Pulse DemodulatorCircuit
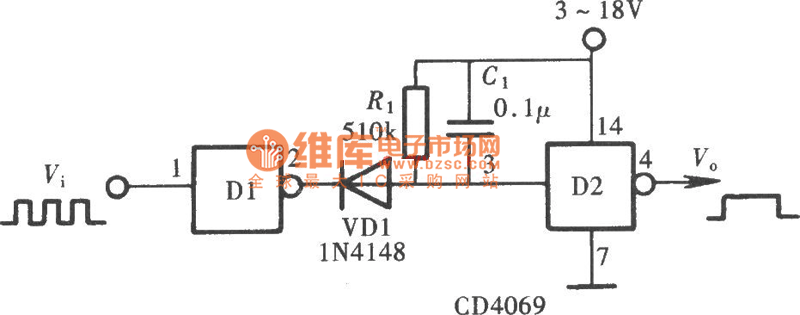
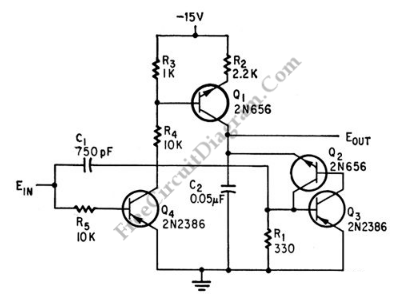
The Pulse Demodulator, as illustrated in the accompanying image, consists of a CMOS Hex Inverter. This circuit is capable of performing envelope detection on amplitude pulses.
The Pulse Demodulator utilizing a CMOS Hex Inverter is designed to extract the envelope of amplitude-modulated signals. The hex inverter configuration allows for multiple signal processing paths within a single integrated circuit, enhancing the efficiency and compactness of the design.
In operation, the incoming amplitude-modulated signal is fed into one of the inverter inputs. The CMOS technology ensures low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for various applications where precision and reliability are critical. The inverter effectively inverts the input signal, producing a square wave that represents the envelope of the original amplitude-modulated signal.
The output from the inverter can be further processed by additional filtering stages to smooth the signal and retrieve the original modulation information. Capacitors and resistors may be employed in conjunction with the inverter to establish time constants that define the response time of the envelope detection.
This Pulse Demodulator circuit finds applications in communications systems, where it can be used for demodulating signals in radio frequency transmissions, as well as in various signal processing tasks requiring envelope detection. The versatility of the CMOS Hex Inverter makes it an essential component in modern electronic designs focused on signal integrity and efficiency.As is shown in the picture, the Pulse Demodulator is composed by CMOS Hex Inverter. This circuit can be used to process envelop detection on Amplitude Pulse.. 🔗 External reference
The Pulse Demodulator utilizing a CMOS Hex Inverter is designed to extract the envelope of amplitude-modulated signals. The hex inverter configuration allows for multiple signal processing paths within a single integrated circuit, enhancing the efficiency and compactness of the design.
In operation, the incoming amplitude-modulated signal is fed into one of the inverter inputs. The CMOS technology ensures low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for various applications where precision and reliability are critical. The inverter effectively inverts the input signal, producing a square wave that represents the envelope of the original amplitude-modulated signal.
The output from the inverter can be further processed by additional filtering stages to smooth the signal and retrieve the original modulation information. Capacitors and resistors may be employed in conjunction with the inverter to establish time constants that define the response time of the envelope detection.
This Pulse Demodulator circuit finds applications in communications systems, where it can be used for demodulating signals in radio frequency transmissions, as well as in various signal processing tasks requiring envelope detection. The versatility of the CMOS Hex Inverter makes it an essential component in modern electronic designs focused on signal integrity and efficiency.As is shown in the picture, the Pulse Demodulator is composed by CMOS Hex Inverter. This circuit can be used to process envelop detection on Amplitude Pulse.. 🔗 External reference