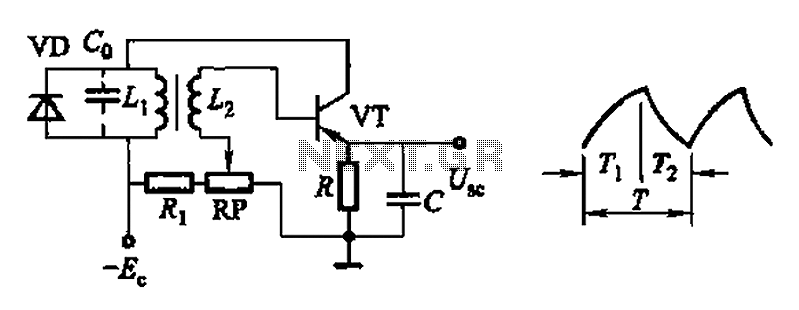
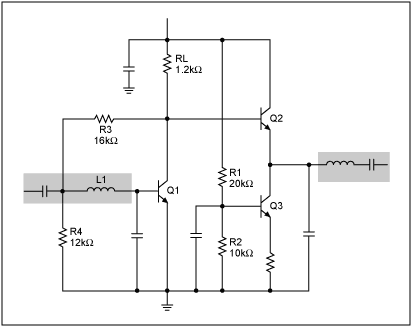
Quick On-Board Junction TesterCircuit

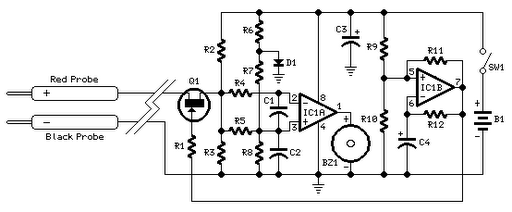
Acoustic check of transistor and diode junctions. Also suitable as a continuity tester. Short circuits or broken PCB tracks can be easily recognized.
The acoustic check of transistor and diode junctions is a method used to assess the functionality of these semiconductor devices. This technique relies on the audible feedback generated when a signal is applied to the junctions. The tester emits a tone that varies in pitch or volume based on the characteristics of the junction being tested. For instance, a healthy diode will produce a distinct sound when forward-biased, while a malfunctioning diode may not generate any sound, indicating an open circuit.
In addition to testing individual components, this device functions as a continuity tester, allowing users to verify the integrity of electrical connections within a circuit. By connecting the tester's probes across the points of interest, the user can detect short circuits or broken tracks on printed circuit boards (PCBs). A continuous tone signifies a good connection, while silence indicates an open circuit or break in the track.
This testing technique is particularly valuable in troubleshooting electronic devices, as it provides immediate auditory feedback, allowing for efficient identification of faults without the need for visual inspection or complex measurement equipment. The simplicity and effectiveness of this method make it an essential tool for electronics engineers and technicians in both design and repair environments.Acoustic check of transistor and diode junctions, Also suitable as continuity tester Short circuits or broken pcb tracks can be easily recognized by means.. 🔗 External reference
The acoustic check of transistor and diode junctions is a method used to assess the functionality of these semiconductor devices. This technique relies on the audible feedback generated when a signal is applied to the junctions. The tester emits a tone that varies in pitch or volume based on the characteristics of the junction being tested. For instance, a healthy diode will produce a distinct sound when forward-biased, while a malfunctioning diode may not generate any sound, indicating an open circuit.
In addition to testing individual components, this device functions as a continuity tester, allowing users to verify the integrity of electrical connections within a circuit. By connecting the tester's probes across the points of interest, the user can detect short circuits or broken tracks on printed circuit boards (PCBs). A continuous tone signifies a good connection, while silence indicates an open circuit or break in the track.
This testing technique is particularly valuable in troubleshooting electronic devices, as it provides immediate auditory feedback, allowing for efficient identification of faults without the need for visual inspection or complex measurement equipment. The simplicity and effectiveness of this method make it an essential tool for electronics engineers and technicians in both design and repair environments.Acoustic check of transistor and diode junctions, Also suitable as continuity tester Short circuits or broken pcb tracks can be easily recognized by means.. 🔗 External reference