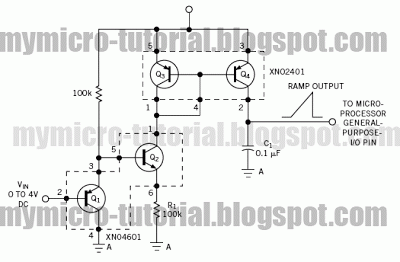
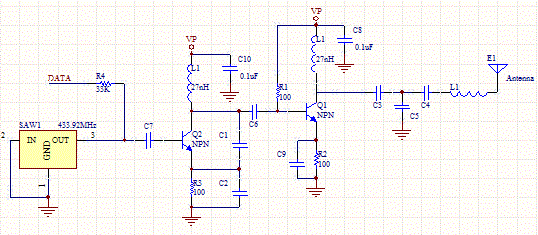
Precision polarity switching circuit by conventional elements
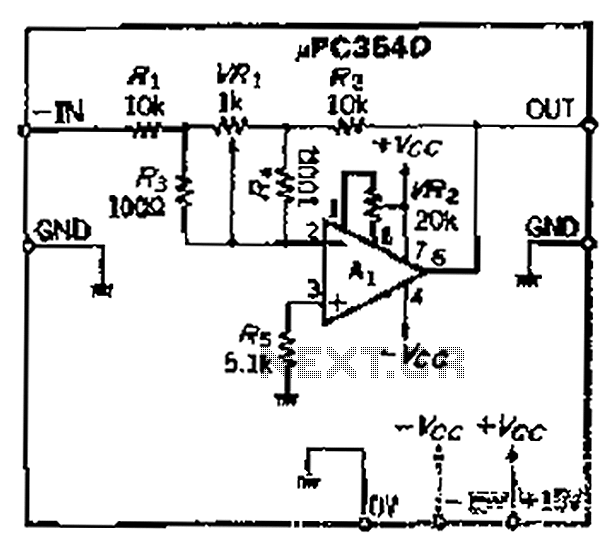
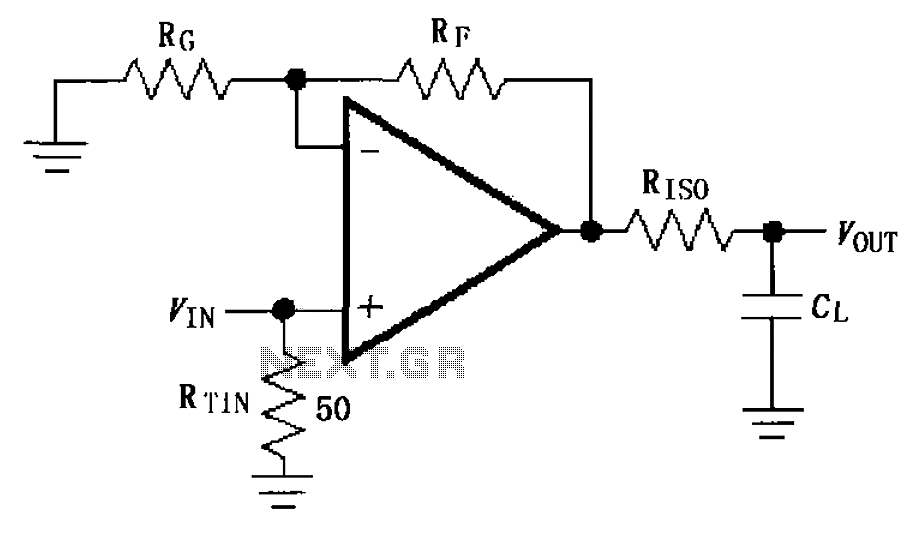
The loop gain of the operational amplifier (OP) is primarily influenced by the ratio of the input resistor to the feedback resistor. Consequently, any resistance error can lead to a corresponding gain error, which necessitates the use of high-precision resistors, particularly within a narrow range for the variable resistor (VRi). The resistances R1 and R2 should have a deviation of 1/100. This deviation can be compensated; for instance, if RL is 9 kΩ and R2 is 10.1 kΩ, the worst-case scenario results in a minimal gain error. Thus, an adjustable range of 1% for VRi is sufficient.
The operational amplifier circuit described focuses on maintaining accurate gain through careful selection of resistors. The loop gain is a critical parameter in determining the overall performance of the amplifier, which is affected by the ratio of the input resistor (R1) and the feedback resistor (R2). Any variation in these resistances can introduce errors in the gain, which can be detrimental to the circuit's performance.
To mitigate these errors, high-precision resistors are recommended, especially for the variable resistor (VRi), which is essential for fine-tuning the circuit's response. The design should ensure that the resistors used have a tolerance of 1% or better to maintain accuracy. In this case, R1 is specified as 9 kΩ, while R2 is set at 10.1 kΩ. The choice of these values is deliberate, as they are close to a standard value and provide a manageable range for adjustments.
The variable resistor (VRi) allows for the adjustment of the gain, and its design must accommodate the necessary precision. The gain adjustment can be fine-tuned within a narrow range, which is crucial for applications requiring high fidelity. The circuit should be laid out to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could further affect the gain stability.
In summary, the operational amplifier circuit relies on the precise ratio of resistances to ensure accurate gain. The use of high-precision resistors and careful design considerations will lead to improved performance, enabling the circuit to meet the stringent requirements of various applications. Because the loop gain of the amplifier OP depends mainly on the dry input resistor and feedback resistor ratio, so the resistance error, an error occurs opening will be a corre sponding gain in order to get more accuracy caused by four, you need high-precision resistors for o narrow range of VRI variable resistor Rs, ugly whose resistance Rl, R2 1/100, this kind of deviation can be compensated resistance, RL is actually g. 9kQ, Rz is 10.1 kQ, this worst-case scenario is very small, so VRi adjustable range of disabilities 1% is enough.
The operational amplifier circuit described focuses on maintaining accurate gain through careful selection of resistors. The loop gain is a critical parameter in determining the overall performance of the amplifier, which is affected by the ratio of the input resistor (R1) and the feedback resistor (R2). Any variation in these resistances can introduce errors in the gain, which can be detrimental to the circuit's performance.
To mitigate these errors, high-precision resistors are recommended, especially for the variable resistor (VRi), which is essential for fine-tuning the circuit's response. The design should ensure that the resistors used have a tolerance of 1% or better to maintain accuracy. In this case, R1 is specified as 9 kΩ, while R2 is set at 10.1 kΩ. The choice of these values is deliberate, as they are close to a standard value and provide a manageable range for adjustments.
The variable resistor (VRi) allows for the adjustment of the gain, and its design must accommodate the necessary precision. The gain adjustment can be fine-tuned within a narrow range, which is crucial for applications requiring high fidelity. The circuit should be laid out to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could further affect the gain stability.
In summary, the operational amplifier circuit relies on the precise ratio of resistances to ensure accurate gain. The use of high-precision resistors and careful design considerations will lead to improved performance, enabling the circuit to meet the stringent requirements of various applications. Because the loop gain of the amplifier OP depends mainly on the dry input resistor and feedback resistor ratio, so the resistance error, an error occurs opening will be a corre sponding gain in order to get more accuracy caused by four, you need high-precision resistors for o narrow range of VRI variable resistor Rs, ugly whose resistance Rl, R2 1/100, this kind of deviation can be compensated resistance, RL is actually g. 9kQ, Rz is 10.1 kQ, this worst-case scenario is very small, so VRi adjustable range of disabilities 1% is enough.