Pulse generator as astable multivibrator
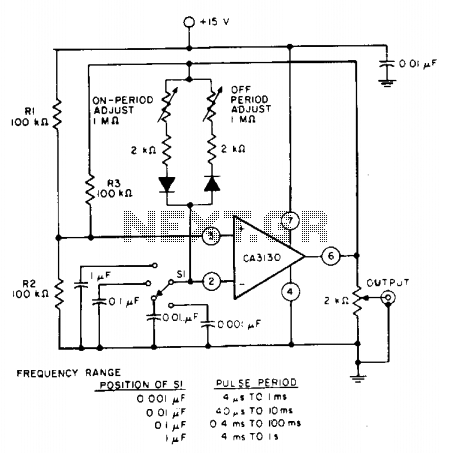
The pulse repetition rate is determined by adjusting switch SI to the desired position, and this rate remains relatively constant even when the resistors that control the on-period and off-period are modified. Resistors R1 and R2 set the biasing of the CA3130 to the midpoint of the supply voltage, while R3 serves as the feedback resistor.
The circuit utilizes a pulse width modulation (PWM) technique to generate a stable pulse repetition rate. The switch SI allows for the selection of different pulse rates, which are crucial in applications such as signal modulation, timing applications, and control systems. The design ensures that the pulse repetition rate remains consistent despite variations in the on-period and off-period resistances, indicating a robust design that can adapt to different operational conditions without significant drift in performance.
Resistors R1 and R2 play a vital role in establishing the operating point of the CA3130 operational amplifier, ensuring that it operates within its linear region. By biasing the amplifier to the midpoint of the supply voltage, the circuit can efficiently process the input signals, thus improving the overall performance of the PWM output. The feedback resistor R3 is essential for controlling the gain of the operational amplifier, which directly influences the width of the output pulses. Adjustments to R3 can fine-tune the output signal characteristics, allowing for precise control over the pulse width and, consequently, the overall behavior of the circuit.
This configuration is commonly used in various electronic applications, including motor control, LED dimming, and audio signal modulation, where accurate timing and pulse generation are critical. The stability of the pulse repetition rate, in conjunction with the adjustable resistors, provides flexibility for designers to tailor the circuit to specific requirements while maintaining reliable operation across a range of conditions. The pulse repetition rate is selected by positioning SI to the desired position and the rate remains essentially constant when the resistors which determine on-period and off-period are adjusted. Resistors Rl and R2 bias the CA3130 to the mid-point of the supply-voltage, and R3 is the feedback resistor.
The circuit utilizes a pulse width modulation (PWM) technique to generate a stable pulse repetition rate. The switch SI allows for the selection of different pulse rates, which are crucial in applications such as signal modulation, timing applications, and control systems. The design ensures that the pulse repetition rate remains consistent despite variations in the on-period and off-period resistances, indicating a robust design that can adapt to different operational conditions without significant drift in performance.
Resistors R1 and R2 play a vital role in establishing the operating point of the CA3130 operational amplifier, ensuring that it operates within its linear region. By biasing the amplifier to the midpoint of the supply voltage, the circuit can efficiently process the input signals, thus improving the overall performance of the PWM output. The feedback resistor R3 is essential for controlling the gain of the operational amplifier, which directly influences the width of the output pulses. Adjustments to R3 can fine-tune the output signal characteristics, allowing for precise control over the pulse width and, consequently, the overall behavior of the circuit.
This configuration is commonly used in various electronic applications, including motor control, LED dimming, and audio signal modulation, where accurate timing and pulse generation are critical. The stability of the pulse repetition rate, in conjunction with the adjustable resistors, provides flexibility for designers to tailor the circuit to specific requirements while maintaining reliable operation across a range of conditions. The pulse repetition rate is selected by positioning SI to the desired position and the rate remains essentially constant when the resistors which determine on-period and off-period are adjusted. Resistors Rl and R2 bias the CA3130 to the mid-point of the supply-voltage, and R3 is the feedback resistor.