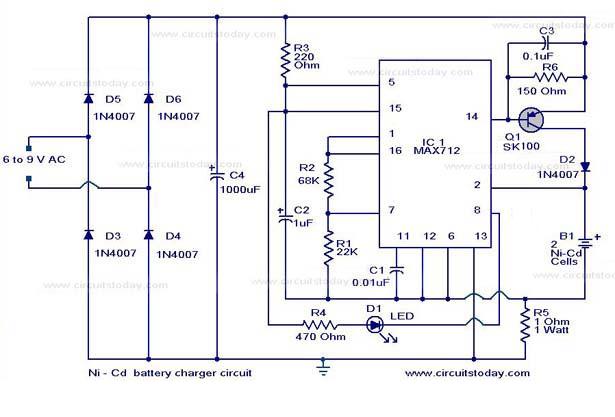
RC Charger
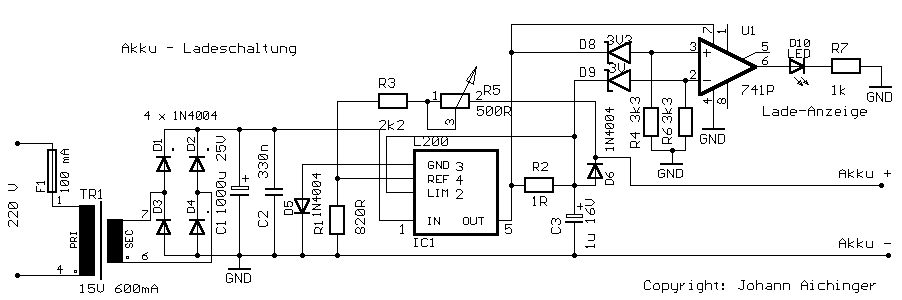
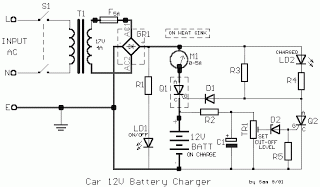
Charge current: I=0.45V/R2 Power-dissipation by R2: (0.45 * 0.45 / R2) Please adjust 13.8V by R5 without connected battery. More: D1 - D4, D6: charge-current less than 1A: 1N4001 (up to 1N4007) charge-current up to 2A: 1N5401 D5: 1N4184, 1N4001. Transformer: 15 V max 2 A The L200 must be cooled.
The circuit described involves a battery charging system that utilizes a transformer, diodes, a variable resistor, and an L200 voltage regulator. The primary function of this circuit is to provide a regulated charging voltage to a battery while ensuring safe operating conditions for the components involved.
The charge current (I) is determined by the equation I = 0.45V/R2, where R2 is a resistor used to limit the current flowing into the battery. The power dissipation across R2 can be calculated using the formula (0.45 * 0.45) / R2, which indicates that the resistor must be rated to handle the calculated power without overheating.
To achieve the desired output voltage of 13.8V for charging, R5 is employed as an adjustable resistor. It is crucial to adjust R5 while the battery is not connected to prevent damage or incorrect charging conditions.
The diodes D1 through D4 and D6 are selected based on the charge current requirements. For charge currents less than 1A, diodes such as the 1N4001 through 1N4007 are suitable. For higher charge currents, specifically up to 2A, the 1N5401 diode is recommended. D5, which may be used for additional protection or regulation, can be either a 1N4184 or a 1N4001, depending on the specific circuit design and requirements.
The transformer is specified to provide a maximum output of 15V at 2A, which is adequate for the intended charging application. The transformer steps down the voltage from the mains supply to a suitable level for the charging circuit.
The L200 voltage regulator is a critical component in this design, providing a stable output voltage and current regulation. Adequate cooling for the L200 is necessary to ensure reliable operation and prevent thermal shutdown. This may involve using a heatsink or other cooling methods to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for battery charging applications, with careful consideration given to component selection, current limiting, and thermal management.Charge current: I=0,45V/R2 Power-dissipation by R2: (0,45 * 0,45 / R2) ! Please adjust 13,8V by R5 without connected battery. D1 - D4, D6 : charge-current less than 1A: 1N4001 (up to 1N4007) charge-current up to 2A: 1N5401 D5: 1N4184 , 1N4001. Transformer: 15 V max 2 A The L200 must be cooled. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a battery charging system that utilizes a transformer, diodes, a variable resistor, and an L200 voltage regulator. The primary function of this circuit is to provide a regulated charging voltage to a battery while ensuring safe operating conditions for the components involved.
The charge current (I) is determined by the equation I = 0.45V/R2, where R2 is a resistor used to limit the current flowing into the battery. The power dissipation across R2 can be calculated using the formula (0.45 * 0.45) / R2, which indicates that the resistor must be rated to handle the calculated power without overheating.
To achieve the desired output voltage of 13.8V for charging, R5 is employed as an adjustable resistor. It is crucial to adjust R5 while the battery is not connected to prevent damage or incorrect charging conditions.
The diodes D1 through D4 and D6 are selected based on the charge current requirements. For charge currents less than 1A, diodes such as the 1N4001 through 1N4007 are suitable. For higher charge currents, specifically up to 2A, the 1N5401 diode is recommended. D5, which may be used for additional protection or regulation, can be either a 1N4184 or a 1N4001, depending on the specific circuit design and requirements.
The transformer is specified to provide a maximum output of 15V at 2A, which is adequate for the intended charging application. The transformer steps down the voltage from the mains supply to a suitable level for the charging circuit.
The L200 voltage regulator is a critical component in this design, providing a stable output voltage and current regulation. Adequate cooling for the L200 is necessary to ensure reliable operation and prevent thermal shutdown. This may involve using a heatsink or other cooling methods to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for battery charging applications, with careful consideration given to component selection, current limiting, and thermal management.Charge current: I=0,45V/R2 Power-dissipation by R2: (0,45 * 0,45 / R2) ! Please adjust 13,8V by R5 without connected battery. D1 - D4, D6 : charge-current less than 1A: 1N4001 (up to 1N4007) charge-current up to 2A: 1N5401 D5: 1N4184 , 1N4001. Transformer: 15 V max 2 A The L200 must be cooled. 🔗 External reference