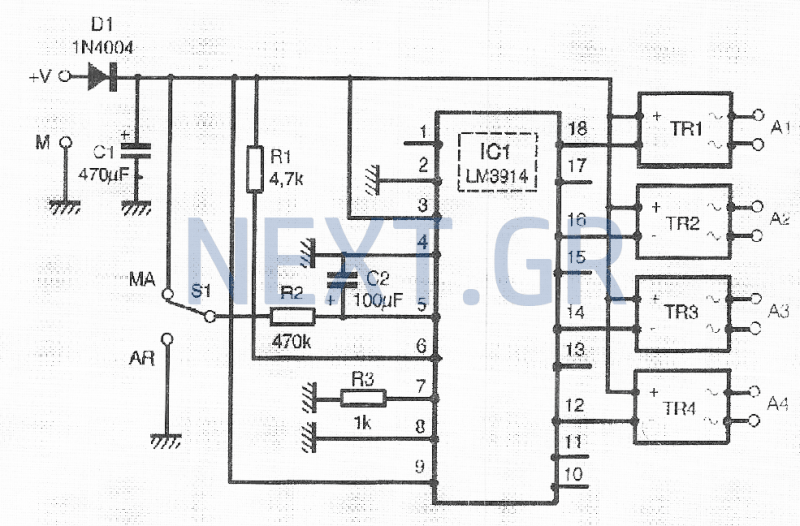
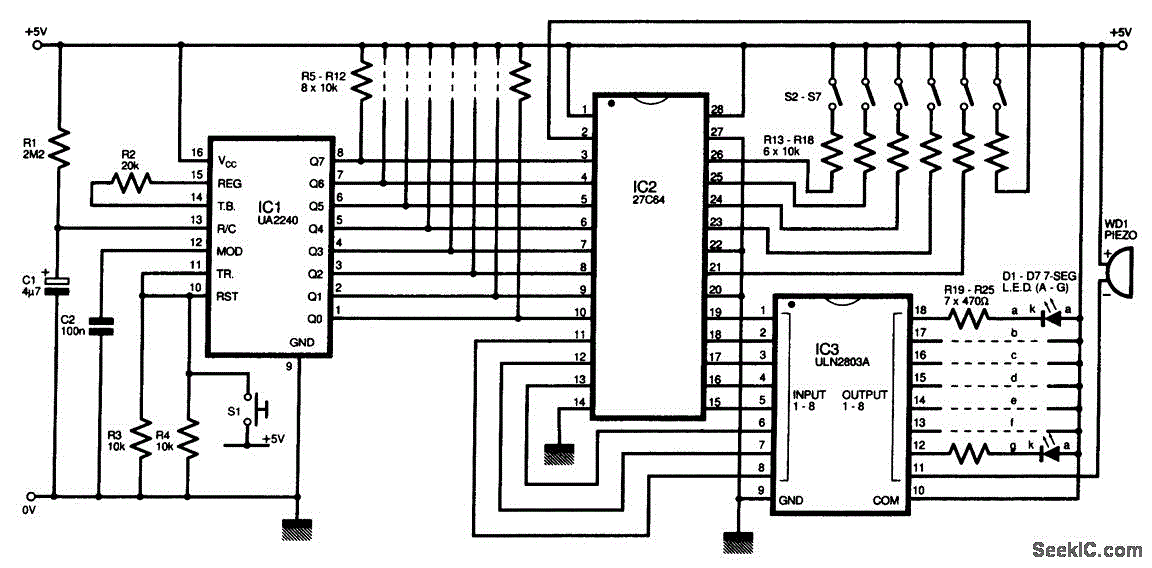
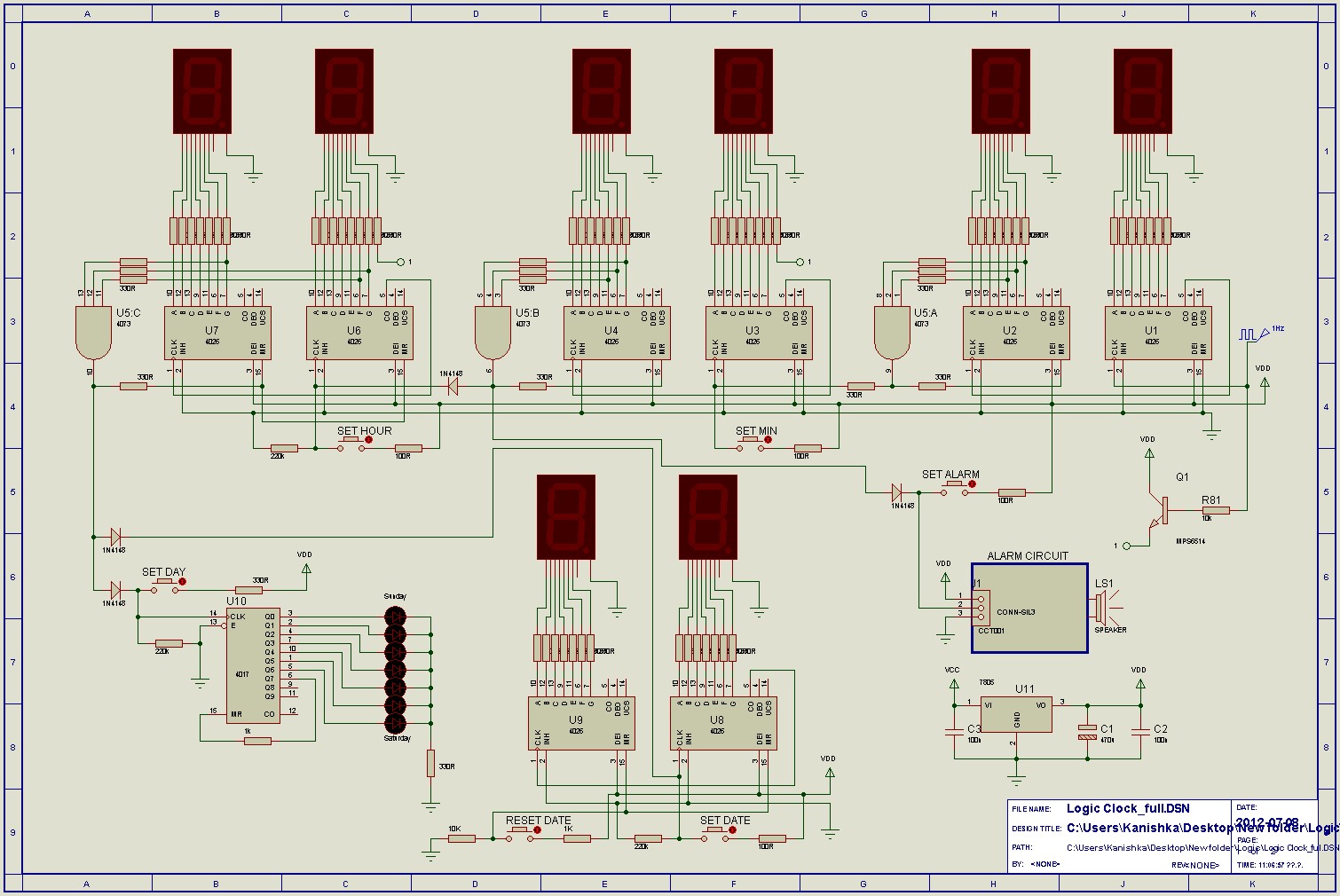
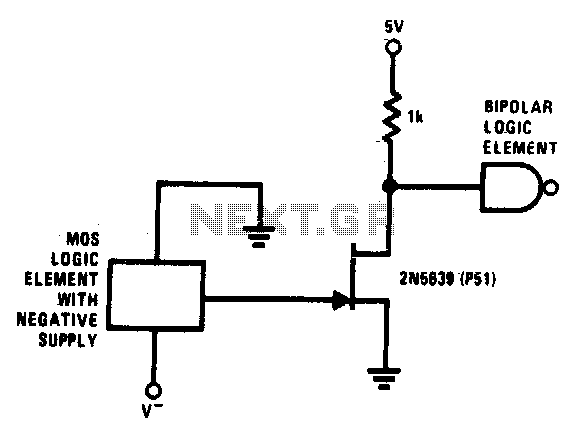
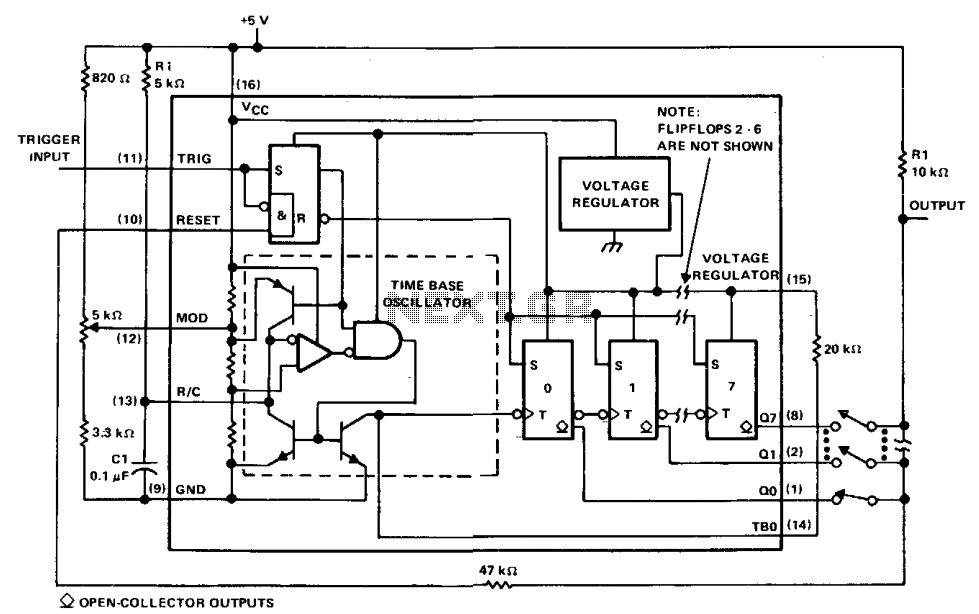
Programmable logic devices (CPLD)
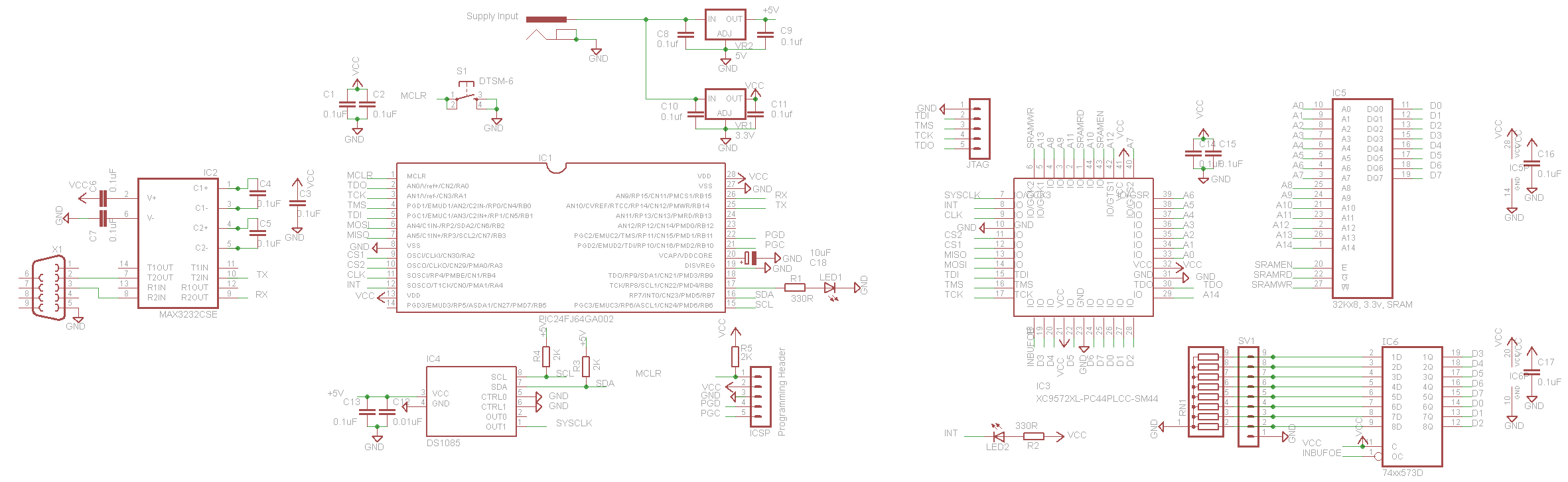
Complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs) contain the building blocks for hundreds of 7400-series logic ICs. Complete circuits can be designed on a PC and then uploaded to a CPLD for instant implementation.
CPLDs are integrated circuits that provide a versatile solution for digital logic design. They consist of an array of programmable logic blocks and interconnects, allowing designers to create complex digital systems without the need for discrete components. The architecture of a CPLD typically includes multiple macrocells, each capable of implementing combinational and sequential logic functions. These macrocells can be configured to perform a variety of tasks, such as multiplexing, demultiplexing, or arithmetic operations.
The design process for a CPLD begins with the use of hardware description languages (HDLs) such as VHDL or Verilog, which allow for the specification of the desired circuit behavior. Once the design is complete, it is synthesized using specialized software tools that translate the HDL code into a configuration file. This file is then uploaded to the CPLD via a programming interface, enabling the device to execute the designed logic functions.
CPLDs are particularly beneficial in applications requiring rapid prototyping or iterative design, as they can be reprogrammed multiple times. This flexibility makes them ideal for use in digital signal processing, communication systems, and control applications. Additionally, CPLDs offer advantages such as reduced board space, lower power consumption, and improved reliability compared to traditional discrete logic solutions. Their ability to implement complex logic functions in a single package streamlines the design process and enhances overall system performance.Complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs) contain the building blocks for hundreds of 7400-serries logic ICs. Complete circuits can be designed on a PC and then uploaded to a CPLD for instant implementation.. 🔗 External reference
CPLDs are integrated circuits that provide a versatile solution for digital logic design. They consist of an array of programmable logic blocks and interconnects, allowing designers to create complex digital systems without the need for discrete components. The architecture of a CPLD typically includes multiple macrocells, each capable of implementing combinational and sequential logic functions. These macrocells can be configured to perform a variety of tasks, such as multiplexing, demultiplexing, or arithmetic operations.
The design process for a CPLD begins with the use of hardware description languages (HDLs) such as VHDL or Verilog, which allow for the specification of the desired circuit behavior. Once the design is complete, it is synthesized using specialized software tools that translate the HDL code into a configuration file. This file is then uploaded to the CPLD via a programming interface, enabling the device to execute the designed logic functions.
CPLDs are particularly beneficial in applications requiring rapid prototyping or iterative design, as they can be reprogrammed multiple times. This flexibility makes them ideal for use in digital signal processing, communication systems, and control applications. Additionally, CPLDs offer advantages such as reduced board space, lower power consumption, and improved reliability compared to traditional discrete logic solutions. Their ability to implement complex logic functions in a single package streamlines the design process and enhances overall system performance.Complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs) contain the building blocks for hundreds of 7400-serries logic ICs. Complete circuits can be designed on a PC and then uploaded to a CPLD for instant implementation.. 🔗 External reference