch from tracking to holding mode, while the 50 ps aperture jitter indicates the stability of the sampling moment, which is essential for high-resolution applications.
The D/A converter is directly connected to the A/D converter, allowing it to reconstruct output signal levels that fall within the specified range of 0 to 5 V. This connection ensures that the digital representation of the analog input is accurately translated back into an analog signal, facilitating various applications such as audio processing, signal conditioning, and control systems. The combination of these components provides a robust solution for analog signal processing, ensuring high fidelity and stability in the output signal. Driving a D/A converter with an A/D converter provides an overall analog-hold function, which though limited in output resolution, offers zero voltage droop and infinite hold time. The A/D converter shown (IC1) includes a 12-bit compatible track/hold at its input. The track/hold specifies a 6-MHz full-power bandwidth, a 30-ns aperture delay, and a 50-ps aperture jitter.
The direct connections shown allow the D/A converter to reconstruct signal levels within the input range of 0 to 5 V.