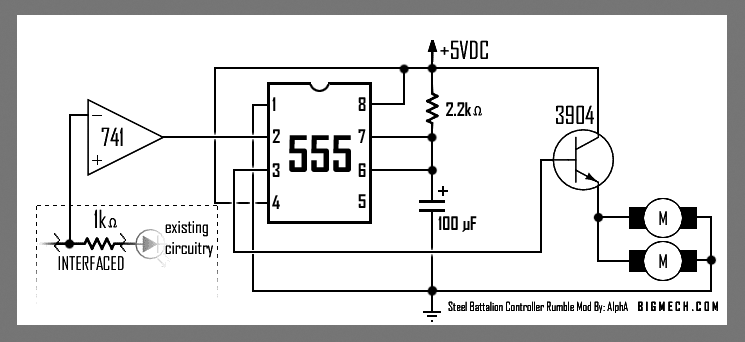
Non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit waveform pulse wave oscillator single-junction oscillator
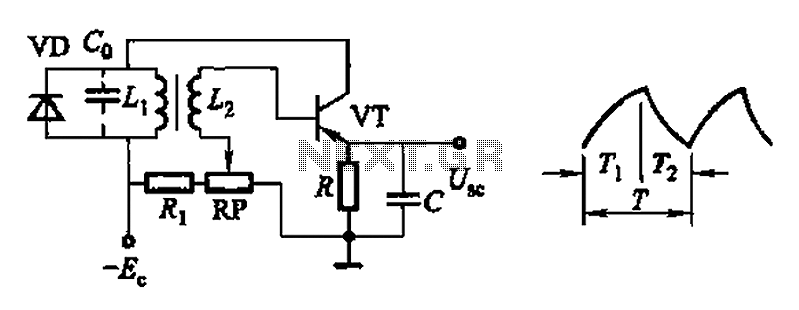
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - single-junction transistor blocking oscillator.
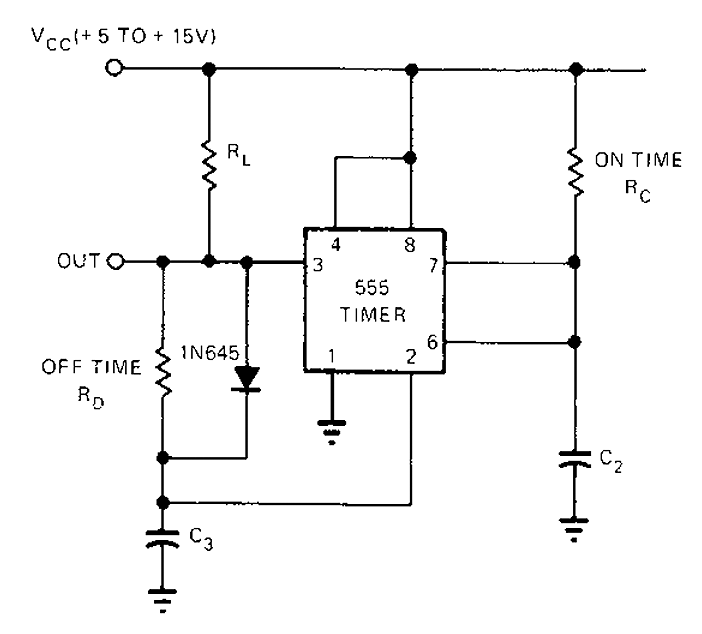
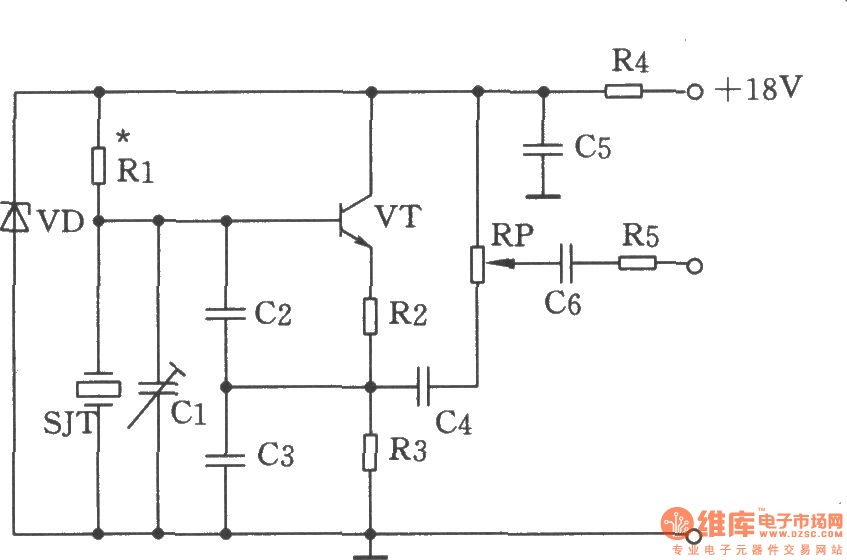
The common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit described is a pulse wave oscillator that utilizes a single-junction transistor in a blocking configuration. This type of oscillator is characterized by its ability to generate square or pulse waveforms, which are essential in various electronic applications such as timing circuits, clock generators, and signal modulators.
In a typical single-junction transistor blocking oscillator circuit, the transistor operates in a switching mode. When the circuit is powered, the transistor is initially turned off, preventing current from flowing through the collector-emitter path. A capacitor is connected to the base of the transistor, charging through a resistor. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a certain threshold, the transistor turns on, allowing current to flow and rapidly discharging the capacitor. This action produces a pulse in the output.
The frequency of the output waveform can be determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor used in the circuit, as well as the characteristics of the transistor. The basic formula for the frequency (f) of the oscillator is given by:
f = 1 / (2 * π * R * C)
where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. This formula indicates that the frequency is inversely proportional to both the resistance and capacitance values; thus, increasing either the resistance or capacitance will decrease the frequency of the oscillation.
The waveform produced by this oscillator is typically a square wave, which can be further manipulated with additional components to achieve desired characteristics such as duty cycle and amplitude. The simplicity and effectiveness of the single-junction transistor blocking oscillator make it a popular choice in various electronic designs that require pulse generation. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - single-junction transistor blocking oscillator
The common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit described is a pulse wave oscillator that utilizes a single-junction transistor in a blocking configuration. This type of oscillator is characterized by its ability to generate square or pulse waveforms, which are essential in various electronic applications such as timing circuits, clock generators, and signal modulators.
In a typical single-junction transistor blocking oscillator circuit, the transistor operates in a switching mode. When the circuit is powered, the transistor is initially turned off, preventing current from flowing through the collector-emitter path. A capacitor is connected to the base of the transistor, charging through a resistor. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a certain threshold, the transistor turns on, allowing current to flow and rapidly discharging the capacitor. This action produces a pulse in the output.
The frequency of the output waveform can be determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor used in the circuit, as well as the characteristics of the transistor. The basic formula for the frequency (f) of the oscillator is given by:
f = 1 / (2 * π * R * C)
where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. This formula indicates that the frequency is inversely proportional to both the resistance and capacitance values; thus, increasing either the resistance or capacitance will decrease the frequency of the oscillation.
The waveform produced by this oscillator is typically a square wave, which can be further manipulated with additional components to achieve desired characteristics such as duty cycle and amplitude. The simplicity and effectiveness of the single-junction transistor blocking oscillator make it a popular choice in various electronic designs that require pulse generation. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - single-junction transistor blocking oscillator