power supply design 5v 7805 voltage regulator
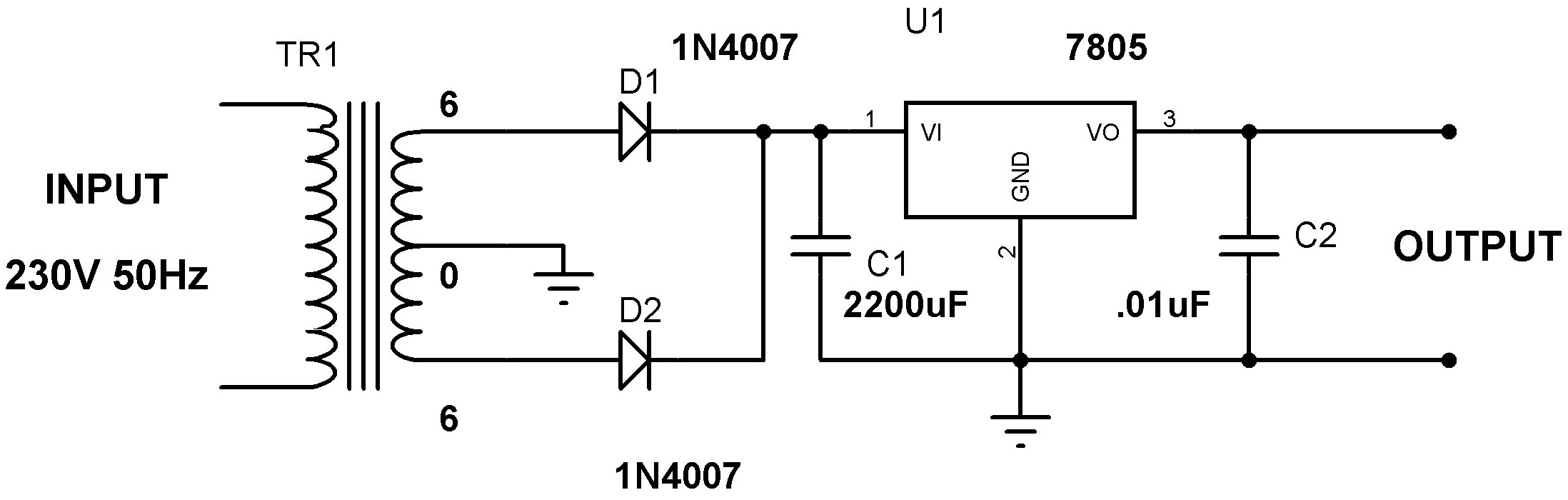
Designing a power supply requires careful consideration of each component. This discussion will focus on the design of a regulated 5V power supply. Note: Any transformer that provides a secondary peak voltage of up to 35V can be used; however, as the voltage increases, the size of the transformer and the power dissipation across the regulator will also increase.
The regulated 5V power supply typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, a voltage regulator, and output capacitors.
1. **Transformer**: The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for the power supply. A transformer with a secondary peak voltage of up to 35V is recommended to ensure adequate voltage for rectification and regulation. The choice of transformer affects both the physical size and heat dissipation of the overall circuit.
2. **Rectifier**: The rectifier converts the AC voltage output from the transformer into a pulsating DC voltage. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used for this purpose, as it provides better efficiency and smoother output compared to a half-wave rectifier. The rectifier should be selected based on the peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating to handle the maximum voltage that can occur across its terminals.
3. **Filter Capacitor**: After rectification, the output voltage will still have ripples. A filter capacitor is employed to smooth out these ripples, providing a more stable DC voltage. The capacitance value must be chosen based on the load current and acceptable ripple voltage. A larger capacitance will yield a lower ripple but will also increase the physical size and cost of the capacitor.
4. **Voltage Regulator**: The voltage regulator is crucial for maintaining a steady output voltage of 5V despite variations in input voltage or load current. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM7805, are commonly used for low-current applications. For higher efficiency, especially in battery-operated devices, a switching regulator may be preferred as it minimizes power loss and heat generation.
5. **Output Capacitors**: Additional output capacitors may be added to further stabilize the output voltage and improve transient response. These capacitors can help filter any high-frequency noise that may be present in the output.
In summary, the design of a regulated 5V power supply involves selecting appropriate components that work together to convert AC voltage to a stable DC output. Consideration must be given to the transformer specifications, rectification method, filtering requirements, and voltage regulation technique to ensure efficient and reliable performance.For making a power supply designing‚ of each and every component is essential. ‚Here I`m going to discuss the designing of ‚regulated 5V Power Supply. NOTE : Any transformer which supplies secondary peak voltage‚ up to35V can be used but as the voltage increases size of the transformer and power dissipation across regulator increases. 🔗 External reference
The regulated 5V power supply typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, a voltage regulator, and output capacitors.
1. **Transformer**: The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for the power supply. A transformer with a secondary peak voltage of up to 35V is recommended to ensure adequate voltage for rectification and regulation. The choice of transformer affects both the physical size and heat dissipation of the overall circuit.
2. **Rectifier**: The rectifier converts the AC voltage output from the transformer into a pulsating DC voltage. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used for this purpose, as it provides better efficiency and smoother output compared to a half-wave rectifier. The rectifier should be selected based on the peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating to handle the maximum voltage that can occur across its terminals.
3. **Filter Capacitor**: After rectification, the output voltage will still have ripples. A filter capacitor is employed to smooth out these ripples, providing a more stable DC voltage. The capacitance value must be chosen based on the load current and acceptable ripple voltage. A larger capacitance will yield a lower ripple but will also increase the physical size and cost of the capacitor.
4. **Voltage Regulator**: The voltage regulator is crucial for maintaining a steady output voltage of 5V despite variations in input voltage or load current. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM7805, are commonly used for low-current applications. For higher efficiency, especially in battery-operated devices, a switching regulator may be preferred as it minimizes power loss and heat generation.
5. **Output Capacitors**: Additional output capacitors may be added to further stabilize the output voltage and improve transient response. These capacitors can help filter any high-frequency noise that may be present in the output.
In summary, the design of a regulated 5V power supply involves selecting appropriate components that work together to convert AC voltage to a stable DC output. Consideration must be given to the transformer specifications, rectification method, filtering requirements, and voltage regulation technique to ensure efficient and reliable performance.For making a power supply designing‚ of each and every component is essential. ‚Here I`m going to discuss the designing of ‚regulated 5V Power Supply. NOTE : Any transformer which supplies secondary peak voltage‚ up to35V can be used but as the voltage increases size of the transformer and power dissipation across regulator increases. 🔗 External reference