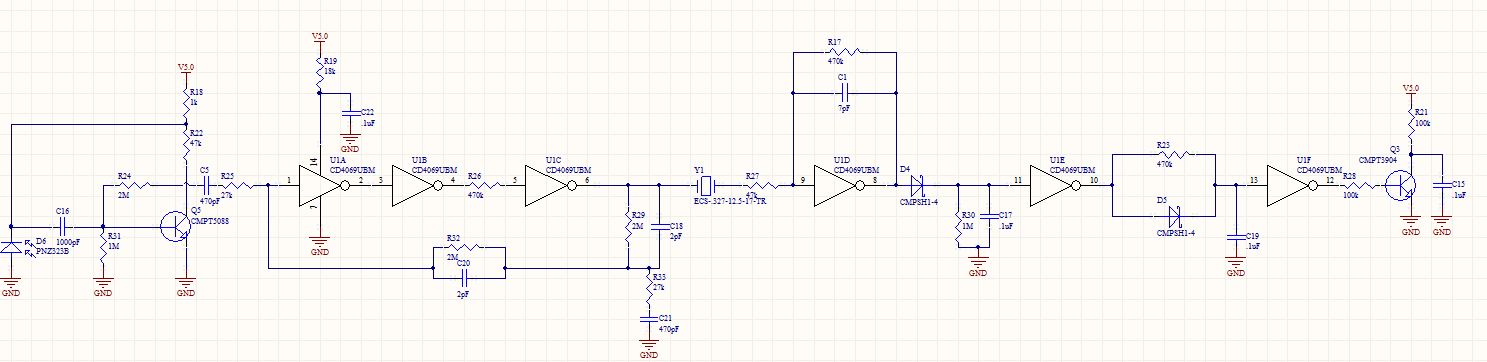
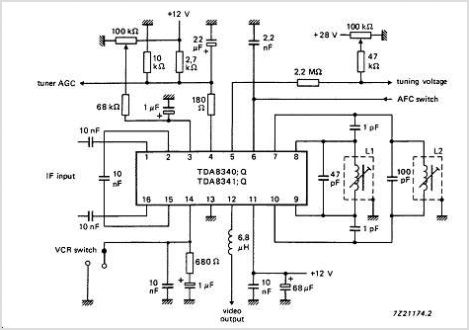
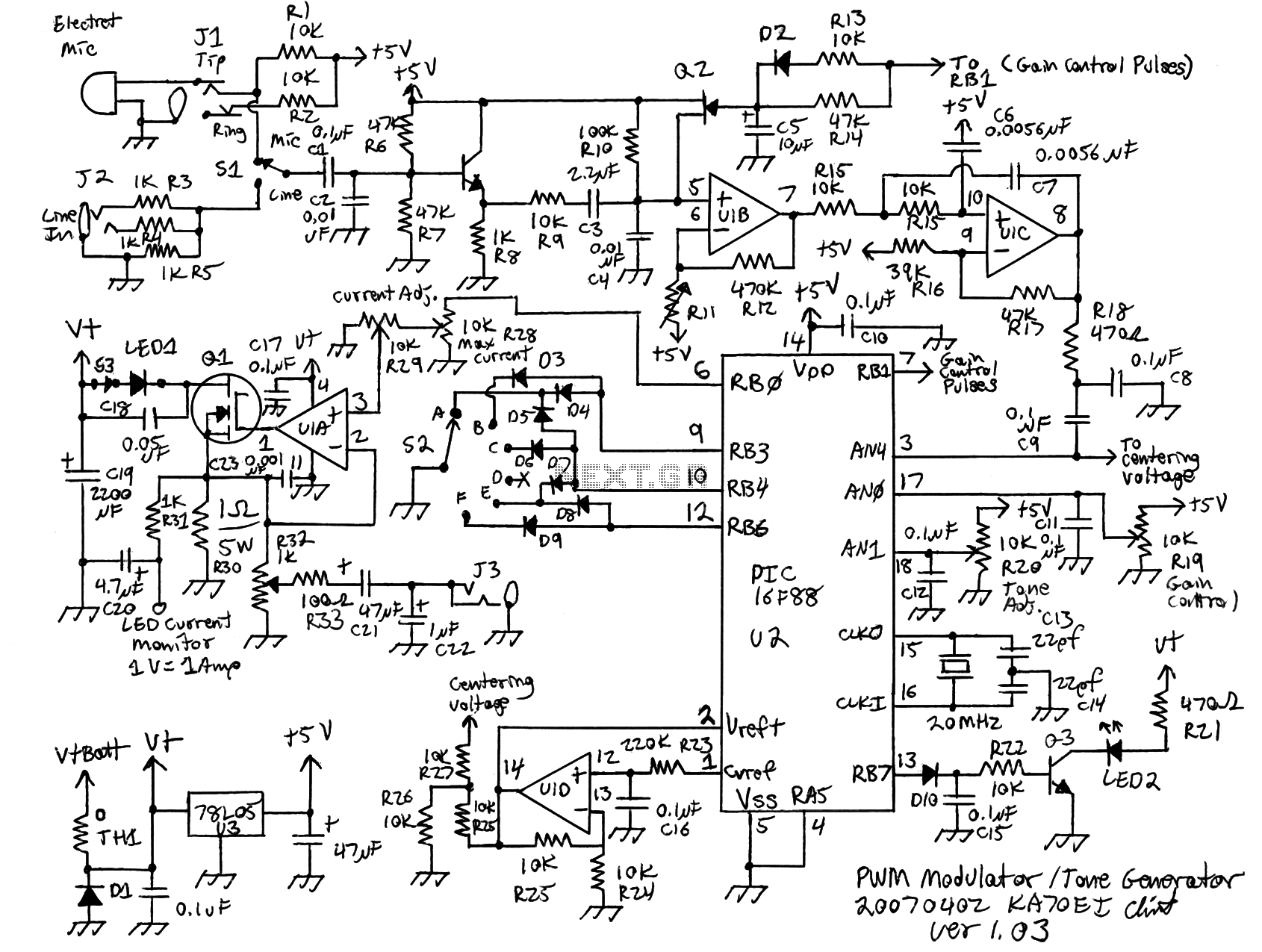
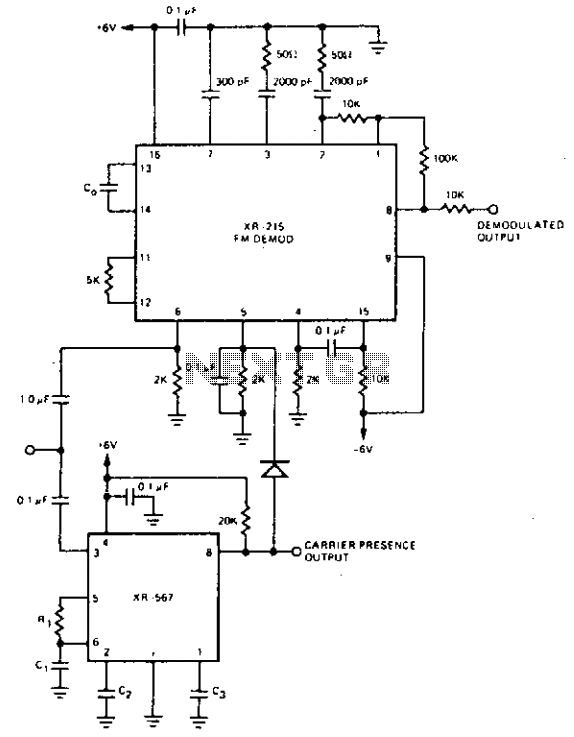
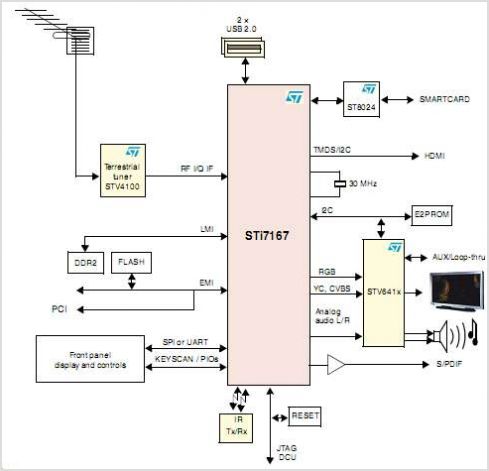
Pulse-position modulator
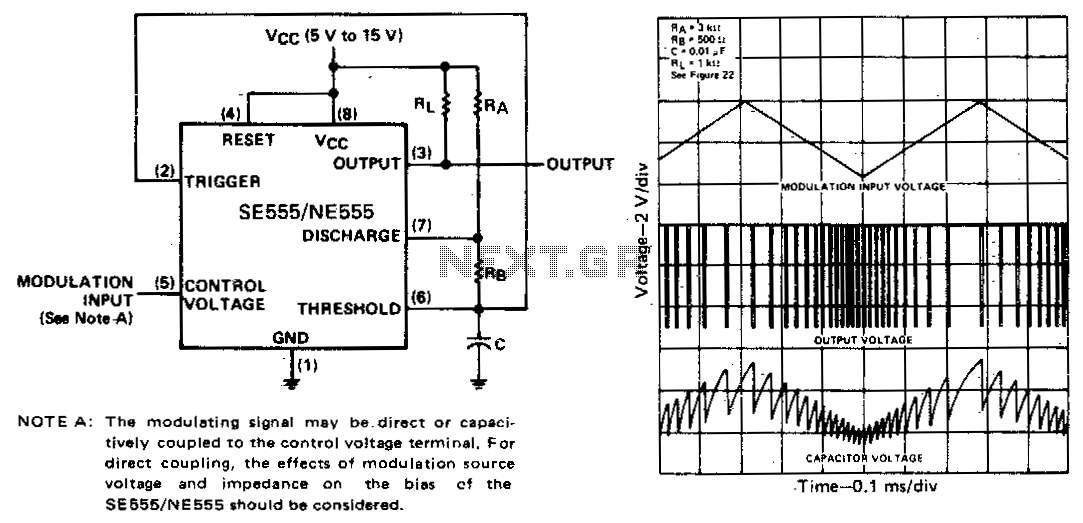
The threshold voltage, and consequently the time delay, of a free-running oscillator is depicted as being modulated by a triangular-wave modulation signal. However, any type of modulating wave shape could be employed.
In a free-running oscillator circuit, the threshold voltage plays a critical role in determining the oscillation frequency and the time delay between successive cycles. The modulation of this threshold voltage using a triangular-wave signal allows for dynamic control over the oscillator's output frequency. The triangular wave provides a linear ramp-up and ramp-down of voltage, which influences the timing of the oscillator's transitions between its high and low states.
The free-running oscillator typically consists of an active device, such as a transistor or operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop. The output signal from the oscillator can be fed back to the input through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that sets the timing characteristics of the oscillator. By integrating a modulation signal, such as a triangular wave, into the feedback loop, the threshold voltage can be adjusted in real-time, resulting in a variable frequency output.
In addition to triangular waves, other wave shapes, such as square waves, sine waves, or sawtooth waves, can also be utilized for modulation. Each wave shape will produce different effects on the oscillator's performance, allowing for a variety of applications in signal generation, frequency modulation, and waveform shaping. The choice of modulation waveform will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired frequency range and the nature of the output signal.
Overall, the implementation of a modulated threshold voltage in a free-running oscillator circuit provides enhanced flexibility and control, enabling the generation of complex waveforms suitable for various electronic applications.The threshold voltage, and thereby the time delay, of a free-running oscillator is shown modulated with a triangular-wave modulation signal however, any modulating wave-shape could be used.
In a free-running oscillator circuit, the threshold voltage plays a critical role in determining the oscillation frequency and the time delay between successive cycles. The modulation of this threshold voltage using a triangular-wave signal allows for dynamic control over the oscillator's output frequency. The triangular wave provides a linear ramp-up and ramp-down of voltage, which influences the timing of the oscillator's transitions between its high and low states.
The free-running oscillator typically consists of an active device, such as a transistor or operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop. The output signal from the oscillator can be fed back to the input through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that sets the timing characteristics of the oscillator. By integrating a modulation signal, such as a triangular wave, into the feedback loop, the threshold voltage can be adjusted in real-time, resulting in a variable frequency output.
In addition to triangular waves, other wave shapes, such as square waves, sine waves, or sawtooth waves, can also be utilized for modulation. Each wave shape will produce different effects on the oscillator's performance, allowing for a variety of applications in signal generation, frequency modulation, and waveform shaping. The choice of modulation waveform will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired frequency range and the nature of the output signal.
Overall, the implementation of a modulated threshold voltage in a free-running oscillator circuit provides enhanced flexibility and control, enabling the generation of complex waveforms suitable for various electronic applications.The threshold voltage, and thereby the time delay, of a free-running oscillator is shown modulated with a triangular-wave modulation signal however, any modulating wave-shape could be used.